Updated May 3, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL ORDER BY
When we receive data from a table using a select query, it will return a row in an unspecified order. To sort this data using specified order, we need to use order by Clause in the select query to retrieve data from a table; we have to use ASC or DESC order to sort data in the specified order; this Clause is used to sort data in ascending and descending order in PostgreSQL. We can use one or more columns in order by Clause to sort data in ascending or descending order, but we ensure this column is in that table.
Syntax:
This Clause specifies the sort order of data in a specific order.
SELECTcolumn-list (list of columns)
FROM table_name (name of table)
[WHERE condition]
[ORDER BY column1, column2, …, columnN (name of columns)] [ASC | DESC];SELECT* (list of columns)
FROM table_name (name of table from we retrieving data)
[WHERE condition]
[ORDER BY column1, column2, …, columnN (name of columns)] [ASC | DESC];Select expressions (column list)
From table_name (name of table)
[WHERE condition]
[ORDER BY expression (name of column) [ASC | DESC | Using operator] [NULLS FIRST | NULLS LAST];Below is the parameter description of the above syntax are as follows:
- Column list: List of columns name from which we have retrieved data.
- Asterisk (*): All columns from the table that we have retrieving data.
- The table name specifies the table name from which we retrieved data. There must be at least one name we have to mention in from Clause.
- Where condition: Where specifies that the specific situation needs to be fulfilled to retrieve data from the table. Where the condition is optional in order by Clause.
- ASC (Ascending): This clause is optional in PostgreSQL order by Clause. It will sort the result in ascending order.
- DESC (Descending): This clause is optional in PostgreSQL order by Clause. It will sort the result in descending order.
- Nulls first: It will sort all null values before non-nulls in PostgreSQL order by clause result set. This is an optional clause in PostgreSQL order by Clause.
- Nulls last: It will sort all null values after non-nulls in PostgreSQL order by clause result set. This is an optional clause.
How ORDER BY Function works in PostgreSQL?
- Typically without using the order by function in PostgreSQL, data retrieve in an unspecified order.
- Our data comes in the specified order using the order by function in PostgreSQL. We have used the ASC function to sort data in ascending order.
- Also, the DESC function is available in PostgreSQL to sort data in descending order.
- We have used the column name in the order by Clause to sort data in our query’s specified order.
- We have also used multiple column names in a query to fetch sorted data from the table.
- This Clause is also used without specifying our query’s ASC and DESC functions. Suppose we have not provided ASC and DESC functions in order by Clause our result is sorted by ascending order.
- The default sequence is in ascending order that will return the smallest value first. If suppose that two rows are equal in some situations, they compare using the expressions. If rows are the same by using the expression, then the result set’s output depends on the expression’s implementation.
- It is not required to append ASC or DESC after any expressions in this Clause.
- Null value sorts will rank higher than the other value sorts in this Clause.
- In this Clause, two operators are used with the help of order by Clause using the keyword to retrieve the result set in ascending or descending order.
Examples
Below are some of the Examples.
Example #1
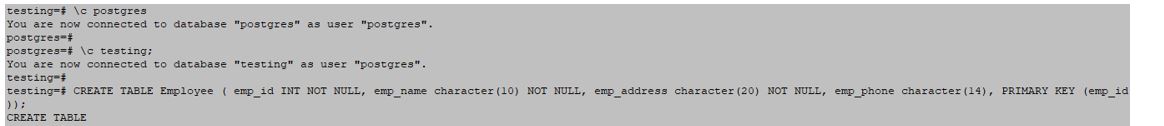
Create an employee table to describe order by Clause in PostgreSQL.
Code:
CREATE TABLE Employee ( emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), PRIMARY KEY (emp_id));Output:
Code:
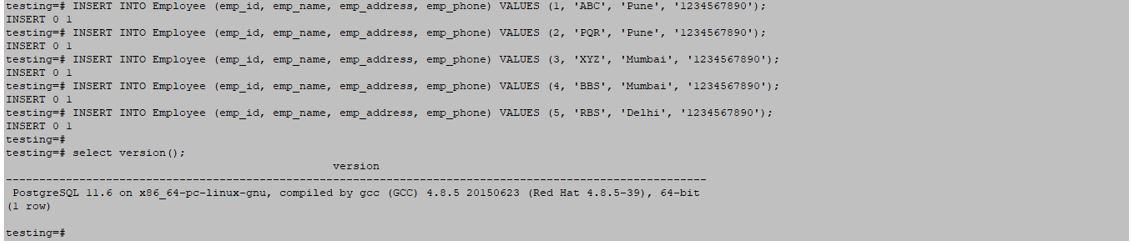
INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone) VALUES (1, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890');
INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone) VALUES (2, 'PQR', 'Pune', '1234567890');
INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone) VALUES (3, 'XYZ', 'Mumbai', '1234567890');
INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone) VALUES (4, 'BBS', 'Mumbai', '1234567890');
INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone) VALUES (5, 'RBS', 'Delhi', '1234567890');Output:
Example #2
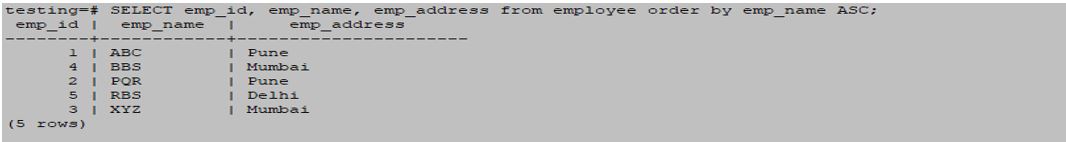
Order By Clause to sort rows with a single column.
Code:
SELECT emp_id, emp_name, emp_address from employee order by emp_name ASC;Output:
Code:
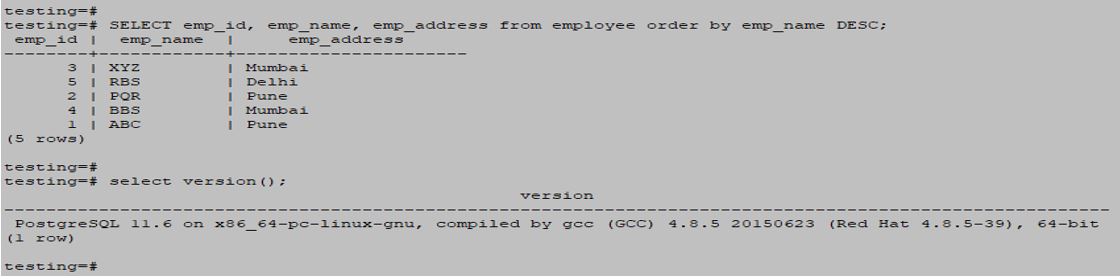
SELECT emp_id, emp_name, emp_address from employee order by emp_name DESC;Output:
Example #3
Order By Clause to sort rows with multiple columns.
Code:
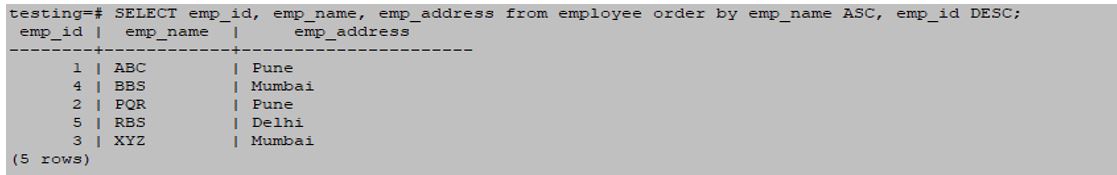
SELECT emp_id, emp_name, emp_address from employee order by emp_name ASC, emp_id DESC;Output:
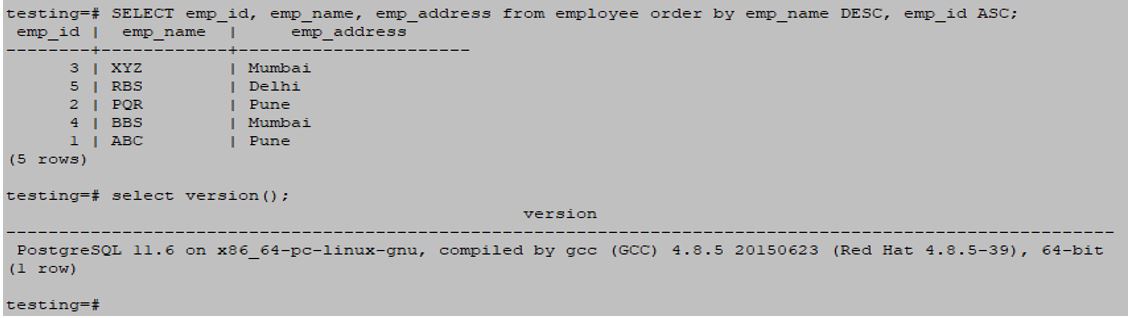
SELECT emp_id, emp_name, emp_address from employee order by emp_name DESC, emp_id ASC;Output:
Example #4
Order By Clause to sort rows with expressions.
Code:
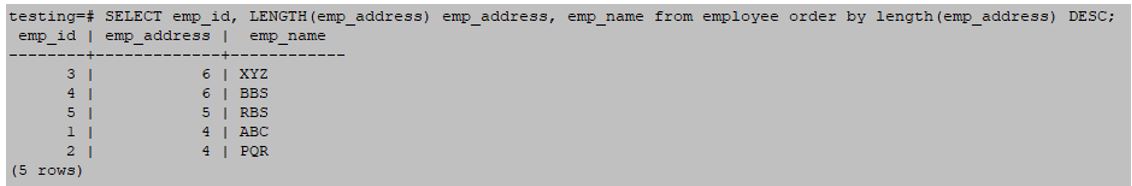
SELECT emp_id, LENGTH(emp_address) emp_address, emp_name from employee order by length(emp_address) DESC;Output:
Code:
SELECT emp_id, LENGTH(emp_address) emp_address, emp_name from employee order by length(emp_address) ASC;Output:
Example #5
PostgreSQL order by Clause to sort rows using Clause.
Code:
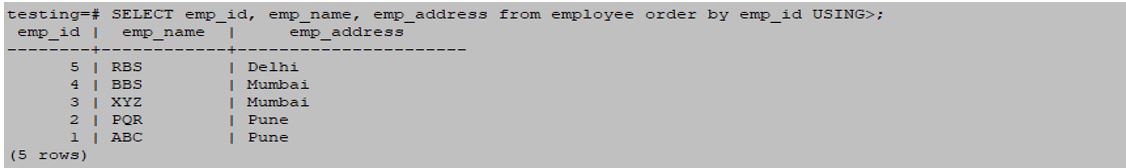
SELECT emp_id, emp_name, emp_address from employee order by emp_id USING>;Output:
Code:
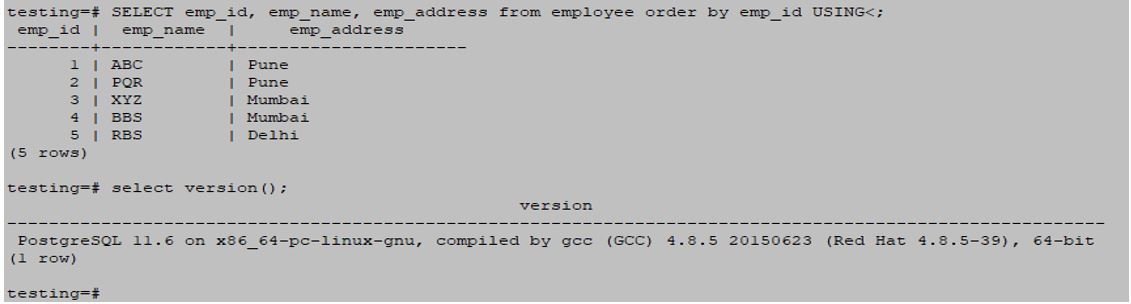
SELECT emp_id, emp_name, emp_address from employee order by emp_id USING<;Output:
Conclusion
PostgreSQL ORDER BY clause sorting is based on ascending or descending order. We can use single or multiple columns in the query to retrieve data in sorted order. This Clause will retrieve data in ascending order by default if we have not defined any sorting function in a query.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL ORDER BY” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.