Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to Aggregate Functions in SQL
Aggregate functions in SQL are used for performing calculations on an entire column(which could have thousands of rows). They are generally used for summarizing large datasets. If you are familiar with Excel, then these functions are similar to the ones which we have in Excel.
Syntax:
The generic syntax for AGGREGATE functions is as follows:
SELECT AGGREGATE_FUNCTION (column_name)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;Parameters:
The different parameters used in the syntax are:
- AGGREGATE_FUNCTION: Mention the type of aggregation function you want to use from { SUM, COUNT, MIN, MAX, AVG }.
- column_name: Mention the column name for which you want to perform COUNT operation.
- FROM table_name: Mention the table name from which the column has to be fetched.
- WHERE condition: Mention the specific criteria for filtering the data i.e. the criteria you want the output record to meet.
Above all the mentioned parameters except the WHERE condition are mandatory. You may use GROUP BY, HAVING and ORDER BY clauses based on your requirement.
Going ahead we will be discussing the above-mentioned functions in great detail.
In order to demonstrate and explain the aggregate functions in SQL effectively, we will be using the following table. It is a sample “customers” table of an online stationery store that contains 15 records with each customer’s id, name, city, the country he/she belongs to, Items purchased by him/her and the amount_paid by them.
The schema for the “customers” table is as follows:
Number of records: 15
| Customers |
| ID(primary key) |
| Customer |
| City |
| Country |
| Items_purchased |
| Amount_paid |
Let’s have a look at the records in the customer’s table. So that later, we can understand how aggregate functions are helpful in calculations.
| ID | Customer | City | Country | Items_purchased | Amount_paid |
| 1 | Peter King | Manchester | England | Books | 120 |
| 2 | Priya Krishna | New Delhi | India | pen | 50 |
| 3 | Jim Halpert | Manchester | England | pencil | 43 |
| 4 | Michael Scott | New York | USA | Books | 250 |
| 5 | Harvey Specter | Birmingham | England | pencil | 100 |
| 6 | Deepa Kamat | Mumbai | India | Books | 370 |
| 7 | Anita Desai | London | England | pencil | 50 |
| 8 | Rachel Zane | Michigan | USA | pen | 70 |
| 9 | Pretoria John | Canberra | Australia | pen | 190 |
| 10 | John L | Budapest | Hungry | Books | 540 |
| 11 | Justin Green | Ottawa City | Canada | pen | 65 |
| 12 | Babita Ghosh | Kolkata | India | pencil | 75 |
| 13 | Krish Pratt | London | England | eraser | 30 |
| 14 | Elizabeth Blunt | London | England | pencil | 340 |
| 15 | Nina Debrov | Amsterdam | Netherlands | Books | 452 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
SQL Aggregate Functions
The SQL aggregate functions are:
- COUNT
- SUM
- MIN / MAX
- AVG
1. COUNT FUNCTION
The COUNT function is used to count the total number of values or records stored in a specified column. It can be customized further by specifying criteria.
Here is an example to illustrate the use of COUNT Function.
Example #1
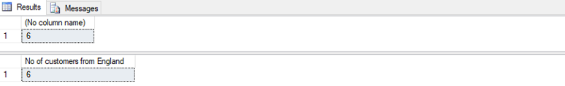
Find out the number of customers who are from England.
SELECT COUNT(Customer)FROM Customers WHERE Country = 'England';
–We can even give a name to the output column
SELECT COUNT(Customer) as "No of customers from England" FROM Customers WHERE Country = 'England';Output:
If you want to consider duplicates and NULL values in your result, then you may use a specialized version of COUNT, ie. COUNT(*).COUNT(*) returns all the records from a column including the NULL and duplicate values.
2. SUM FUNCTION
Sum function is used to calculate the sum of all the values present in a particular column. Unlike count, it works only on numeric data fields only. For customization, you may also specify criteria.
Here are a few examples to illustrate the SUM function.
Example #2
Find the total of money spent by customers from India.
SELECT SUM(Amount_paid)FROM Customers WHERE Country = 'India';Example #3
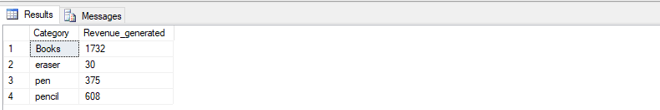
Find the total revenue collected along with different categories of stationery items.
SELECT Items_purchased as "Category", SUM(Amount_paid) as "Revenue_generated"
FROM Customers
GROUP BY Items_purchased;3. MIN/MAX FUNCTION
MIN function is used to return the lowest value in a particular column. Whereas MAX function is used to find out the highest value in a particular column.
Here are a few examples to illustrate the use of MIN/MAX functions.
Example #4
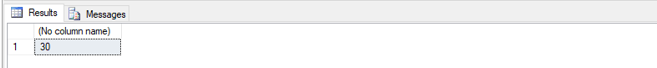
Find out the min price of a stationary item.
SELECT MIN(Amount_paid) FROM Customers;Example #5
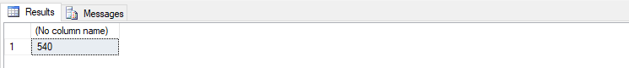
Find out the max price of a stationary item.
SELECT MAX(Amount_paid) FROM Customers;Example #6
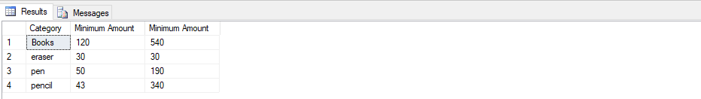
Find the min and max values of stationery items along with different categories.
SELECT Items_purchased as "Category", MIN(Amount_paid) as "Minimum Amount", MAX(Amount_paid) as "Minimum Amount"
FROM Customers
GROUP BY Items_purchased
ORDER BY Items_purchased;4. AVG FUNCTION
AVG function is used to calculate the average value of all the records present in the selected column. When calculating the average, the AVG function completely ignores NULL values.
Here are a few examples to illustrate the usage of the AVG function.
Example #7
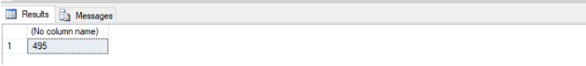
Find the average price of the stationery item.
SELECT AVG(Amount_paid)FROM Customers;Output:
Example #8
Find the average revenue generated by different categories of stationery items, ordered by the average revenue in ascending order.
SELECT Items_purchased as "Category", AVG(Amount_paid) as "Average Revenue"
FROM Customers
GROUP BY Items_purchased
ORDER BY 2;–We can simply use the column number in the group by or order by clause for the simplicity of code.
Output:
Some limitations of SQL Aggregate Functions
- All aggregate functions exclude NULL values before operating on the column
- All aggregate functions, except COUNT, works only on numeric data values
Conclusion
So in this article, we have learned about SQL aggregate functions which are very useful in calculating, summarizing and understanding the patterns in a huge dataset.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Aggregate Functions in SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.