Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Oracle Procedures
Procedures in Oracle can be called as subprograms, that are stored in the database used to execute specific operations on the contents of the database or tables. Like any other program, procedures should also have a few mandatory parameters so as to call and execute the procedure successfully, such as, procedure name, Arguments like IN, OUT or IN OUT for passing the values when the procedure is called, a declaration section for declaring the variables and the datatypes, and finally the main section that is to be executed.
Syntax for Creating a Procedure:
CREATE OR REPLACE procedure_name ([optional argument])
IS
[declaration section]
BEGIN
[executable section]
END
Parameters of Oracle Procedures:
The description of the different parameters used in the syntax are provided below:
1. procedure_name: The name of the procedure which is getting created.
2. Optional Argument: It refers to the argument that will get passed when the procedure is called. There are three types of arguments:
- IN: It is a default parameter. It is used to pass a value to the parameter. We can pass a constant, literal or expression as an IN parameter. Their values cannot be changed inside a subprogram.
- OUT: It is used to return a value to the caller of the procedure. We can update the value of the OUT parameter inside the procedure.
- IN OUT: It passes an initial value to the procedure and returns an updated value to the caller. An INOUT parameter is typically a string buffer that is read inside the program and then updated.
3. Declaration Section: It is used to declare variables and their data types.
4. Executable Section: This section consists of statements that are actually executed to retrieve or update values in the database.
Syntax for Calling a Procedure:
BEGIN
Procedure_name(arguments)
END
Here we are giving the name of the stored procedure along with arguments if any between BEGIN and END to call the procedure. So, now we are going to see how the actual procedure works in oracle.
How Do Oracle Procedures Work?
So, since we have already gone through the syntax of procedures. Let us now discuss actually how procedures get executed. Procedures, as discussed above, are a named subprogram in PL/SQL which is generally used when we want to have reusability. So one important point to keep in mind since procedures is a named subprogram is stored in the schema level in the database. So, it is stored in the database until we drop the procedure.
A procedure consists of three parts. The first part is declarative, the second one is executable and the third one is an exception. The control first goes to the declarative part contains the declaration of cursors, types, constants, expressions and also nested subprograms. The declared items are local to the procedure and ceased to exist as soon as the procedure completes execution.
After that, we have the executable part in which we actually manipulate the data by executing the statements. If we get any error while execution than we will have an exception handling section where the exception is handled during run-time. One point to keep in mind is that both the declarative and Exception Handling section is optional. It is a good practiced to handle run-time exceptions in procedures.
There are two types of parameters in Procedures formal parameters and actual parameters. Formal Parameters are variables declared in the header whereas actual parameters are the values that we pass to the subprogram when we actually invoke it.
Now we will look or go through some examples to check how to create and execute procedures that we help us to get a better understanding.
Examples of Oracle Procedures
Below are examples of oracle procedures:
1. Creating a Procedure to Print the Input Name
In this example, we are creating a procedure in which we take a name as input and then print that name with a message as output. Let us look at the example below:
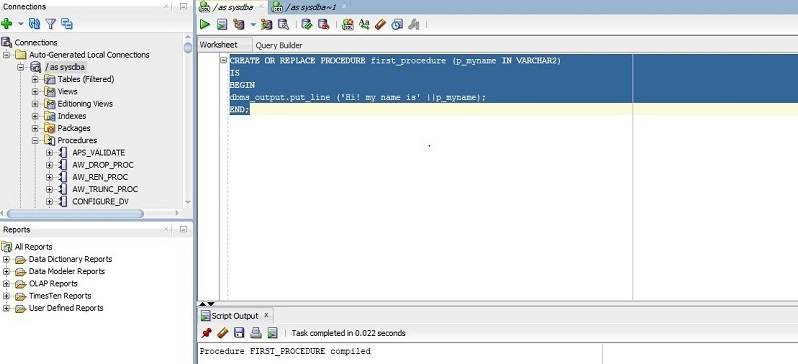
Query for Creating a Procedure:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE first_procedure (p_myname IN VARCHAR2)
IS
BEGIN
dbms_output.put_line ('Hi! my name is' ||p_myname);
END;
Now let us go through the code the first line says us the name of the procedure and what type of parameter it is taking as an input. In our case, the name is ‘first_procedure’ and parameter ‘p_myname’ of type IN.
In the executable section which is present after the BEGIN keyword, we are printing the message by concatenating the input name. Now let us run the above query in SQL developer and the below screenshot shows us the same.
Output:
2. Executing a Procedure to Print the Input Name
In this example, we are executing a procedure. Let us look at the example below:
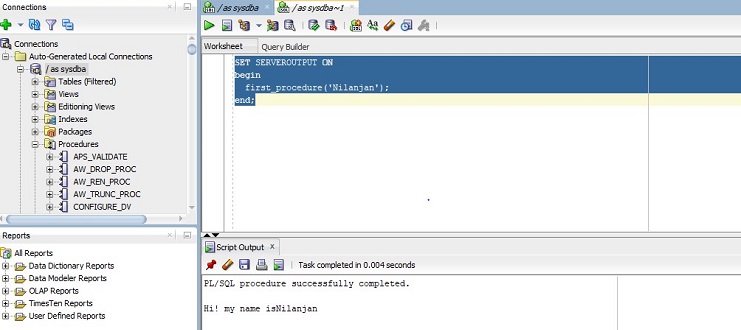
Query for Executing a Procedure:
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON
BEGIN
first_procedure('Nilanjan');
END;
In this above query, we are executing the above-created procedure bypassing the input parameter in the parenthesis. One important point to note is that if we are using SQL developer we have to set the server output ON first. The same is not required in SQL*Plus.
Now let us execute the query in SQL developer and we get the below output.
Output:
As you can see in executing the procedure it prints the name along with a message.
3. Dropping a Procedure
In this example, we are dropping a procedure. Let us look at the example below:
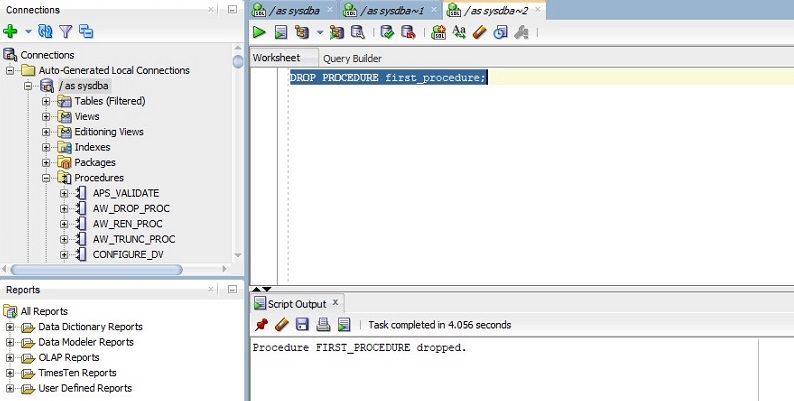
Query for Dropping a Procedure:
A procedure remains in the database until we drop it from the database. So, in case we want to remove a procedure from the database we will have to use DROP. The below query shows how to drop a procedure from the database.
DROP PROCEDURE first_procedure;
In the above query, we are just providing the procedure name with the DROP keyword. Once the procedure is dropped it is removed from the database and hence we cannot execute it. Let us run the above query in SQL developer and we can see the output of the above query in the below screenshot.
Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about the procedures in ORACLE and how to use them. The article also discusses the syntax and their parameters. We also saw how to create and delete procedures in oracle database through an example.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle Procedures. Here we discuss the Parameters of Oracle Procedures along with the Working and Examples. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –