Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to Sample Database for Oracle
This article will give you an outline of Oracle Database and help you step by step to create a sample database using Oracle database server. Oracle database is a multi-model database management system created and distributed by Oracle Corporation. A database server is supposed to manage enormous amounts of data in a concurrent multi-user environment. In such a scenario, a DBMS server is required to be providing high performance, authorized access and failure recovery features.
Oracle database is designed for enterprise grid computing and used for online transaction processing & data warehousing. The latest database versions from Oracle e.g. Oracle Database 19C are now available on cloud or in a hybrid cloud environment.
The main features of an Oracle database include:
- Portability
- Application Clusters
- Enterprise Manager
- SQL
- Automatic Storage Management
- Backup and Failure of recovery
How to Create Sample Database?
We can create a database during the Oracle database software installation. However, we can also create a database after the installation. Before moving to database creation, it is a prerequisite to install the software.
We can create a database in two ways:
- With Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA), a graphical tool.
- Create a Database SQL statement.
However, the first way is strongly recommended by Oracle as it is a more automated and non-hectic approach. So, we will create one by using DBCA with following steps:
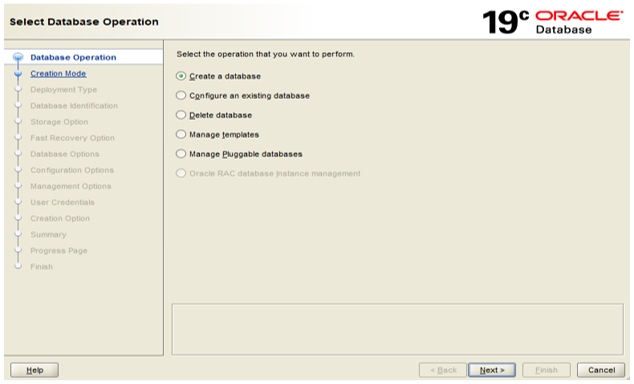
Step 1: This is the first step to create a database. First of all, launch the DBCA tool from Start >> Programs. Here, we get a list of options to create a new database, configure an existing database, delete a database, and manage template and pluggable databases. Since we are creating a new one, so we need to select ‘Create a new Database’ (selected by default).
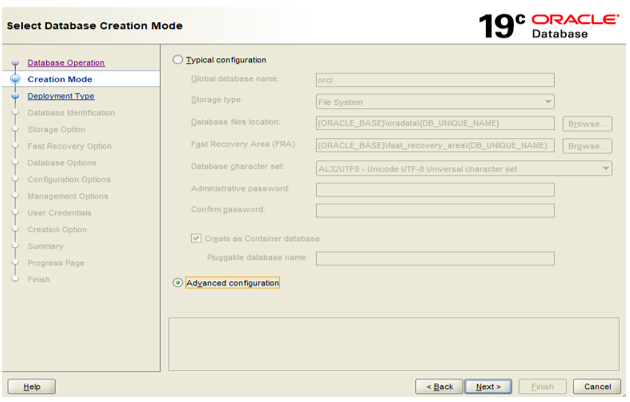
Step 2: Choose the ‘Advanced Configuration’ and click on ‘Next’.
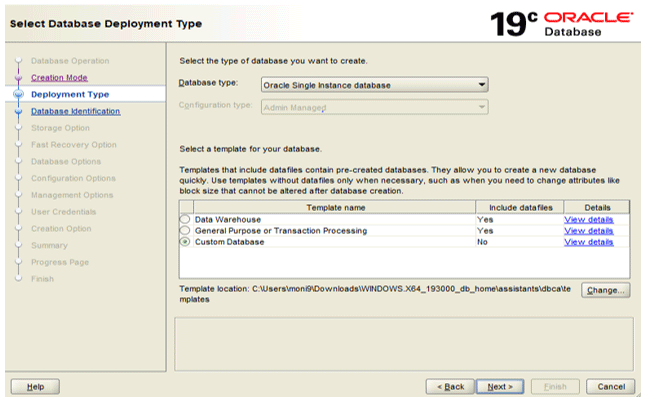
Step 3: Now, we need to select the database type and template. Select ‘Custom Database’ for now. We can check the details of other types by clicking on ‘details’.
Following are the all template options available:
- Data Warehouse
- General purpose
- Custom Database
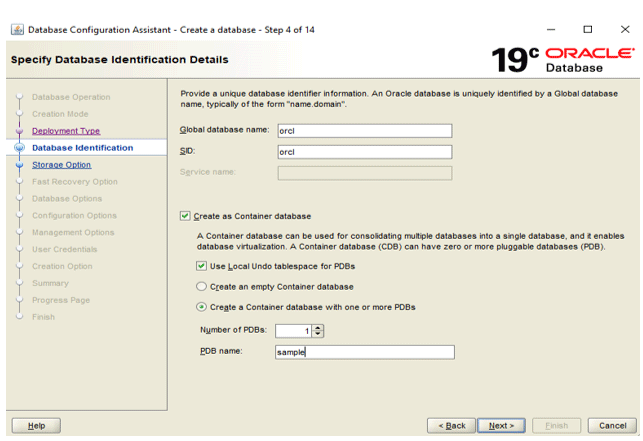
Step 4: Provide ‘Global Database Name’ and ‘SID’ name. Here, you can choose to create a database container with single or multiple PDBs (pluggable databases).
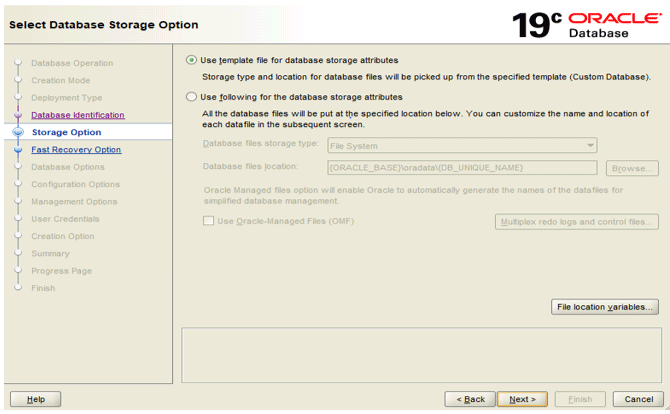
Step 5: Select the location to store the files. With the first option, the storage type and location for the database will be picked from the selected template. However, you can also choose your preferred location by selecting the other option.
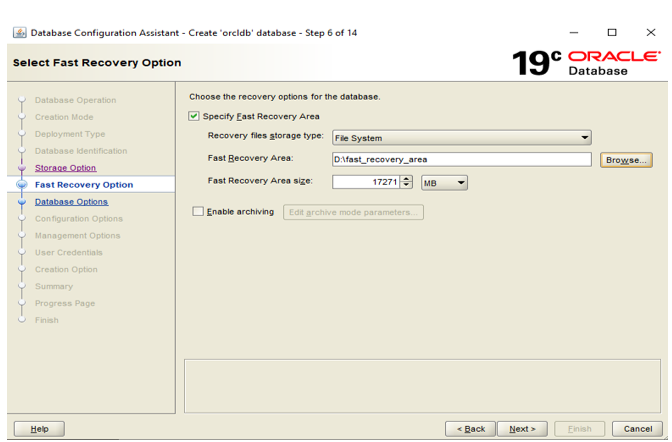
Step 6: Choose the storage location for backup and recovery files. Fast Recovery Area is a disk space that can contain backup files, log files and control files. It is always recommended to configure this location.
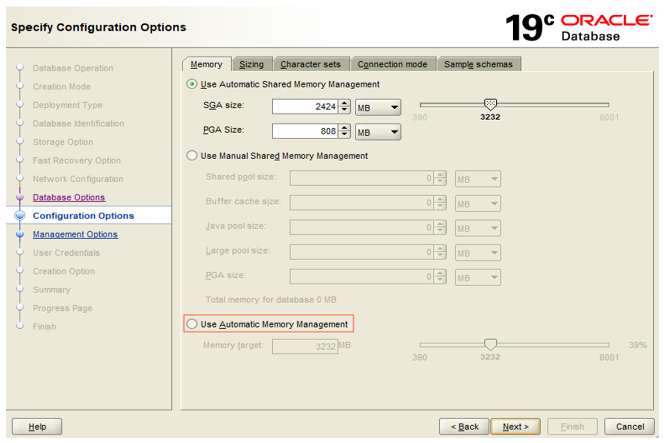
Step 7: Next, we need to Memory Management for SGA and PGA. For this, we should select the ‘Use Automatic Memory Management’. It will assign one larger chunk and Oracle will manage the memory.
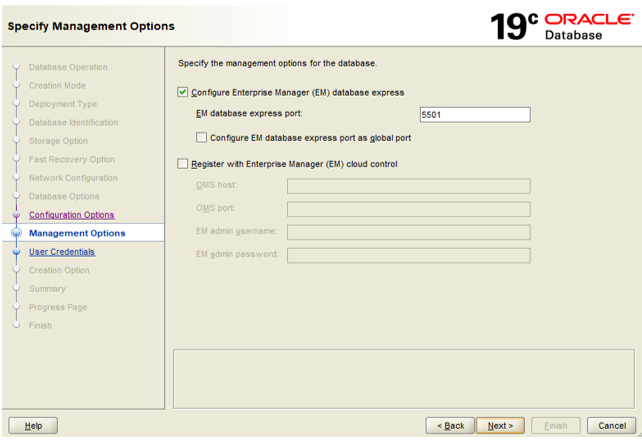
Step 8: Specify the manager for the database. We get two options i.e. Enterprise Manager Database Express and Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. As we are creating the database in our local system, we should choose the default ‘Configure EM database Express’ option only.
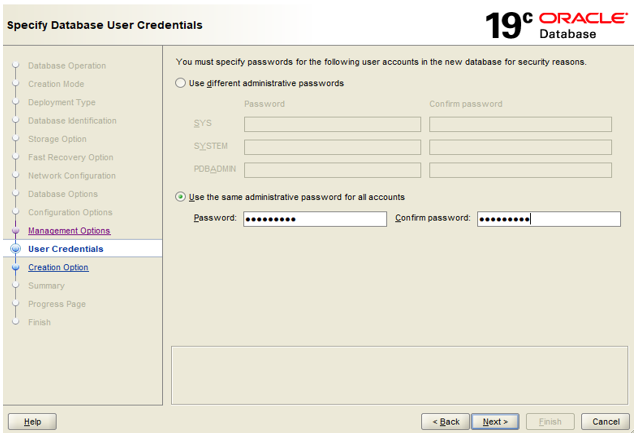
Step 9: Set user credentials for the database. We can set different or same passwords for SYS, SYSTEM and PDB_ADMIN users. We are keeping the same credentials for all accounts.
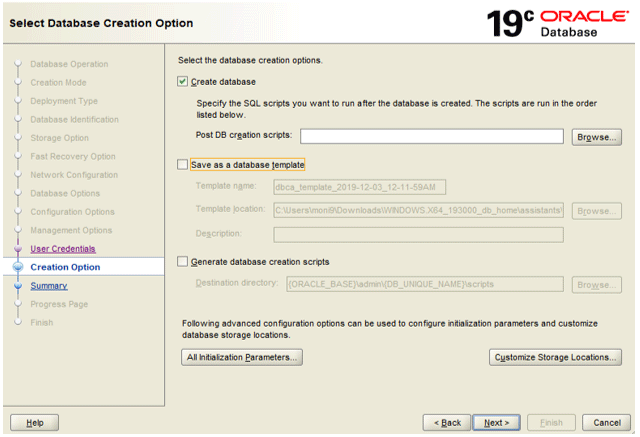
Step 10: Select ‘Create Database’ as the creation option and click ‘Next’.
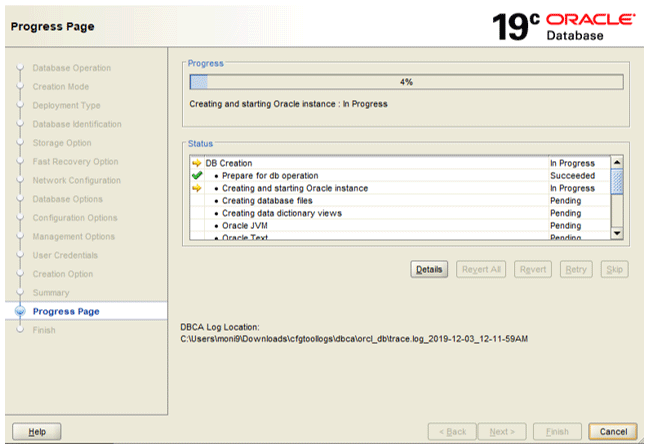
Step 11: We can see the summary of the database in the ‘Summary’ section. Click ‘Next’ to proceed. Now, the database creation is in progress. Breathe, it may take some time to finish.
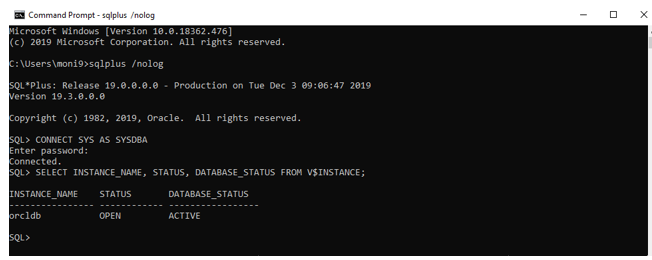
Step 12: Once it is finished, you can close the DBCA window, the database will be created in the system. We can check the status of the database by running these commands in command prompt or SQLPLUS.
CONNECT SYS as SYSDBA – to connect to the database server.
SELECT INSTANCE_NAME, STATUS, DATABASE_STATUS FROM V$INSTANCE
As we can check, our database is active and ready to use. Now, we can populate our database with tables and data using SQL commands.
How does Oracle Database Work?
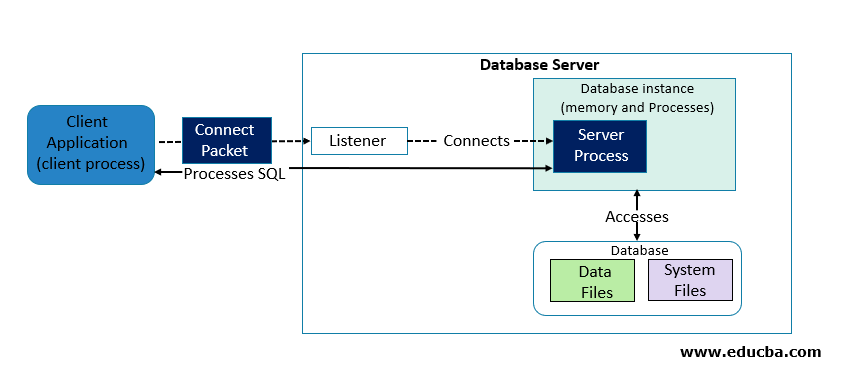
In an Oracle Database, there are two main components i.e. database and instance. The collection of memory and processes which contributes to the running installation is called as instance whereas a collection of files that store data is called a database.
That’s how the architecture of a database server looks like:
Now let’s try to understand how Oracle stores data. An Oracle database storage has two storage structures i.e. Physical Storage Structure and Logical Storage Structure.
1. Physical Structure
The Physical structure includes the files in which data reside. Whenever we create a database, a bunch of Data files, Control files, redo log files, Backup files Network files and parameter files is generated.
2. Logical Structure
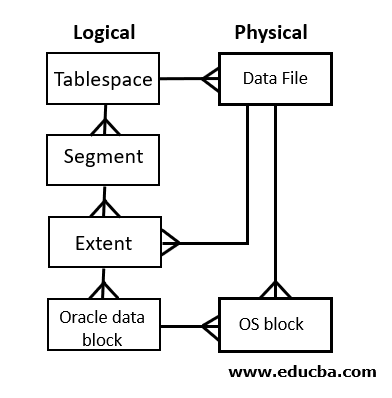
Oracle uses a logical structure to control disk space usage. Following are the elements of the logical storage structure of an Oracle database:
- Data Blocks – Oracle database stores data in blocks. A block refers to a number of bytes on the disk. Data blocks are also known as logical or Oracle blocks or pages.
- Extent – It refers to a number of logically adjacent blocks used to store particular information.
- Segments – A segment consists of extents allocated to store database object like a table or an index.
- Tablespaces – A database is comprised of logical storage units known as tablespaces. A tablespace acts as a container for a segment. Each tablespace contains at least one data file.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about the Oracle database and its working architecture. It would have also helped you to know how to create one using Oracle DBCA which is Oracle recommended way.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Sample Database for Oracle. Here we discuss step by step instructions on how to create a sample database in oracle. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –