Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to DISTINCT in Oracle
DISTINCT keyword in Oracle database separates or filters the duplicate rows in the result set returned by the SELECT statement (result set contains the column/columns present in the SELECT statement) so that the column or columns returned by the query contains all the values or records which are not duplicate and are unique to each other as the DISTINCT keyword compares each value of the column/columns present in the result set returned by the query with each other.
Syntax
We will look now into the syntax of the distinct keyword in Oracle. We have two options in this case for syntax. The first syntax is to use distinct keyword without conditions and the second syntax is to use distinct keyword with conditions.
Syntax without Condition: Select DISTINCT(expressions) from table_names;
Syntax with the Condition:Select DISTINCT(expressions) from table_names [where conditions];
Parameters
We will now look at the various parameters used in the two above syntaxes.
- expressions: we provide the column names or expressions that we want to execute.
- table_names: We provide the table names from which we want the records. Important information to note here is that there should be at least one table name after the clause.
- [Where conditions]: It is optional If we provide the where condition than we will retrieve the values after query execution only if the condition that was mentioned is satisfied.
Note: One Important Information to keep in mind is that the DISTINCT keyword considers null value also as a unique value. So, in case if we have null values in a column and we are using the DISTINCT keyword to fetch unique values then it will also display the NULL value in the output.
How to Use DISTINCT in Oracle?
By now we have discussed what is a DISTINCT keyword in oracle, the syntax of DISTINCT keyword and the various parameters used in the syntax.
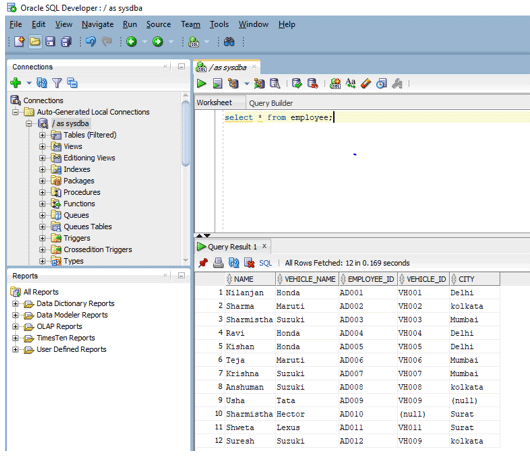
Now we will look into various examples to learn how to efficiently use DISTINCT in Oracle. Before we move into the examples, we will use the EMPLOYEE table already created in the database. The table consists of five columns which are NAME, VEHICLE_NAME, EMPLOYEE_ID, VEHICLE_ID, and CITY. Below is the screenshot of the values present in the employee table. The query we will be using for this is the basic SELECT statement
SELECT * from employee;
On executing in SQL developer we get all the values as shown below.
Output: Employee table
Now let us begin with the examples.
1. Unique Values in a Column without Condition
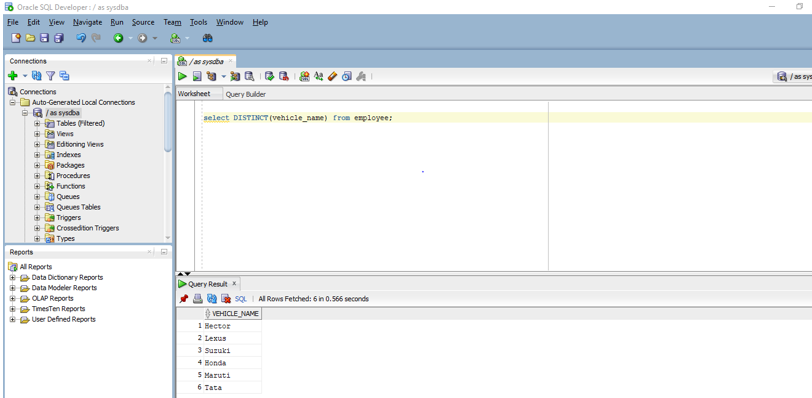
In this example, we are going to use DISTINCT to find the unique values in a particular column of a table without having any conditions. As an example, we are going to find the unique values present in the vehicle column of the employee table. The query is shown below:
Code:
select DISTINCT(vehicle_name) from employee;
Output:
In the above query as you can see we have provided the column name as well as the table name. On executing the above query in SQL developer we get the below output.
2. Unique Values in a Column with Condition
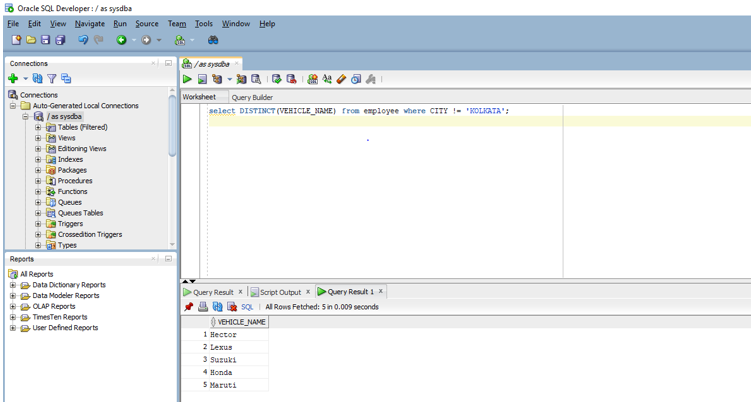
In this example, we are going to find unique values in a column just like the previous example but with a slight modification. In this, we are going to extract the unique values based on some condition. As an example let us get the unique values of column vehicle name from employee table when the city is not Kolkata. The query for the same is provided below.
Code:
select DISTINCT(VEHICLE_NAME) from employee where CITY != 'KOLKATA';
Output:
If you see the above query the query should return the values which satisfy the where condition. On executing the above query in SQL developer we get the below output.
As you can see in the previous example we had six unique values whereas in the second example we have five unique values as we had added a specific condition in the second example.
3. Unique Values From Multiple Columns
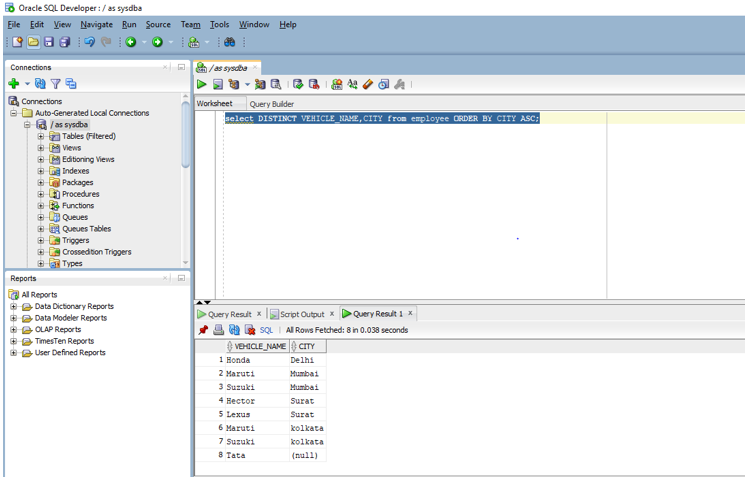
In this example, we are going to find unique values on multiple columns by using DISTINCT. So earlier examples we had used single columns but in this case, we are going to use multiple columns. For example, suppose we want to find the unique values of both vehicle name and city and the results should be in ascending order based on the column city. Let us look at the query for the same below.
Code:
select DISTINCT VEHICLE_NAME,CITY from employee ORDER BY CITY ASC;
Output:
In the above query first, the data is extracted in ascending order based on column city and then both values in the columns vehicle name and city are used to get the unique pairs. On executing the above query in SQL developer we get the below output.
4. DISTINCT with NULL values
Earlier in the article, we had discussed that DISTINCT treats NULL values as unique values so if we have a column with null values in it. It will be treated as a unique value. For example, we have null values in the CITY column which you can see in the screenshot provided at the beginning of the article where all values of the employee table are shown. So, we will apply DISTINCT on the Column CITY to find out the impact of null values on the result. The query for the same is shown below.
Code:
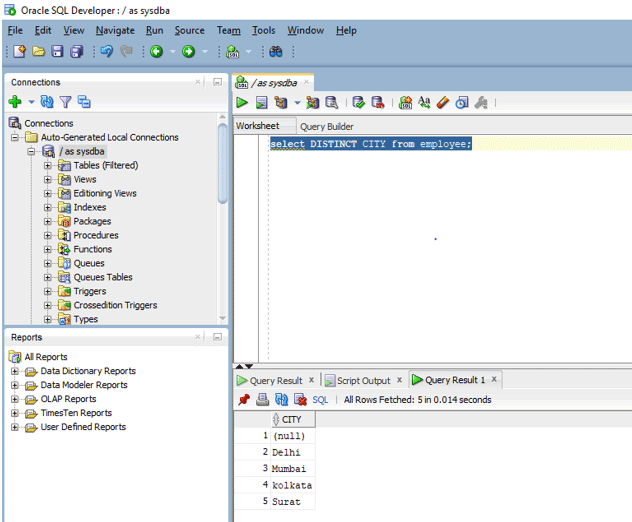
select DISTINCT CITY from employee;
Output:
On executing the above query in SQL developer we get the below output.
As we can see the output shows null as a distinct value. So this shows that DISTINCT treats null as a unique value.
Conclusion – DISTINCT in Oracle
In this article, we discussed the DISTINCT keyword in oracle, the syntaxes used for using DISTINCT in queries, the parameters used in those syntaxes and then through various examples we came to know how we can use DISTINCT in oracle to solve our required tasks.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DISTINCT in Oracle. Here we discuss DISTINCT keyword in oracle, the syntaxes used for using DISTINCT in codes and output. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –