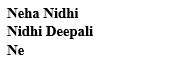Introduction to Array in Unix
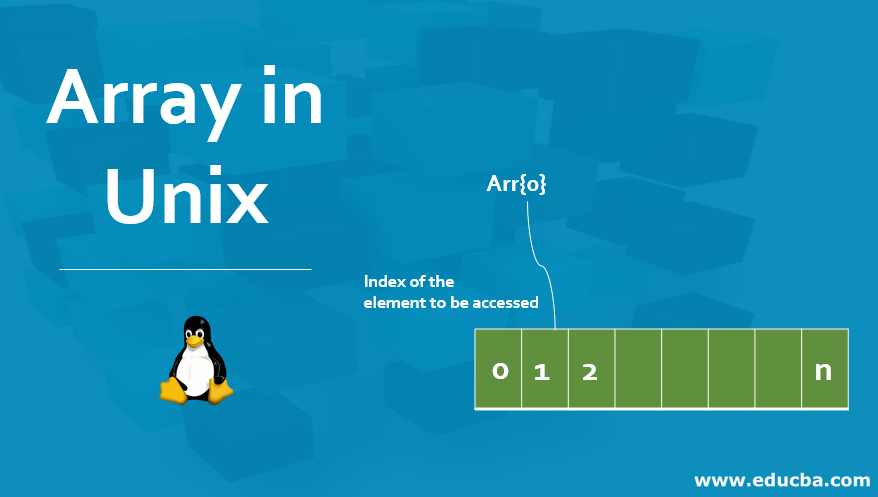
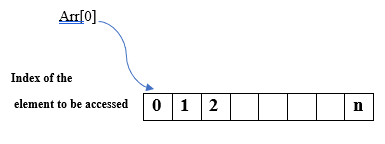
Array in Unix is a data structure consisting of a collection of elements stored in a memory location which is contiguous, whose data type can be the same or different like integer, strings, etc, and referenced by the index beginning with zero. So, an array in Unix is called zero-based, formed either by indirect declaration, explicit declaration, or compound assignment, and there is no limit on the array size.
The array data structure is also available in Unix.
- Array in Unix: It is the collection of elements that may or may not be the same data type.
- Index: Elements in the array reference indices starting at zero, following a zero-based indexing system.
- Size: There is no maximum limit on the size of the array
Syntax of Array in Unix
There are different ways of forming an array in shell scripting. Let us go through each one of them in detail:
1. Indirect Declaration: Here, a value is assigned for a particular index on the go. An example of it is provided below.
Syntax:
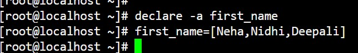
array_name[index] = value2. Explicit Declaration: First, the array is declared, and then later, the values are assigned to it. Declare is a built-in keyword, and -a is an option of reading built-in, which allows reading and assigning values.
Syntax:
declare -a array_name3. Compound Assignment: Here, the array is declared with multiple values at a time.
Syntax:
array_name = (value1 value2 value3 . . . valueN)Or
array_name = ([0]=value1, [1]=value2,[2]=value3..)If an index is not provided, the assignment of the value determines the next available index by adding one to the last index.
How Does Array Work in Unix?
We have learned different ways to create an array in Unix. Now, let’s explore various operations that can be performed on the Unix array.
1. We will create an array of names
2. To access all the elements of the array, use either [*] or [@]
Code:
echo ${first_name[*]}
echo ${first_name[@]}Syntax:
echo [options] [arguments]3. To access any specific element of the string using its index.
Code:
echo ${first_name[0]}
echo ${first_name[1]}
echo ${first_name[2]}Output:
4. To print the elements in a range. The syntax for the same is as follows:
Syntax:
echo $array_name[which element]:starting_index:count_element]Let us familiarize ourselves with the same.
Code:
echo ${first_name[@]:0:2}
echo ${first_name[@]:2:3}
echo ${first_name[0]:1:2}Output:
@ – refers to all the elements of the array
In the command echo ${first_name[@]:0:2}
@ consider all the elements of the array. 0 – means to start with this particular index, and 2 displays the number of elements from the starting point
2 displays a number of elements from the starting point
In this command echo ${first_name[0]:1:2}
0 – consider the 0th element of the array. 1- is the starting point, and 2 – is the count of the number of elements from the starting point
5. To get the size of the array
Code:
echo ${#first_name[@]}
or
echo ${#first_name[*]}Output:
6. To find the length of a specific element of an array
Code:
echo ${#first_name[0]}Output:
7. To get the array index, use the below command.
Code:
echo ${!first_name[@]}Output:
8. To delete the array in the script, you can use the unset command. It is a built-in command to destroy an array or any element of the array
Syntax:
unset array_nameCode:
unset first_name9. To delete an element at any specific index
unset first_name[2]This will delete the element at index 2.
10. To search for a specific pattern in the array.
Code:
echo ${first_name[@]/*[aA]*/}Output:
Here, first_name[@]: refers to all the elements of the array
/pattern to be searched/: It is the pattern in the array or its element.
If a match is found, it will return 1; otherwise, it will return 0.
11. To search for a specific pattern and replace it in the given array.
Code:
echo ${first_name[@]//a/A}first_name[@]: Consider all the elements of the array
//pattern to be searched/replacement string/: Search & replacement string
Output:
first_name[2]: Search and replace operations on the element with index 2.
While performing the search and replace operation, the array’s original value remains unchanged. Instead, it returns a new value that you can store in the same or different variables.
12. To operate on an array’s elements, we can use the Loops. Like any other programming language, Bourne shell supports two loops, i.e., for loop and while loop. Let us look at an example to iterate over an array for a loop.
Code:
Arr = (1 2 3 4 5)
for i in "${Arr[@]}"
do
echo $i
doneOutput:
Similarly, you can iterate over an array using a while loop as well.
Please keep in mind that various types of shells are available in Unix, like Bash, K shell, Bourne shell, etc. Shell is an interface to Unix systems with different commands and functions.So, different types of shells have associated syntax for arrays and their operations, with a slight variation in the command syntax mentioned earlier.
Bash Shell also permits the array operations on the variables without the variables being explicitly declared as an array. Let us look at the example to understand the above statement better.
Code:
String_variable = India is a democratic country
echo "${string[0]}"Output:
Conclusion
The array stores a collection of items in a contiguous memory location. The purpose of forming an array is to store multiple items of the same type with the same or different data types. In a practical scenario, why array structure lags popularity due to its lack of compatibility with various shell and complex structures.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Array in Unix” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.