Updated September 6, 2023
Introduction to C++
C++ is a dynamic and versatile programming language that combines high-level and low-level programming features. It was developed as an extension of the C programming language, aiming to provide enhanced capabilities for object-oriented programming (OOP) while still maintaining the efficiency and performance associated with C. C++ offers a wide range of features, including classes, templates, inheritance, polymorphism, and exception handling, which make it suitable for developing a variety of software applications, from system-level programs to complex graphical user interfaces and games. Its ability to manage memory directly and efficiently gives programmers a great deal of control over system resources. With its widespread use in industries like game development, system programming, and software engineering, it remains a fundamental language for developers seeking a balance between high-level abstractions and low-level control.
C++ is a robust and versatile programming language that originated from C. Bjarne Stroustrup, who developed it at Bell Labs during the early 1980s to provide object-oriented programming tools while preserving C’s efficiency and low-level capabilities. C++ operates as a compiled language, transforming the source code into machine code before execution, yielding high-performance applications.
Table of Contents
Key Highlights
- C++ is a general-purpose programming language that extends the C programming language.
- It supports object-oriented programming, inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation.
- The advantages include its high performance, portability, and wide range of software development, gaming, and scientific computing applications.
- The disadvantages include its steep learning curve, the potential for memory leaks, and the complexity of syntax.
- It finds applications in various areas, such as operating systems, web browsers, game engines, embedded systems, and more.
History
| Year | Milestone |
| 1979 | Bjarne Stroustrup begins work on “C with Classes,” the predecessor to C++. |
| 1982 | Development of C++ starts as a successor to “C with Classes,” adding new features and improvements. |
| 1984 | First implementation of stream I/O library and introduction of the output operator (<<). |
| 1985 | The first edition of “The C++ Programming Language” was released, becoming a definitive reference. The first commercial implementation of C++ was released. |
| 1989 | C++ 2.0 is released, introducing multiple inheritance, abstract classes, and other features. |
| 1990 | “The Annotated C++ Reference Manual” is published, becoming the basis for the future standard. |
| 1998 | C++98 is standardized, bringing a standardized version of the language. |
| 2003 | C++03, a minor update to C++98, is released. |
| 2011 | C++11 is released, introducing numerous new features and expanding the standard library. |
| 2014 | C++14 update is released, adding various new additions to the language. |
| 2017 | C++17 is released, introducing further enhancements and features. |
| 2020 | C++20 standard is finalized and officially published. |
| 2018 | Bjarne Stroustrup was awarded the Charles Stark Draper Prize for Engineering for developing C++. |
| 2022 | C++ ranks third on the TIOBE index, surpassing Java for the first time. |
Components of C++
Below are the components as follows:
1. First Component
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<"Welcome to EDUCBA";
}The first component in this program is the header file denoted by #include<iostream> command and uses the std namespace, which contains the cout command that is being used to print ‘Welcome to EDUCBA’ in this case. There could be other header functions as well, depending on the problem statement.
2. Second Component
The second component is the ‘int main()’ statement which is the Master Program Function and is a prerequisite of every program to have the main function at the beginning of execution. The opening parenthesis after the main should have a matching closing parenthesis. The ‘int’ is the return type that states the type of value that the program is returning.
3. Third Component
void function() //function that doesn't return a value
{
double d = 2.2; //initialize floating-point number
int i = 7; //initialize integer
d = d+i; //assign sum to d
i = d*i; //assign product to i (truncating the double d*i to an int)
}The third component is the declaration of variables, which are ‘d’ and ‘i’ in this case. A variable is assigned a name with regards to which it stores data in the memory. It needs to support the inbuilt data types.
Declaration of variables should abide by the following rules:
- Allowed Characters: Variables consist of letters (uppercase and lowercase), digits, and underscores.
- Start with Alphabetical Letter: Variable names should begin with an alphabetical letter (A-Z or a-z) or an underscore (_).
- Case Sensitivity: Uppercase and lowercase letters are considered different. So, variables like myVariable and myvariable would be treated as distinct.
- Reserved Words: Certain words are reserved as keywords, which cannot be used as variable names. Examples of reserved words include int, double, if, for, while, etc.
- Initial Values: Variables can be assigned an initial value at the time of declaration, or they can be assigned a value later using the = operator.
4. Fourth Component
void copy_fct()
{
int v1[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int v2[10]; //to become a copy of v1
for (int i=0; i<10; ++i) //copy elements
v2[i]=v1[i];
// .....
}The program statement in this code snippet utilizes a for loop to transfer values from one array to another. The code also employs comments for single-line (//) and multi-line (/* … */) to provide explanations and documentation within the program, enhancing readability and understanding.
5. Fifth Component
Operators are another component.
The types of operators are:
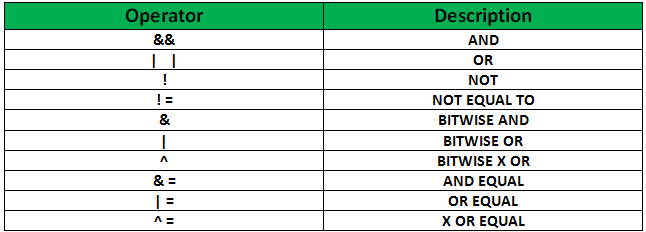
- Logical Operators such as &&, ||, etc.
- Arithmetic Operators such as +, %, etc.
- Relational Operators such as ==. !=, etc.
What are OOPs in C++?
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm centered on “objects,” class instances. C++ is an object-oriented programming language that allows developers to construct modular and organized code by utilizing classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation, and polymorphism. “OOP” is an abbreviation for “Object-Oriented Programming,” it refers to a collection of concepts and practices that improve code reusability, maintainability, and flexibility.
Here’s an explanation of the key concepts in OOP using C++:
1. Class: A class is a blueprint for constructing objects. It specifies attributes (data members) and methods (functions) that the objects will have.
Syntax:
class ClassName {
public:
// Data members (attributes)
dataType attributeName;
// Member functions (methods)
returnType methodName(parameters);
};2. Object: An object is a type of class instance. It represents a concrete entity based on the class blueprint.
Syntax:
ClassName objectName; // Creating an object3. Constructor: A particular member function is automatically called when an object of the class is created. It initializes the object’s attributes.
Syntax:
ClassName(parameters) {
// Constructor code
}4. Destructor: A specific member function is invoked when an object is no longer in scope. It releases resources held by the object.
Syntax:
~ClassName() {
// Destructor code
}5. Encapsulation: The class’s internal details are hidden, with only necessary functionalities exposed through methods.
6. Inheritance: The ability to construct a new class (derived or child class) that inherits properties and behaviors from an existing class (base or parent class).
7. Polymorphism: The ability to display the same interface for diverse data or objects allows different classes to be considered instances of a single base class.
Example
Here’s a simple example of a Person class with attributes and methods:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person {
private:
string name;
string add;
public:
Person(string n, string a) {
name = n;
add = a;
}
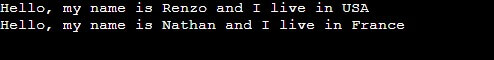
void introduce() {
cout << "Hello, my name is " << name << " and I live in " << add << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Person person1("Renzo", "USA");
Person person2("Nathan", "France");
person1.introduce();
person2.introduce();
return 0;
}Output:
In this example, the Person class has the attributes name and live, and the function introduce(). The Person class yields two objects, person and person2, each with its attributes. The method introduce() calls on each object to display its information.
Constructor and Destructor in C++
Classes in C++ use constructors and destructors to initialize and clean up objects. In object-oriented programming, objects execute these actions automatically upon their creation and destruction, rendering them essential.
Constructor
A constructor represents a specialized member function sharing the class’s name. When generating a class object, it automatically executes. Constructors configure the object’s attributes and allocate any necessary resources. They support overloading, allowing a class to possess multiple constructors featuring different argument lists.
Syntax:
class ClassName {
public:
ClassName(parameters) {
// Constructor code
}
};Destructors
A destructor is a particular member function of a class that the system invokes automatically when a class object goes out of scope, or someone explicitly deletes it. It releases the object’s resources, such as memory, file handles, or network connections.
Syntax:
class ClassName {
public:
~ClassName() {
// Destructor code
}
};Example of Constructor and Destructor
Here’s an example of a simple Car class with a constructor and a destructor:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Car {
private:
string brand;
public:
// Constructor
Car(string b) {
brand = b;
cout << "A " << brand << " car is created." << endl;
}
// Destructor
~Car() {
cout << "The " << brand << " car is destroyed." << endl;
}
};
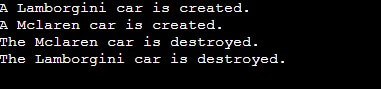
int main() {
Car car1("Lamborgini"); // Constructor called
{
Car car2("Mclaren"); // Constructor called
} // car2 goes out of scope, Destructor called for car2
// car1 goes out of scope, Destructor called for car1
return 0;
}Output:
In this example, the Car class contains a constructor that accepts a brand parameter to initialize the brand data member. When creating the objects car1 and car2, they invoke their constructors, which in turn write the relevant messages. As these objects exit the scope, their destructors are invoked, causing the linked messages to be composed. The destructor for car2 is called when it goes out of scope within the inner block, while the destructor for car1 is executed upon completing the main function.
Exception Handling in C++
Exception handling is a programming technique that deals with errors and unexpected situations during program execution. It lets you handle unexpected situations gracefully and prevents your program from crashing.
Syntax:
try {
// Code that might throw an exception
} catch (ExceptionType e) {
// Code to handle the exception
}Example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
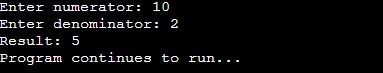
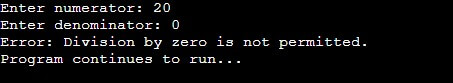
int numerator, denominator, result;
cout << "Enter numerator: ";
cin >> numerator;
cout << "Enter denominator: ";
cin >> denominator;
try {
if (denominator == 0) {
throw "Division by zero is not permitted.";
}
result = numerator / denominator;
cout << "Result: " << result << endl;
} catch (const char* error) {
cout << "Error: " << error << endl;
}
cout << "Program continues to run..." << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
Valid Division:
Division by Zero:
Virtual Base Class in C++
A virtual base class is used in C++ to solve the “diamond problem” in many inheritance circumstances. When a class is virtually inherited, just one instance of the base class is shared by all classes derived from it, saving data members from being duplicated. This is very helpful when dealing with complicated inheritance hierarchies.
Syntax:
class Base {
public:
// Base class members
};
class Derived1 : virtual public Base {
public:
// Derived1 class members
};
class Derived2 : virtual public Base {
public:
// Derived2 class members
};
class FinalDerived : public Derived1, public Derived2 {
public:
// FinalDerived class members
};Example
Here’s a simple example of how to utilize a virtual base class.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class France {
public:
void French() {
cout << "France French" << endl;
}
};
class Germany : virtual public France {
public:
void German() {
cout << "Germany German" << endl;
}
};
class India : virtual public France {
public:
void Hindi() {
cout << "India Hindi" << endl;
}
};
class Country : public Germany, public India {
public:
void Language() {
cout << "Countries with their National Language" << endl;
}
};
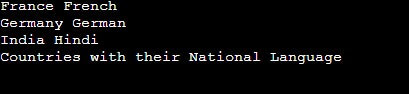
int main() {
Country Country;
Country.French();
Country.German();
Country.Hindi();
Country.Language();
return 0;
}Output:
France is a virtual base class in this example. The German and Indian classes inherited almost entirely from France. The Country class then inherits from both Germany and India. By utilizing virtual inheritance, there is just one shared instance of France within the Country, removing any possible ambiguity caused by the diamond problem. The program displays the inheritance hierarchy and function calls on the derived class objects.
What is an array in C++?
An array is a collection of elements stored in contiguous memory locations with the same data type. It provides an indexed way to access and manage a group of values.
Syntax:
dataType arrayName[arraySize];Example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int numbers[6];
numbers[0] = 12;
numbers[1] = 20;
numbers[2] = 25;
numbers[3] = 32;
numbers[4] = 40;
numbers[5] = 55;
cout << "collection of elements: ";
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) {
cout << numbers[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
This example declares an array of size six to store integers. It initializes the array elements with values using indices that range from 0 to 5. The program then utilizes a loop to display the elements of the array.
What is Inheritance in C++?
In object-oriented programming, inheritance refers to the process of developing a new class (a subclass) from an existing class (a superclass). The derived class inherits the base class’s properties (data members and member functions) and can add new or alter existing ones.
Inheritance lets you create a class hierarchy with similar traits and behaviors, encouraging code reuse and organization.
Syntax:
class BaseClass {
// Base class members
};
class DerivedClass : accessSpecifier BaseClass {
// Derived class members
};In inheritance, three access specifiers are public, protected, and private. The access specifier influences how the derived class accesses base class members.
Example of Inheritance
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Colours {
public:
void display() {
cout << "Below are Flowers with their Colours" << endl;
}
};
class Red : public Colours {
public:
void display() {
cout << "Red Rose" << endl;
}
};
class Yellow : public Colours {
public:
void display() {
cout << "Yellow Sunflower" << endl;
}
};
class Orange : public Colours {
public:
void display() {
cout << "Orange Marigold" << endl;
}
};
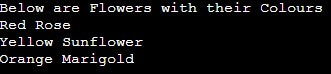
int main() {
Colours Colours;
Red Red;
Yellow Yellow;
Orange Orange;
Colours.display();
Red.display();
Yellow.display();
Orange.display();
return 0;
}Output:
In this example, the base class is Colours, and the derived classes are Red, Yellow, and Orange. They inherit the basic class’s show() function but override it with their implementations. When you invoke the display() method on an object of a derived class, it executes the overridden method of that derived class.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Here are some advantages and disadvantages:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Powerful and Efficient: C++ is known for its efficiency and high performance because of its low-level memory management capabilities. | Complexity: C++ can be more complex and difficult to comprehend than other programming languages, especially for beginners. |
| Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): By adhering to OOP principles, C++ promotes code organization, reusability, and maintainability. | Memory Management: When working with C++, knowing manual memory management through pointers is essential. Improper management can lead to memory leaks and undefined behavior. |
| Standard Template Library (STL): The STL includes many data structures and algorithms that ease basic programming tasks. | Lack of Garbage Collection: Unlike other languages, it does not have automatic garbage collection, making it prone to memory-related bugs if not appropriately managed. |
| Flexibility: C++ supports high-level and low-level programming, giving developers fine-grained control over system resources. | Potential for Undefined Behavior: If not utilized appropriately, it allows for direct memory access, which can result in undefined behavior and defects. |
| Platform Independence: C++ code may be portable and run on various systems. | Steeper Learning Curve: The various features and complexities of the language might make it difficult for newbies to learn and master. |
| Legacy Code and Interoperability: It may connect with existing C code and link to code written in other languages, increasing compatibility. | Lack of Built-in GUI Library: Because C++ lacks a standard built-in GUI library, GUI development must rely on third-party libraries. |
| Large Community and Libraries: It has a large developer community that provides a wealth of materials, libraries, and tools for C++ development. | Longer Development Time: Because of manual memory management and lower-level programming requirements, developing in C++ may take longer. |
| Performance-Critical Applications: C++ is ideal for creating high-performance applications such as games and system-level software. | Code Security: Inadequate management of pointer-related mistakes could result in security vulnerabilities such as buffer overflows. |
Uses of C++
C++ is a flexible programming language that finds applications in various domains due to features such as high performance, object-oriented programming, and compatibility with the C programming language. Here are some common uses:
- System Programming: Finds utilization in developing system software, operating systems, and device drivers due to its capability to connect with hardware and manage low-level memory directly.
- Application Software: Creates various applications, such as desktop applications, graphical user interfaces (GUIs), office suites, and multimedia software.
- Game Development: Because of its high performance, it is a popular choice for game development. C++ is the programming language for various gaming engines, including Unreal Engine.
- Embedded Systems: Finds application in embedded system programming, where efficiency and precise control over hardware play a critical role. Various sectors use it, such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
- High-Performance Computing: Finds applications in creating high-computing-power-demanding applications like scientific simulations, numerical analysis, and data processing.
- Graphics and Computer Vision: It is a programming language in computer graphics, such as rendering engines and image processing. People commonly use OpenCV libraries in computer vision applications.
- Networking: C++ finds applications in network programming, encompassing the development of server-side applications, networking protocols, and communication libraries.
- Financial Software: In finance, developers use it to create trading systems, build risk management software, and develop financial modeling tools.
- Compiler Development: People often use to develop compilers and interpreters for various programming languages.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: It may be utilized for AI and machine learning projects, mainly where performance optimization is crucial.
- Operating Systems: It serve as a foundation for constructing components of operating systems, system libraries, and system utilities.
- Robotics: Due to its real-time capabilities and efficient control over hardware components, programmers use C++ in robotics programming.
- Industrial Automation: In industrial automation, C++ can operate machinery, process control, and monitoring systems.
- Medical Software: Medical imaging software, simulation tools, and medical equipment control software use C++ for their operations.
- Database Systems: A programming language for developing database management systems and applications associated with databases.
Conclusion
C++ is a competent and adaptable programming language that remains important in the software development industry. Its proficiency, speed, and versatility make it ideal for various applications, such as game development, performance-critical systems programming, and high-level applications.
Despite the emergence of many new programming languages, various areas like finance, gaming, real-time systems, and embedded applications use C++ widely. Its continued popularity proves its reliability and relevance in the constantly changing field of software development. As technology progresses, it will probably remain a crucial tool for skilled programmers who want to explore the limits of performance and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Does C++ have garbage collection?
Ans: C++, unlike specific other languages (such as Java or C#), it does not offer automated garbage collection. Memory management in C++ is manual, and developers must allocate and deallocate memory using pointers.
Q2. What is the difference between C and C++?
Ans: C++ is a programming language that extends C. While C finds its primary use in procedural programming, C++ supports both procedural and object-oriented programming paradigms. C++ also introduces additional features such as classes, inheritance, and polymorphism, making it more versatile and expressive.
Q3. Can I use C++ to create graphical user interfaces (GUIs)?
Ans: Even though C++ does not have a built-in GUI library, developers can utilize third-party libraries (such as Qt and wxWidgets) to create graphical user interfaces for desktop applications.
Q4. Is C++ still relevant in 2023?
Ans: Yes, C++ is still useful in 2023. Many still favor and extensively utilize this language, especially in domains that necessitate high performance, such as systems programming, game development, and real-time applications.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “What is C++” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.