Updated June 9, 2023
Difference Between Hadoop vs RDBMS
Hadoop software framework work is very well structured semi-structured and unstructured data. This also supports various data formats in real-time, such as XML, JSON, and text-based flat file formats. RDBMS works efficiently when an entity-relationship flow is defined perfectly; therefore, the database schema or structure can grow and be unmanaged otherwise. i.e., An RDBMS works well with structured data. Hadoop will be a good choice in environments where there is a need for big data processing in which the data being processed does not have dependable relationships.
What is Hadoop?
Hadoop is fundamentally an open-source infrastructure software framework that allows distributed storage and processing of a huge amount of data, i.e., Big Data. It’s a cluster system that works as a Master-Slave Architecture. Therefore, this architecture can store and process large data in parallel. Structured data (in tables), unstructured data (such as logs, email bodies, and blog text), and semi-structured data (including media file metadata, XML, and HTML) can all be analyzed.
Components of Hadoop
- HDFS: Hadoop Distributed File System. Google published the paper GFS, and based on that, HDFS was developed. It is stated that the files will be broken into blocks and stored in nodes over the distributed architecture. Doug Cutting and Yahoo! reverse-engineered the model GFS and built a parallel Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
- Yarn: Yet Another Resource Negotiator is used for job scheduling and manages the cluster. It was introduced in Hadoop 2.
- Map Reduce: This framework helps Java programs do parallel computation on data using a key-value pair. The Map converts input data into a data set that can be computed in Key value pair. A reduced task consumes the output of Map, and then the out-of-reducer gives the desired result.
- Hadoop Common: Other Hadoop modules utilize these Java libraries to launch Hadoop.
What is RDBMS?
RDBMS stands for the relational database management system. It is a database system based on the relational model specified by Edgar F. Codd in 1970. Database management software like Oracle server, My SQL, and IBM DB2 are based on the relational database management system.
The data represented in the RDBMS is in the form of rows or tuples. This table is a collection of related data objects consisting of columns and rows. Normalization plays a crucial role in RDBMS. It contains the group of the tables; each table contains the primary key.
Components of RDBMS
The components of RDBMS are mentioned below.
- Tables: RDBMS stores records in a vertical and horizontal grid, each represented by a table. Fields that store data, such as names, addresses, and products, make up the composition of a table.
- Rows: The rows in each table represent horizontal values.
- Columns: A horizontally-stored column in a table represents each field of data.
- Keys: They are identification tags for each row of data.
Hadoop and RDBMS have different concepts for storing, processing, and retrieving data/information. Hadoop is new in the market, but RDBMS is approx. 50 years old. Data and data analysis and reporting demands are growing exponentially as time passes. Storing and processing this huge amount of data within a rational amount of time has become vital in current industries. RDBMS is more suitable for relational data as it works on tables. The main feature of the relational database includes the ability to use tables for data storage while maintaining and enforcing certain data relationships.
Head to Head Comparison Between Hadoop vs RDBMS (Infographics)
Below is the top 8 Difference Between Hadoop vs RDBMS:
Key Difference Between Hadoop vs RDBMS
Following is the key difference between Hadoop vs RDBMS:
An RDBMS works well with structured data. Hadoop will be a good choice in environments where there is a need for big data processing in which the data being processed does not have dependable relationships. When the data size is too big for complex processing and storing, or it is not easy to define the relationships between the data, it becomes difficult to save the extracted information in an RDBMS with a coherent relationship. Hadoop software framework work is very well structured semi-structured and unstructured data. Highly-supportive world-class companies use RDBMS database technology because it is proven, consistent, mature, and reliable. It works well with data descriptions such as data types, relationships among the data, constraints, etc. Hence, this is more appropriate for online transaction processing (OLTP).
What will be the future of RDBMS compared to Bigdata and Hadoop? Do you think RDBMS will be abolished anytime soon?
“There’s no relationship between the RDBMS and Hadoop right now — they will be complementary. It’s NOT about rip and replaces: we’re not going to get rid of RDBMS or MPP, but instead use the right tool for the right job — and that will very much be driven by price.”- Alisdair Anderson said at a Hadoop Summit.
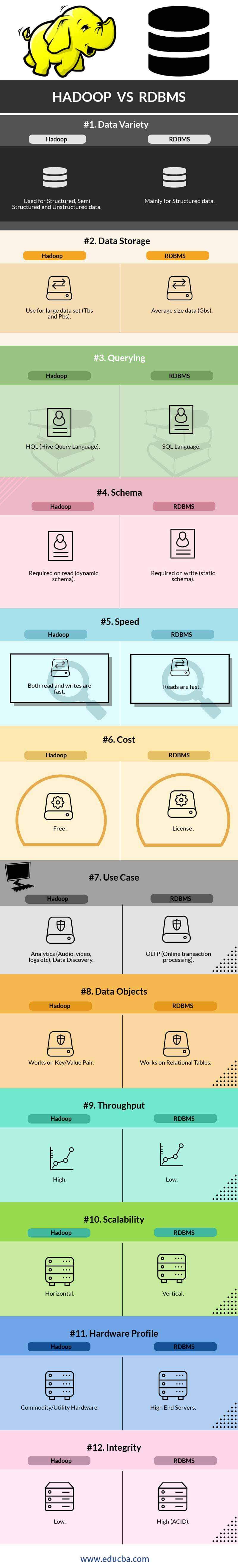
Hadoop vs RDBMS Comparison Table
Below is the comparison table between Hadoop vs RDBMS.
| Feature | RDBMS | Hadoop |
| Data Variety | Mainly for Structured data | Used for Structured, Semi-Structured, and Unstructured data |
| Data Storage | Average size data (GBS) | Use for large data sets (Tbs and Pbs) |
| Querying | SQL Language | HQL (Hive Query Language) |
| Schema | Required on write (static schema) | Required on reading (dynamic schema) |
| Speed | Reads are fast | Both reads and writes are fast |
| Cost | License | Free |
| Use Case | OLTP (Online transaction processing) | Analytics (Audio, video, logs, etc.), Data Discovery |
| Data Objects | Works on Relational Tables | Works on Key/Value Pair |
| Throughput | Low | High |
| Scalability | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Hardware Profile | High-End Servers | Commodity/Utility Hardware |
| Integrity | High (ACID) | Low |
Conclusion
The above comparison concludes that Hadoop is a better technique for handling Big Data than RDBMS. As day by day, the data used increases, and therefore, a better way of handling such a massive amount of data is becoming a hectic task. Analysis and storage of Big Data are more convenient only with the help of the Hadoop eco-system than the traditional RDBMS. The Hadoop software framework is open-source and dedicated to scalable, distributed, data-intensive computing at a large scale. This framework breakdowns extensive data into smaller parallelizable data sets and handles scheduling maps for each part to an intermediate value is Fault-tolerant, reliable, and supports thousands of nodes and petabytes of data currently used in the development, production, and testing environment and implementation options.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Hadoop vs RDBMS. Here we have discussed Hadoop vs RDBMS head-to-head comparison, key differences, infographics, and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –