Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction
OLTP, or Online Transaction Processing, is a type of data processing approach in which transactions play a significant role in manipulating data within a database. This approach provides facts and statistics necessary for Business Intelligence, which is required for making informed business decisions. Typically, it has usage in applications related to e-commerce, online banking, online shopping, sales, service platforms, and so on. This type of data processing is notable for its high performance, fast accessibility, and reliable and consistent data.
Key Features
OLTP supports only pre-defined operations. For instance, in the case of online airline booking, the process of booking an airline requires insertion of data into the database. It ensures availability of the selected airline in the cart and manages concurrency when multiple users access the same website simultaneously. The following characteristics help achieve this:
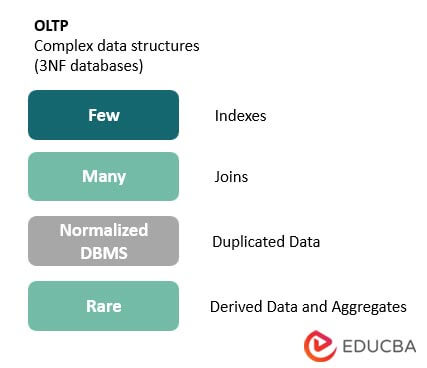
- 3NF databases: OLTP uses fully normalized databases to ensure consistency and optimization of all transactional tasks.
- Predefined operations: It strictly performs only the predefined operations on a small number of records.
- Direct access to database updates for end-users.
- Processing of only a small number of records, such as retrieving money from an ATM.
- Historical data maintenance: OLTP stores records from the last few days or a week to perform transactions successfully.
How does OLTP make working so easy?
Online transaction process concerns concurrency and atomicity.
- When two users attempt to access the same data in a database system, neither can modify the data until one user completes their transaction. This is known as concurrency control.
- Atomicity controls ensure that all steps in a transaction are completed successfully as a group. If any step fails, all other steps must also fail.
OLTP operates on normalized databases with a small number of records at a time in a decentralized system, which optimizes all predefined transactional tasks. It stores less historical data, which makes it efficient.
As it only performs the task related to insertion/deletion, it maintains the consistency and concurrency of the data in the databases, which always ensures the availability of the databases.
What can one do with OLTP?
- The goal of OLTP is availability, speed, concurrency, and recoverability.
- A large number of users can conduct short transactions using OLTP systems.
- These systems can perform operations that involve simple database queries, require fast response times (usually less than a second), and return relatively few records.
Working with OLTP
- Online transaction processing (OLTP) is a type of data processing that involves collecting information as input, processing the data according to specific requirements, and updating the data to reflect the processed information. It is typically used in a client-server system.
- In decentralized database systems, OLTP brokering programs can distribute transaction processes among multiple computers on a network.
- OLTP also has uses in service-oriented architecture (SOA) and web services,
Some crucial components that affect the performance of OLTP
- Rollback segments: These segments record transactions that are rolled back to ensure database consistency among users. They also aid database recovery to prevent data loss.
- Clusters: This schema contains records of columns common among different tables, which aids in optimizing join operations.
- Discrete transactions: Transactions that revert all changes made to the database until the last commit refers to discrete transactions. These are crucial for short and non-distributed transactions.
- Blocksize: The block size should be a multiple of the operating system size to avoid non-required I/O operations.
- Buffer cache size: This prevents unnecessary resource utilization by SQL statements.
- Dynamic allocation: This refers to the space allocated to tables and rollback segments.
- Transaction processing: This coordinates different transactions over multiple computing devices, similar to an operating system to maintain multithreaded operations.
- Partition (database): This helps increase performance for parts that have regular transactions while still maintaining availability and security.
- Database tuning: An OLTP system can maximize its performance efficiently and rapidly using database tuning.
Advantages
Concurrency: OLTP ensures that transactions made into the database do not compromise concurrency between different users. Otherwise, users will not be able to change data, or they may have to wait for other users to complete their transactions to avoid a deadlock situation.
ACID Compliance: ACID stands for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. These properties are essential for a database that records financial transactions. One failure could result in significant losses. Thus, OLTP ensures that there is no loss of transactions and maintains the ACID property in its databases.
Availability: The latest data is available to all users, as concurrency is properly maintained in OLTP.
Integrity: OLTP maintains a normalized database, which ensures data integrity at every step during transactions.
Disadvantages:
To achieve concurrency, availability, and faster transactions, OLTP often requires support for transactions that involve multiple company networks. Therefore, in today’s era, we require a more decentralized system.
Examples
Some examples of OLTP systems include:
- Order entry
- Retail sales
- Financial transaction systems
- CICS: At times, OLTP depends on transaction management software and database optimization tactics to process a greater number of simultaneous OLTP-oriented databases.
Why use OLTP?
- It reduces the need for paper-based transactions and provides faster and more accurate predictions of revenues and expenses.
- The system that requires offline maintenance makes a good requirement for online transaction processing.
- The availability, concurrency, and atomicity of data are critical for OLTP systems, as they ensure the consistency and integrity of the database.
Why do we need OLTP?
OLTP is crucial for performing tasks, which are often performed by the system and require only a smaller number of records. These tasks are primarily concerned with the insertion, deletion, or update of data in databases. In order to ensure greater availability, it is essential to maintain consistency and concurrency in the database. OLTP systems ensure the maintenance of normalized databases and decentralized systems, which result in increased availability and consistency. Moreover, they help maintain concurrency in the database. OLTP systems operate differently in batch processing and grid computing as compared to OLAP (Online Analytic Processing), which is primarily concerned with complex databases used in business intelligence tasks.
Conclusion
OLTP refers to a data processing method that involves a significant number of users performing transactions such as insertion, updation, or deletion of a relatively smaller number of records. This approach emphasizes the importance of concurrency, atomicity, and data availability by utilizing normalized databases, decentralized systems, and retaining minimal historical data. By ensuring these features, OLTP aims to maintain the consistency and reliability of data in the database, making it a suitable method for real-time transactional processing.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further related articles for expanding understanding: