Updated April 26, 2023
Difference Between Hadoop vs Hive
Hadoop is a Framework or Software invented to manage huge data or Big Data. Hadoop stores and processes extensive data distributed across a cluster of commodity servers. Hadoop stores the data using Hadoop distributed file system and process/query it using the Map-Reduce programming model. Hive is an application that runs over the Hadoop framework and provides an SQL-like interface for processing/querying the data. Hive was designed and developed by Facebook before becoming part of the Apache-Hadoop project. Hive runs its query using HQL (Hive query language). Hive has the same structure as RDBMS, and almost the same commands can be used in Hive. Hive can store the data in external tables, so it’s not mandatory to use HDFS. Also, it supports file formats such as ORC, Avro files, Sequence Files and Text files, etc.
Hadoop’s Major Components
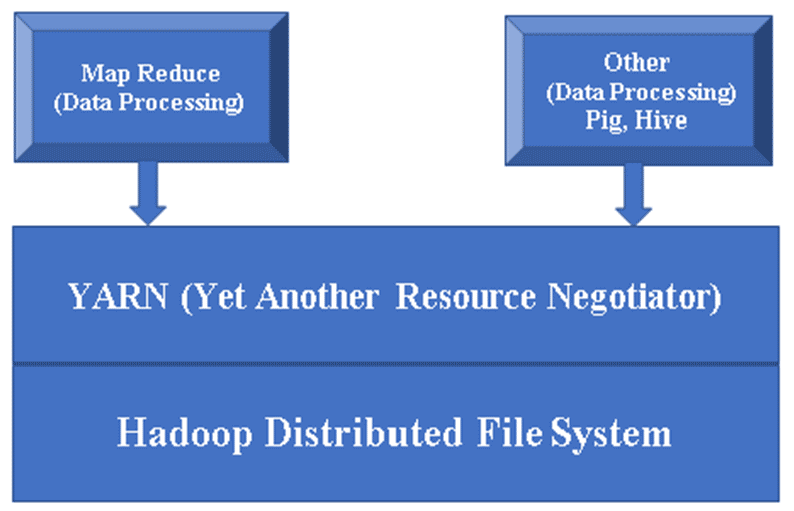
Figure 1, a Basic architecture of a Hadoop component.
Hadoop Base/Common: Hadoop Common will provide one platform to install all its components.
HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System): HDFS is a major part of the Hadoop framework. It takes care of all the data in the Hadoop Cluster. It works on Master/Slave Architecture and stores the data using replication.
Master/Slave Architecture & Replication
- Master Node/Name Node: The name node stores the metadata of each block/file stored in HDFS; HDFS can have only one Master Node (Incase of HA, another Master Node will work as a Secondary Master Node).
- Slave Node/Data Node: Data nodes contain actual data files in blocks. HDFS can have multiple Data Nodes.
- Replication: HDFS stores its data by dividing it into blocks. The default block size is 64 MB. Due to replication, data gets stored into 3 (Default Replication factor, which can be increased as per requirement) different Data Nodes; hence there is the slightest possibility of losing the data in case of any node failure.
YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator): It manages Hadoop resources. Also, it plays a vital role in scheduling users’ applications.
MR (Map Reduce): This is the primary programming model of Hadoop. It is used to process/query the data within the Hadoop framework.
Hive’s Major Components
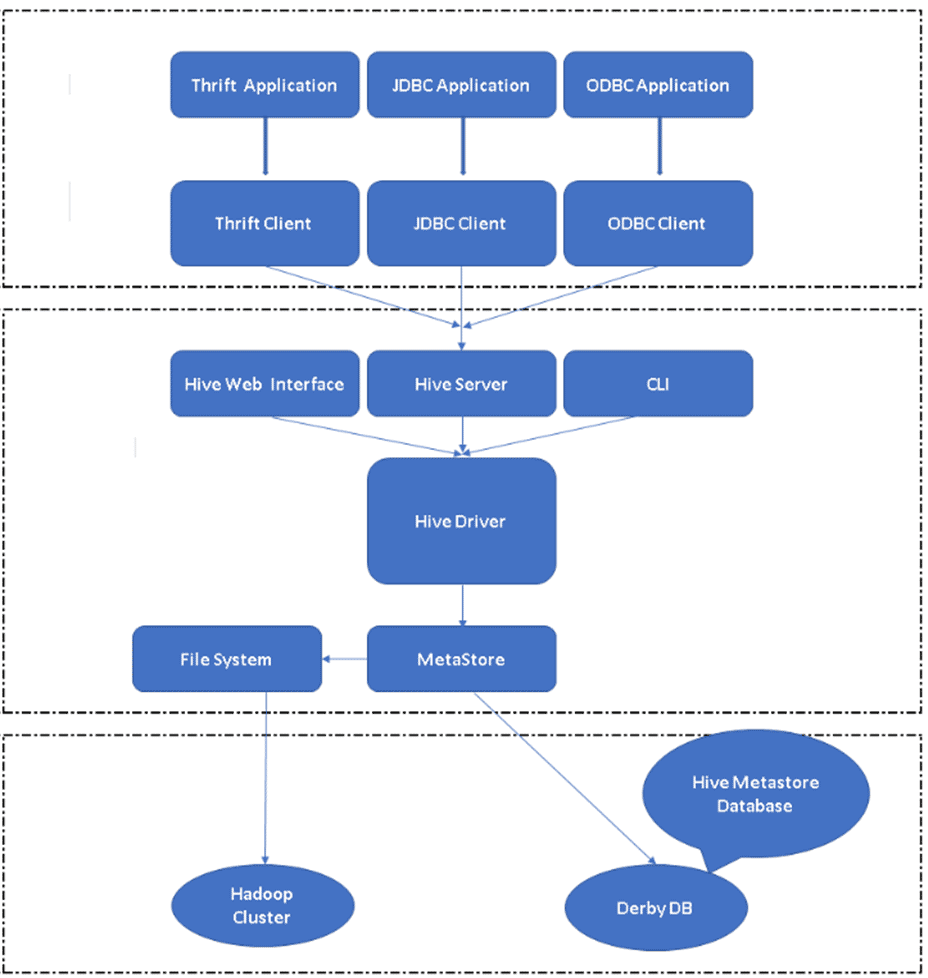
Figure 2: Hive’s Architecture & Its Major Components
Hive Clients: Besides SQL, Hive also supports programming languages like Java, C, and Python using various drivers such as ODBC, JDBC, and Thrift. One can write any Hive client application in other languages and can run in Hive using these Clients.
Hive Services: Under Hive services, execution of commands and queries take place. Hive Web Interface has five sub-components.
- CLI: Default command line interface provided by Hive for the execution of Hive queries/commands.
- Hive Web Interfaces: It is a simple graphical user interface. This provides an alternative to the Hive command line and enables running queries and commands within the Hive application.
- Hive Server: It is also called Apache Thrift. It is responsible for taking commands from different command-line interfaces and submitting all the commands/queries to Hive; also, it retrieves the final result.
- Apache Hive Driver: It is responsible for taking the inputs from the CLI, the web UI, ODBC, JDBC, or Thrift interfaces by a client and passing the information to the meta store where all the file information is stored.
- Metastore: Metastore is a repository to store all Hive metadata information. Hive’s metadata stores information such as the structure of tables, partitions & column type, etc.
Hive Storage: It is where the actual task gets performed; all the queries running from Hive act as Hive storage.
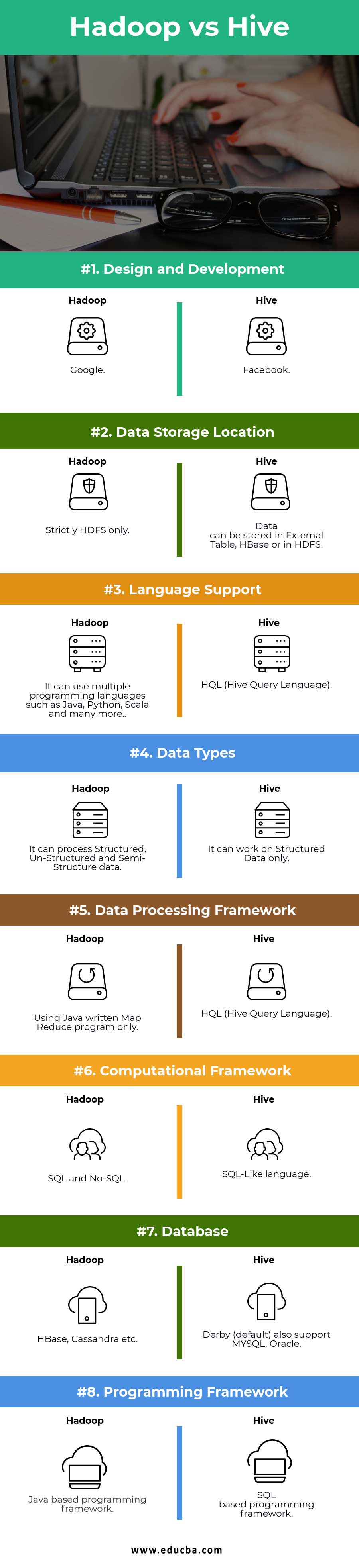
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Hadoop vs Hive (Infographics)
Below is the top 8 difference between Hadoop vs Hive:
Key Differences Between Hadoop vs Hive
Below are the lists of points that describe the key differences between Hadoop vs Hive:
- Hadoop is a framework to process/query the Big data, while Hive is an SQL Based tool that builds over Hadoop to process the data.
- Hive process/queries all the data using HQL (Hive Query Language). It’s SQL-Like Language, while Hadoop can understand Map Reduce only.
- Map Reduce is an integral part of Hadoop; Hive’s query first gets converted into Map Reduce and then processed by Hadoop to query the data.
- Hive works on SQL Like queries, while Hadoop only understands it using Java-based Map Reduce.
- In Hive, earlier used traditional “Relational Database’s” commands can also be used to query big data, while in Hadoop, we have to write complex Map Reduce programs using Java, which is not similar to traditional Java.
- Hive can only process/query structured data, while Hadoop is meant for all data types, whether Structured, Unstructured, or Semi-Structured.
- Using Hive, one can process/query the data without complex programming, while in the simple Hadoop ecosystem, the need to write complex Java programs for the same data.
- On one side, Hadoop frameworks need 100s lines for preparing Java-based MR programs. Another side Hadoop with Hive can query the same data using 8 to 10 lines of HQL.
- In Hive, it isn’t easy to insert the output of one query as the input of another, while the same query can be done easily using Hadoop with MR.
- Having Metastore within the Hadoop cluster is not mandatory, while it stores all its metadata inside HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System).
Hadoop vs Hive Comparision Table
Let us look at the comparison table between Hadoop vs Hive:
| Comparison Points | Hive | Hadoop |
| Design and Development | ||
| Data Storage Location | Data can be stored in the External Table, HBase, or HDFS | Strictly HDFS only |
| Language Support | HQL (Hive Query Language) | It can use multiple programming languages such as Java, Python, Scala, etc |
| Data Types | It can work on Structured Data only | It can process Structured, Un-Structured, and Semi-Structure data |
| Data Processing Framework | HQL (Hive Query Language) | Using Java-written Map Reduce program only |
| Computational Framework | SQL-Like language | SQL and No-SQL |
| Database | Derby (default) also supports MYSQL, Oracle… | HBase, Cassandra, etc… |
| Programming Framework | SQL-based programming framework | Java-based programming framework |
Conclusion
Hadoop and Hive are both used to process Big data. Hadoop is a framework that provides a platform for other applications to query/process Big Data, while Hive is just an SQL-based application that processes the data using HQL (Hive Query Language). Processing big data with Hadoop is possible without using Hive, whereas using Hive without Hadoop can be difficult. In conclusion, we can’t compare Hadoop and Hive anyhow and in any aspect. Both Hadoop and Hive are entirely different. Running both technologies together can make the Big Data query process much easier and more comfortable for Big Data Users.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Hadoop vs Hive. Here we discuss the components of Hadoop and Hive, head-to-head comparisons with infographics, and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –