What is DaaS in Cloud Computing?
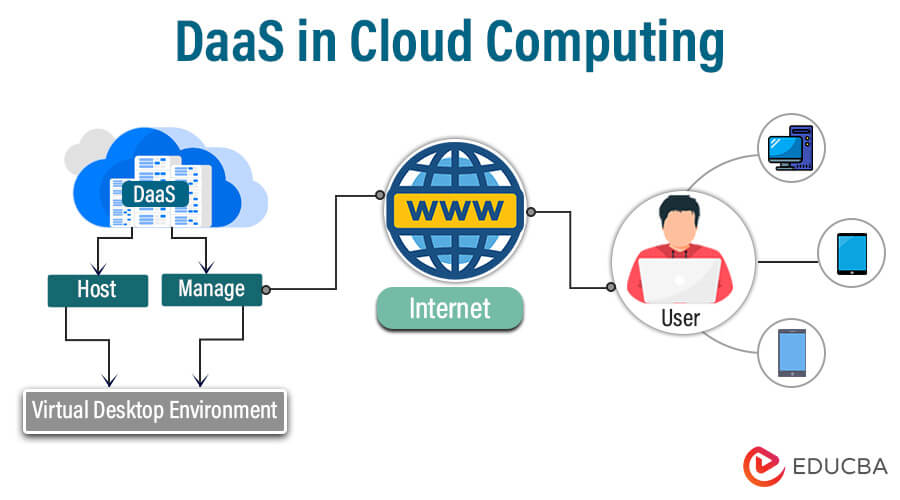
DaaS, also known as Desktop as a Service, represents a cloud computing paradigm in which virtual desktops are housed and overseen by a third-party entity. Users can access these desktop environments remotely from any device via the internet. DaaS obviates the necessity for physical desktop infrastructure and offers scalability, adaptability, and cost-effectiveness. Organizations profit from centralized management, with the service provider responsible for infrastructure upkeep, updates, and security measures. This model facilitates remote work, streamlines IT management, and presents a convenient means of accessing desktop environments from any location. It has become a progressively favored choice for enterprises seeking effective and adaptable desktop solutions in the cloud.
Table of Contents
- What is DaaS in Cloud Computing
- Evolution Of DaaS
- Role of DaaS in Cloud Computing
- Benefits of Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
- Types of desktops available in DaaS
- Key components of DaaS architecture
- Working of DaaS in Cloud computing
- How Is DaaS Different from VDI?
- Use cases for DaaS
- How to Choose a DaaS Provider?
- Application of DaaS in Cloud Computing
- Challenges and Considerations
- Future Trends in DaaS and Cloud Computing
Key Takeaways
- DaaS eliminates the need for physical desktop infrastructure.
- It enables access to desktop environments from any device.
- Organizations benefit from reduced hardware costs.
- DaaS simplifies software deployment and updates.
- The service provider manages security measures.
- Remote work becomes more accessible and efficient.
- Scalability allows for easy adjustment to changing needs.
- DaaS enhances flexibility in workspace arrangements.
Evolution Of DaaS
| Evolution Stage | Description |
| Early Stages (2000s) | The concept of DaaS emerged alongside the rise of virtualization technologies pioneered by companies like VMware. It facilitated desktop centralization through multiple virtual desktop instances. |
| Commercialization (2010s) | DaaS gained momentum commercially, with companies like Citrix and AWS offering cloud-hosted virtual desktop solutions. This allowed remote access to desktop environments, reducing dependence on on-premises infrastructure. |
| Maturation (Mid-2010s) | Cloud computing advancements led to significant progress in DaaS offerings, with improved security, scalability, and integration with other cloud services. Networking technologies like SD-WAN enhanced performance and dependability. |
| Diversification (Late 2010s – Early 2020s) | DaaS expanded into diverse applications, including disaster recovery, remote work facilitation, BYOD initiatives, and support for mobile workers. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this transition, emphasizing the importance of remote work solutions. |
| Incorporation with Emerging Technologies (Current) | DaaS continues to evolve by integrating emerging technologies like AI, ML, and containerization to enhance automation, resource utilization, and security. |
| Emphasis on User Experience and Mobility | DaaS providers prioritize enhancing user experiences across different devices and network situations, accommodating mobile devices, enabling offline access, and tailoring desktop environments to individual preferences. |
Role of DaaS in Cloud Computing
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) holds a prominent position within the sphere of cloud computing, providing numerous benefits and capabilities:
- Outsourcing Infrastructure Management: DaaS enables organizations to delegate desktop infrastructure management to cloud service providers. Organizations can utilize virtual desktops hosted in the cloud rather than maintaining physical desktop hardware and software on-site.
- Improved Resource Utilization: DaaS enables the infrastructure of the cloud provider to dynamically allocate resources, such as memory, processing power, and storage, based on demand. It ensures efficient resource utilization and scalability, empowering organizations to manage their desktop environments effectively without excessive hardware provisioning.
- Remote Accessibility: Access to DaaS solutions’ cloud-based desktops is possible from any location with an internet connection. It facilitates remote work scenarios, supports BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies, and enhances workforce mobility by enabling users to access their desktops from varied devices and locations.
- Centralised Management: DaaS platforms provide centralized management capabilities, enabling IT administrators to provision, deploy, update, and monitor virtual desktops from a singular interface. It simplifies management tasks, lowers administrative overhead, and ensures uniformity across desktop environments.
- Cost Reduction: Through the adoption of DaaS, businesses can decrease initial hardware expenditure, continual maintenance expenses, and the costs related to desktop management. DaaS operates on a subscription-based pricing structure, providing consistent and adaptable costs by usage and user needs.
- Enhanced Security: DaaS providers enforce strong security measures to safeguard desktop environments, data, and network communications, incorporating encryption, access controls, multi-factor authentication, threat detection, and compliance with industry regulations. Additionally, centralized management ensures streamlined security policy enforcement and updates.
Benefits of Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) plays a big and diverse role in cloud computing.
Accessibility: Regardless of the device used, DaaS allows users to view their desktop environments from any location with an internet connection. Because of its accessibility, users can work from various places, increasing productivity and making remote work more accessible.
Scalability: DaaS provides scalability, making it simple for businesses to modify the number of desktops in response to changing demand. Virtual desktops allow companies to offer PCs quickly or de-provision them as needed without being constrained by traditional hardware infrastructure.
Cost-effectiveness: Organizations can cut capital expenses for buying and maintaining physical hardware by moving desktop infrastructure to the cloud. DaaS uses a subscription-based business model, eliminating upfront fees and allowing for predictable operating expenses.
Centralized maintenance: DaaS centralizes the maintenance of desktop applications, including security patches, software upgrades, and data backups. This centralized method guarantees uniform user experiences across all virtual desktops, enhances security, and simplifies IT administration.
Enhanced Security: DaaS providers use robust security protocols to protect cloud-hosted data and apps. These measures may include encryption, access controls, multi-factor authentication, and intrusion detection systems, bolstering security posture compared to on-premises solutions.
Flexibility: DaaS provides enterprises with software deployment flexibility by enabling them to swiftly deliver standardized desktop environments or alter configurations to user needs. This adaptability encourages agility and responsiveness to shifting business requirements.
Types of desktops available in DaaS
The two main types of desktops available in Desktop as a Service (DaaS) are:
Persistent Desktops: Individual users are assigned persistent desktops that retain their configuration, settings, and data between sessions. Every time users log in, it ensures a consistent desktop experience, making persistent desktops suitable for personalized tasks or prolonged use. Users can customize their desktop environment with applications, files, and preferences, and these modifications persist across sessions. These persistent desktops are particularly well-suited for individuals requiring continual access to their personalized workspace, such as knowledge workers, executives, or employees with specialized software requirements.
Non-Persistent Desktops: Within DaaS environments, multiple users utilize non-persistent desktops that are reset to a standard state after each session. In contrast to persistent desktops, any changes made during a session are discarded upon logout, ensuring a clean and consistent desktop environment for the next user. These desktops, such as virtual labs, training environments, or kiosks, are commonly employed for temporary or task-specific purposes. They are easily reproducible and require fewer resources to manage than persistent desktops, making them cost-effective and efficient for scenarios with high user turnover or where personalized environments are unnecessary.
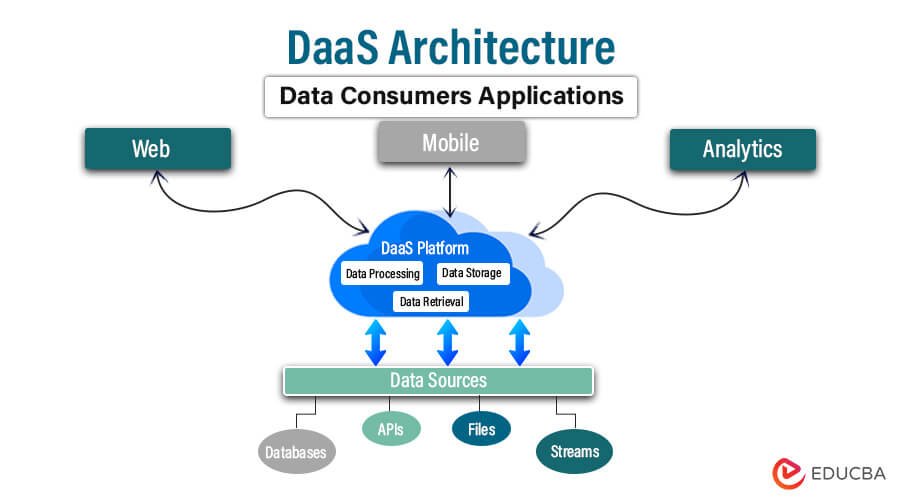
Key components of DaaS architecture
Virtualization Infrastructure:
- Server Infrastructure: This infrastructure hosts virtual desktop instances, providing the necessary computing power to operate OS and applications.
- Storage Infrastructure: Virtual desktop images, user data, and profiles are stored on centralized storage systems to ensure accessibility and data integrity.
- Networking Infrastructure: Networking components facilitate communication between virtual desktops, users, and other infrastructure components, ensuring connectivity and data transfer.
Connection Brokers:
- Assignment: Connection brokers actively allocate virtual desktops to users, ensuring each user connects to the appropriate desktop instance based on their credentials and requirements.
- Load Balancing: The administrator must evenly distribute user connections across multiple servers to optimize resource utilization and ensure high availability and performance.
- Session Management: Connection brokers manage session-related tasks such as initiation, termination, and reconnection, ensuring a smooth and uninterrupted user experience.
Desktop Delivery Controllers:
- Provisioning: The task of these controllers is to manage the deployment and provisioning of virtual desktops, guaranteeing that users have timely access to their desktop environments.
- Optimization: Desktop delivery controllers streamline resource allocation and performance by dynamically adjusting desktop configurations in response to user demand and available resources.
- Monitoring: They oversee desktop performance and resource utilization, identifying potential bottlenecks or issues and taking corrective measures to ensure optimal performance.
Desktop Images and Templates:
- Customization: Desktop images and templates are blueprints for creating virtual desktop instances containing the operating system, applications, configurations, and settings.
- Standardization: By using standardized images and templates, organizations can ensure consistency across virtual desktop environments, simplifying management and support tasks.
- Update Management: Desktop images and templates can be updated centrally, allowing organizations to deploy patches, updates, and new applications efficiently across all virtual desktop instances.
Interfaces for User Access
- Accessibility: User access interfaces enable users to connect to virtual desktops from diverse devices and locations, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity.
- Authentication: They manage user authentication and authorization to ensure that only authorized users can enter their desktop environments.
- User Experience: Designers craft user access interfaces to provide an intuitive and user-friendly experience, empowering users to navigate their desktop environments and access applications and data seamlessly.
Working of DaaS in Cloud computing
Core Components:
- Virtual Desktops: These encompass fully operational desktop environments hosted on the cloud provider’s infrastructure. Each virtual desktop contains an operating system, applications, settings, and user data, thus emulating the experience of using a physical desktop computer.
- Cloud Provider: The cloud provider oversees the virtual desktops’ infrastructure, security, and upkeep. They manage the underlying servers, storage, networking, and virtualization technologies necessary to deliver the DaaS solution.
- End User Devices: Users can log into their virtual desktops from any internet-enabled device, such as laptops, desktop computers, tablets, or thin clients. These devices function as the interface through which users can engage with their virtual desktop environments.
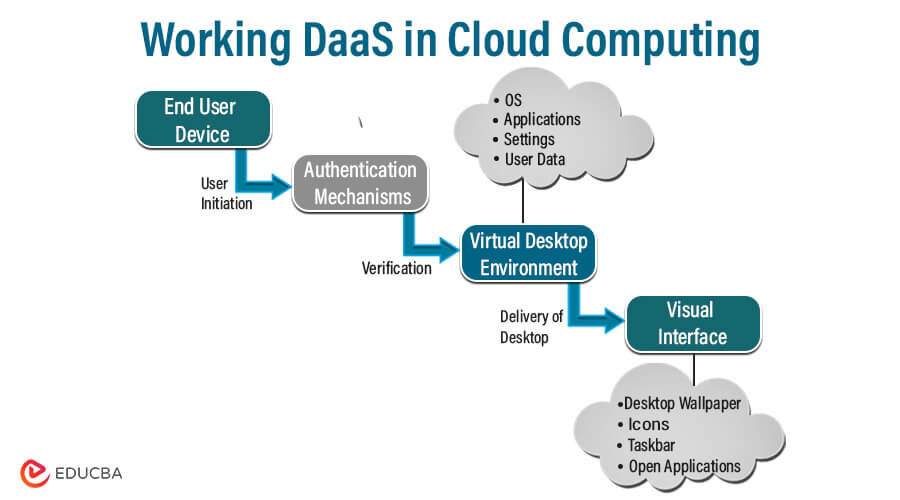
Process of Work:
- User Initiation: Users commence access to virtual desktops using a web browser or dedicated DaaS software installed on their devices. They navigate to the cloud provider’s platform and authenticate their login with their credentials.
- Verification: The cloud provider’s authentication mechanisms validate the user’s identity and permissions upon login. Once authenticated, the user can access their designated virtual desktop environment.
- Delivery of Desktop: The cloud provider streams the virtual desktop environment to the user’s device over the internet. It involves transmitting the visual interface of the desktop, including the desktop wallpaper, icons, taskbar, and open applications, to the user’s screen.
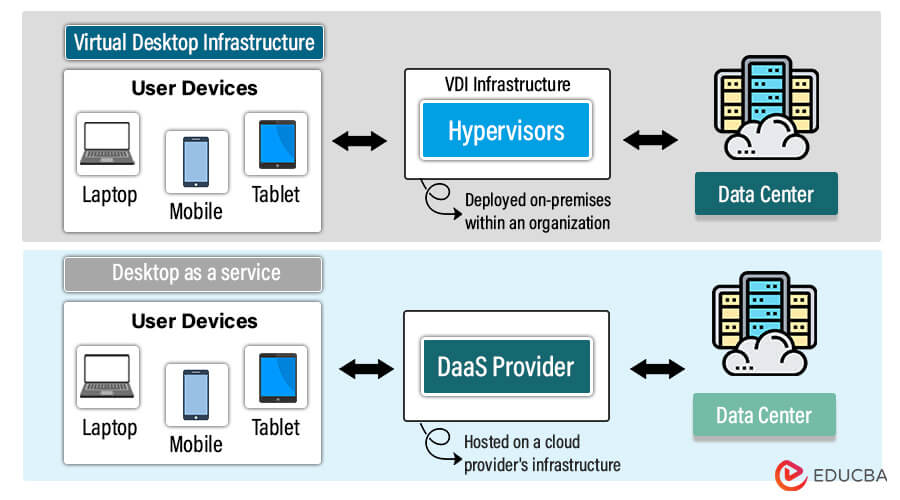
How Is DaaS Different from VDI?
| Section | DaaS | VDI |
| Deployment | Hosted on a cloud provider’s infrastructure | Typically deployed on-premises within an organization |
| Infrastructure | Managed by the cloud provider | Managed by the organization’s IT department |
| Scalability | Easily scalable, resources are provisioned dynamically by the provider | Scalability may be limited by on-premises hardware and infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Managed and maintained by the provider | Requires in-house IT staff to handle maintenance tasks |
| Capital Expenditure | Minimal upfront costs, subscription-based pricing model | Higher upfront costs for hardware, software, and infrastructure |
| Accessibility | Accessible from any internet-connected device | Accessible within the organization’s network or through a VPN |
| Security | Provider-managed security measures in place | Security is managed internally, subject to organizational policies and controls. |
| Flexibility | Offers flexibility to add or remove desktops as needed | Requires additional hardware procurement and setup for scaling |
| Control | Less direct control over infrastructure and management | Greater control over infrastructure and management tasks |
| Implementation Time | Typically, faster deployment due to reliance on cloud infrastructure | Longer deployment times due to setup and configuration of on-premises infrastructure |
| Compliance | Provider may offer compliance certifications | Compliance requirements are managed internally by the organization |
Use cases for DaaS
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) offers a variety of use cases across different industries and organizational environments. Some common scenarios where DaaS can be advantageous include:
- Remote Work: DaaS empowers employees to access their desktop setups from any location with an internet connection, facilitating remote work arrangements. This flexibility is invaluable when employees need to work from home or in other remote areas during catastrophes, including natural disasters or public health issues.
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD): DaaS enables organizations to support BYOD policies by providing employees with secure access to corporate desktop setups from their devices. It fosters flexibility and productivity while upholding security and compliance standards.
- Contractors and Temporary Staff: Companies can effortlessly set up virtual desktops for contractors, temporary staff, or seasonal employees using DaaS. This guarantees that these staff members can access the required applications and resources without requiring dedicated hardware or extensive setup.
- Branch Offices and Offsite Locations: DaaS is well-suited for delivering consistent desktop environments to employees in branch offices or remote locations. Organizations can ensure uniformity, security, and compliance across all sites by centralizing desktop management in the cloud.
- Software Development and Testing: DaaS offers developers access to isolated virtual environments for software development, testing, and debugging. It enables swift provisioning and de-provisioning of development environments, reducing lead times and infrastructure costs.
- Compliance and Security: DaaS aids organizations in meeting compliance and security requirements through centralized management, encryption, access controls, and auditing capabilities. It ensures the protection of sensitive data and applications in accordance with regulatory standards.
How to Choose a DaaS Provider?
To select an appropriate Data as a Service (DaaS) provider, it is essential to carefully assess and choose a provider that aligns with your unique needs. The following are steps to guide you in selecting the most suitable DaaS provider:
- Specify Your Requirements: Commence by outlining your organization’s requirements and objectives for employing DaaS. Consider considerations such as the type and quantity of data required, data quality standards, integration capabilities, security and compliance prerequisites, and financial limitations.
- Assessing Data Quality and Diversity: Evaluate each provider’s quality and diversity of data. Verify that the data meets your accuracy, relevance, and completeness standards. Consider the variety of data sources the provider offers and assess how well they align with your requirements.
- Evaluating Data Security and Regulatory Compliance: Data security and regulatory compliance are crucial factors in selecting a DaaS provider. Assess the provider’s security measures, including encryption protocols, access controls, and compliance certifications (e.g., GDPR or HIPAA). Ensure that the provider follows industry best practices for data protection and privacy.
- Assess Integration Capabilities: Evaluate the provider’s ability to integrate with your current systems and tools. Confirm that the DaaS solution seamlessly integrates with your data management infrastructure and applications. Seek providers that furnish strong APIs, connectors, and data integration tools.
- Scalability and Adaptability: Select a DaaS provider with scalability and adaptability to meet your changing data requirements. Ensure that the provider can accommodate increasing data volumes and adjust to modifications in your business needs over time. Look for adaptable pricing models that enable you to adjust your usage as per demand.
- Assessing Performance and Reliability: Evaluate the performance and reliability of each DaaS provider’s platform, focusing on high availability, minimal downtime, and fast data delivery speeds. Consider data latency, uptime guarantees, and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Evaluating Cost and Pricing: Assess the cost structure and pricing plans provided by each DaaS provider, considering subscription fees, usage-based pricing, and additional charges for premium features or support services. Choose a supplier who provides value for your money and has clear pricing.
- Check Customer Support and Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Consider the level of customer support and service each DaaS provider provides. Seek out suppliers who give paperwork, training materials, attentive customer assistance, and service level agreements (SLAs) that ensure uptime and performance.
Providers of DaaS in Cloud Computing
Here are some prominent providers of Desktop as a Service (DaaS) in cloud computing, along with brief explanations of each:
Amazon WorkSpaces:
- Description: Amazon WorkSpaces represents a Desktop as a Service (DaaS) solution offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS), delivering fully supervised, protected virtual desktop environments within the cloud.
- Features: It presents an array of desktop setups, encompassing Windows and Linux alternatives, complete with adjustable CPU, memory, and storage preferences. WorkSpaces seamlessly integrates with other AWS amenities to fortify security, expand scalability, and boost management capabilities.
- Benefits: Amazon WorkSpaces delivers adaptable pricing choices, pay-as-you-go billing, and effortless compatibility with current AWS infrastructure and services. It ensures top-notch performance, dependability, and security, supported by AWS’s expansive global infrastructure and cutting-edge security measures.
Microsoft Windows Virtual Desktop (WVD):
Description: Microsoft Windows Virtual Desktop (WVD) is a Desktop as a Service (DaaS) solution offered by Microsoft Azure, providing virtual desktops and applications hosted on Azure infrastructure.
Features: WVD enables multi-session Windows 10, allowing multiple users to utilize a single virtual machine for cost-effectiveness and productivity. It integrates with Microsoft 365 and Azure Active Directory for user authentication and access control. Additionally, WVD offers management and optimization tools through the Microsoft Endpoint Manager platform.
Benefits: Windows Virtual Desktop delivers a familiar Windows 10 environment with enhanced performance, security, and productivity features. It presents adaptable licensing choices for Microsoft 365 subscribers and Azure clients, rendering it a compelling option for organizations with existing investments in the Microsoft ecosystem.
VMware Horizon Cloud:
- Description: VMware Horizon Cloud is a Desktop as a Service (DaaS) product offering virtual desktops and apps hosted on major public clouds such as AWS and Azure or VMware’s cloud infrastructure.
- Features: Horizon Cloud supports hosted desktop and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) models by providing simplified management and delivery of virtual desktops and applications via a single platform. It incorporates functionalities such as instant clone technology, application layering, and support for graphics-intensive applications.
- Benefits: VMware Horizon Cloud ensures a uniform user experience across various devices and locations, offering high performance, scalability, and flexibility. It seamlessly integrates with VMware’s more comprehensive range of solutions, including VMware Workspace ONE, to provide secure access and identity management.
How to get started with DaaS?
- Establishing Objectives and Requirements:
Establish the objectives of your organization in implementing DaaS. Identify specific use cases, such as supporting remote work, enabling BYOD, or achieving cost efficiencies. Evaluate the requirements for virtual desktops, considering user capacity, performance criteria, and security considerations.
- Exploring DaaS Providers:
Investigate various DaaS providers and their services. Evaluate features, pricing, scalability, security, and customer support. Seek suppliers with a strong history of reliability and excellent customer service.
Choose a Data as a Service (DaaS) Provider
Opt for a DaaS provider that closely matches your organization’s goals and needs. Consider factors such as the provider’s reputation, service-level agreements (SLAs), compliance certifications, and integration capabilities.
Create Your Deployment Strategy:
Develop a strategic plan for deploying DaaS within your organization, detailing the necessary steps for implementation. Establish deadlines, specify roles and responsibilities in detail, and distribute resources wisely. Consider considerations such as network preparedness, data migration, and user training.
Ready Your Infrastructure:
Verify that your network infrastructure aligns with the requirements for DaaS implementation. Evaluate network bandwidth, latency, and reliability to accommodate virtual desktop connections. Make any essential upgrades or modifications to enhance network performance.
Configuring Virtual Desktops:
Collaborate with your selected DaaS provider to tailor virtual desktop environments to meet your organization’s requirements. Customize desktop images, install essential applications, and establish user access policies and permissions.
Integrating with Existing Systems:
Incorporate DaaS with your current IT systems and workflows to ensure smooth operation. Configure single sign-on (SSO) authentication, integrate directory services, and synchronize data to streamline user access and management.
Testing and Pilot:
Thoroughly test and pilot the DaaS environment before full deployment. Evaluate virtual desktop performance, application compatibility, and user experience across various devices and network conditions. Collect feedback from pilot users to identify and resolve any issues.
User Training:
Deliver training and assistance to users to acquaint them with the DaaS environment. Provide training sessions, user guides, and support resources to enable users to navigate virtual desktops proficiently and troubleshoot common issues.
Deployment and Ongoing Monitoring:
Execute the deployment of the DaaS environment into production following the conclusion of testing and training. Continuously monitor virtual desktop performance, user activity, and security events. Enact proactive maintenance and optimization procedures to uphold peak performance and user contentment.
Application of DaaS in Cloud Computing
Remote Workforce Enablement:
In the current digital and mobile-focused work landscape, Desktop as a Service (DaaS) is pivotal in facilitating remote work. Through DaaS, companies can offer their employees secure access to their desktop setups from any place with internet connectivity. It empowers employees to effectively work from home, on the go, or from distant offices, promoting adaptability and harmony between work and personal life.
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) Initiatives:
Many companies implement BYOD policies to satisfy employees’ desire to utilize their devices for work. DaaS facilitates BYOD efforts by furnishing a secure framework for accessing corporate desktop environments from personal devices such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones. It enables employees to utilize their preferred devices while upholding data security and adhering to corporate policies.
Temporary or Contract Workers:
Businesses frequently engage temporary or contract staff to fulfill specific projects or duties. These individuals may necessitate access to desktop applications and resources for a defined period. DaaS facilitates organizations’ rapid and efficient provisioning of virtual desktops for temporary personnel, guaranteeing that they have the necessary tools and resources to carry out their responsibilities effectively.
Software Development and Testing:
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) is extensively utilized in software development and testing settings, catering to the needs of developers and testers who require access to tailored configurations and environments for coding, debugging, and testing applications. DaaS empowers organizations to provision virtual desktops equipped with the necessary software stack and development tools, thereby reducing setup time and costs associated with maintaining physical development environments.
Education and Training:
Educational institutions and training organizations utilize DaaS to grant students and trainees access to virtual desktop environments containing educational software, course materials, and collaboration tools. DaaS guarantees uniform access to resources irrespective of students’ locations or devices, thus enabling remote learning and collaboration among students and instructors.
Challenges and Considerations
Reliance on Internet Connectivity:
DaaS relies on a reliable, high-speed internet connection to allow users to reach their virtual desktops. Any disruptions or variations in the network may lead to reduced performance, latency problems, or even the total unavailability of desktop resources.
Potential for Latency:
Latency, which refers to the delay between a user’s action and the response from the virtual desktop, can present a significant challenge in DaaS. It is particularly critical for interactive applications or tasks requiring real-time responsiveness, such as video conferencing, gaming, or high-frequency trading.
Security Considerations:
The storage of sensitive data and desktop environments in the cloud gives rise to security considerations. It is crucial for organizations to guarantee the encryption of data during transmission and while at rest, implement access controls and authentication mechanisms, and regularly update security protocols to reduce the likelihood of data breaches or unauthorized access.
Potential Vendor Lock-in:
The process of migrating between Desktop as a Service (DaaS) providers can be intricate due to proprietary configurations, data formats, and integration dependencies. It may result in organizations being bound by contracts or encountering difficulties in transferring data and configurations between providers, which ultimately constrains their flexibility and agility.
Limited Customization:
DaaS solutions may offer limited customization options compared to on-premises desktop environments. Organizations may encounter challenges in tailoring virtual desktops to specific user preferences, business workflows, or industry-specific requirements.
Future Trends in DaaS and Cloud Computing
- Adoption of Hybrid and Multi-cloud Deployments
Today, organizations are increasingly embracing hybrid and multi-cloud approaches to capitalize on the unique strengths offered by various cloud providers and environments. This shift is also evident in Desktop as a Service (DaaS), as organizations utilize multiple cloud platforms to host virtual desktops based on performance, cost, and compliance requirements.
- Integration of Edge Computing:
The growing adoption of edge computing, characterized by the processing of data in proximity to the source or end-users, has resulted in the integration of DaaS solutions with edge computing infrastructure. This integration aims to deliver low-latency virtual desktop experiences and support edge devices such as IoT devices and smart sensors.
- Incorporation of AI and Machine Learning:
DaaS platforms incorporate AI and machine learning technologies to improve user experiences, optimize resource allocation, and enhance security. These platforms can offer insights into user behavior, application performance, and security threats through AI-driven analytics, allowing for proactive management and optimization of virtual desktop environments.
- Improved Security Measures:
In reaction to how cyberthreats are changing, DaaS providers are bolstering security measures to defend against data breaches, malware, and unauthorized access. It involves the implementation of advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, endpoint security, and threat detection capabilities to protect virtual desktop environments and sensitive data.
- Utilization of Containerization and Microservices Architecture:
Containerization and microservices architecture are becoming increasingly prevalent in cloud computing. DaaS solutions may integrate containerized desktop environments and infrastructure based on microservices to enhance scalability, resource efficiency, and agility in the deployment and management of virtual desktops.
Conclusion
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) transforms desktop computing by providing flexible, scalable, and easily accessible solutions via the cloud. By lowering costs, simplifying management, improving security, and enabling workforce mobility, DaaS is primed to become a fundamental component of contemporary workspace strategies. It allows businesses to adjust to evolving requirements, streamline IT operations, and foster innovation, rendering it an essential tool for organizations seeking efficiency and adaptability in the digital era.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What strategies can organizations employ to facilitate a seamless transition to DaaS?
Answer: To achieve a seamless transition to DaaS, organizations need to:
- Perform a comprehensive evaluation of their existing IT infrastructure and needs.
- Create a migration strategy encompassing data migration, application compatibility testing, and user education.
- Collaborate closely with their selected DaaS provider to resolve issues and guarantee a smooth transition.
Q2. Can DaaS be integrated with existing IT systems?
Answer: DaaS can be incorporated into existing IT systems using APIs and other integration techniques. This allows organizations to make use of their current infrastructure while harnessing the scalability and flexibility provided by DaaS.
Q3. How does DaaS differ from traditional data management approaches?
Answer: Traditional data management stores and manages data locally, while Data as a Service (DaaS) stores data in the cloud and enables access over the internet. It eliminates the necessity for local storage infrastructure and facilitates enhanced scalability and accessibility.
Q4. Can DaaS be used for real-time data processing?
Answer: Real-time data processing using DaaS is feasible, contingent on the capabilities and infrastructure of the DaaS provider. This capability empowers organizations to analyze and act on data as it is generated, facilitating quicker decision-making and response to events.
Q5. Can DaaS support graphics-intensive applications and multimedia content?
Answer: Desktop as a Service (DaaS) can accommodate graphics-intensive applications and multimedia content by leveraging technologies like GPU acceleration and streaming protocols. DaaS providers present customized solutions designed specifically for the needs of graphics professionals, designers, and multimedia content creators. These solutions deliver high-performance virtual desktops that are finely tuned for multimedia workloads.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “DaaS in Cloud Computing” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.