Updated May 9, 2023
Overview to Connect Database to MySQL
Before we discuss how to Connect the Database to MySQL, we will see the introduction of MySQL. MySQL is a free and open-source database. It is a relational database management system (RDBMS).
MySQL is open-source and free software under the General Public License (GNU) terms and is also available under proprietary licenses. It was developed by the Swedish company MySQL AB and later bought by Sun Microsystems, now Oracle Corporation.
MySQL is used in many web applications based on database-driven like WordPress, which is on-demand now, Drupal, phpBB, and Joomla; also MySQL is used by many popular websites, like Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, and Flickr.
Features of MySQL
MySQL is offered under two different editions: the open-source MySQL Community Server and the proprietary Enterprise Server. MySQL Enterprise Server is differentiated by a series of proprietary extensions which install as server plugins but otherwise share the version numbering system and is built from the same code base.
Major features as available in MySQL 5.6:
- It supports cross-platform.
- Can create stored procedures using procedural language.
- Create Triggers.
- Can create Cursors.
- Views can be updated.
- With the help of InnoDB Storage Engine can create an Online Data Definition Language (DDL); also, using InnoDB and NDB Cluster Storage Engines can do ACID compliance.
- It supports built-in replication like Asynchronous, Semi-synchronous, Synchronous, and Virtual Synchronous.
- It also supports full-text search, indexing, and partitioned tables in an optimizer to store huge data and run in less execution time.
- The Federated, Archive, InnoDB, Memory (heap), MyISAM, Merge, Blackhole, CSV, and NDB Cluster are native storage engines.
How to Connect Database to MySQL?
To connect to the MySQL database, first, we will see the steps to install MySQL; download the MySQL workbench from this URL: https://www.mysql.com/products/workbench/.
We will create a new Connect database to MySQL after installation:
Creating a new connection may be an initial connection or an additional connection. An instance of MySQL server must be installed, started, and accessible to MySQL Workbench before creating a new connection.
To create a new connection, follow these steps:
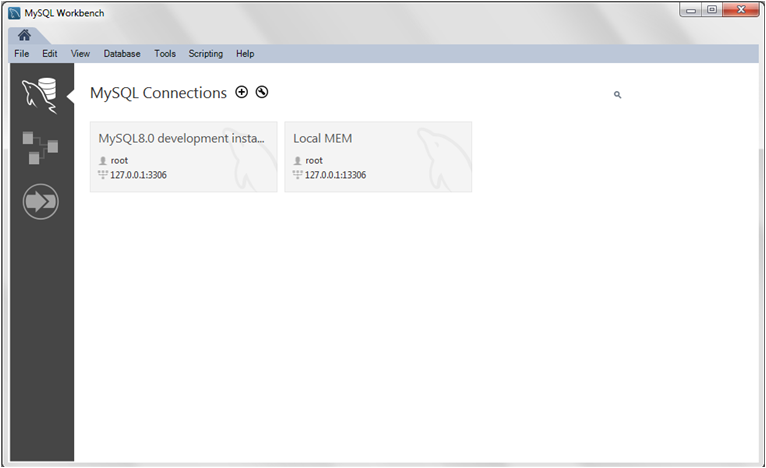
Step 1: Start MySQL Workbench with the double clock on it. Once it is open, you will see the MySQL Connections option; if you click on it, you will see the existing connections; otherwise, no connections exist if it is the first time using as in the figure below.
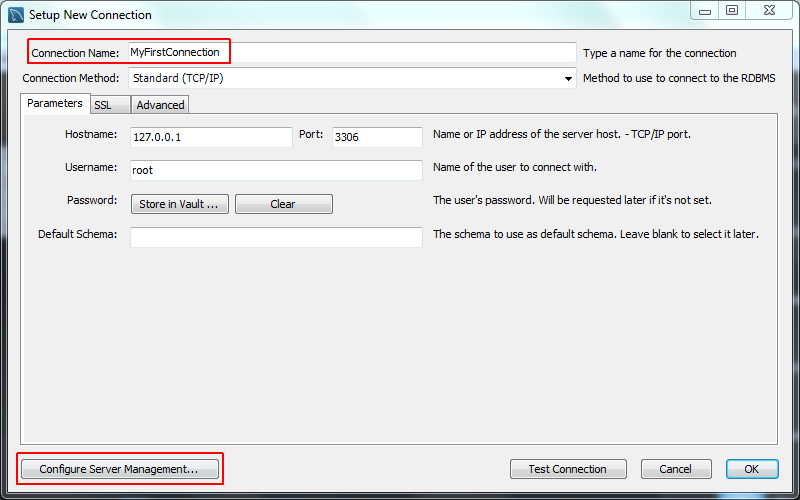
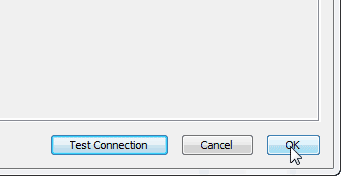
Step 2: Click the [+] icon from the MySQL Workbench screen near MySQL Connections, and then open-label option Setup New Connection wizard. Provide all the details in the Setup New Connection wizard Connection, connection name, for example; we will give “MyFirstConnection” and keep all other fields as the default values and then click the Test Connection button. If the test connection shows successful, then go to create the connection by clicking the ok button.
Step 3: Further, if you want to do some configuration settings, then click on Configure Server Management button and provide the details like the location of configuration files, SSH login-based management, the correct start and stop commands to use for the connection, native windows remote management all those setting can be done depending on the requirements.
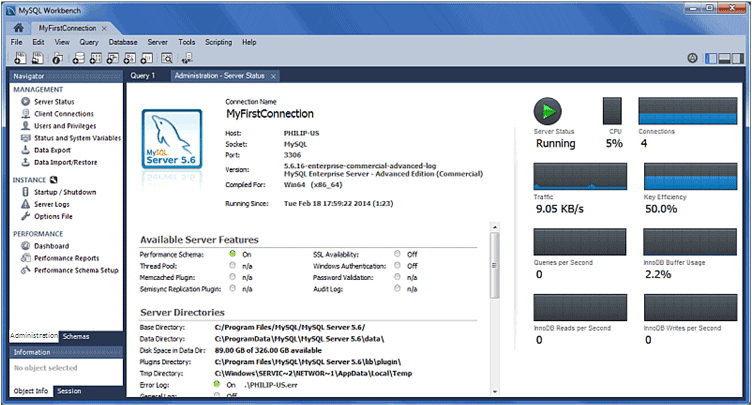
Once you click on the ok button, it displays the below image.
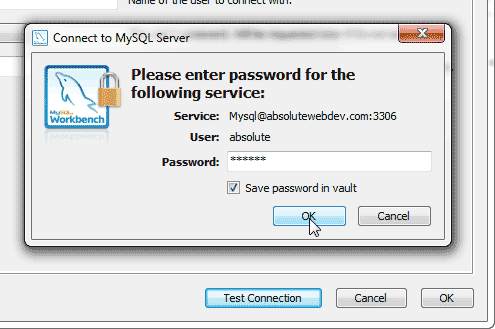
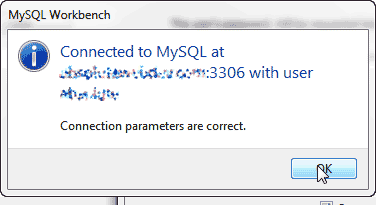
Step 4: In this window, it asks for the password, so provide it and click ok.
After clicking on ok, it displays a window to show the message connection parameters are correct; then again, click the ok button.
After ok, you return to the connection window and click the ok button again.
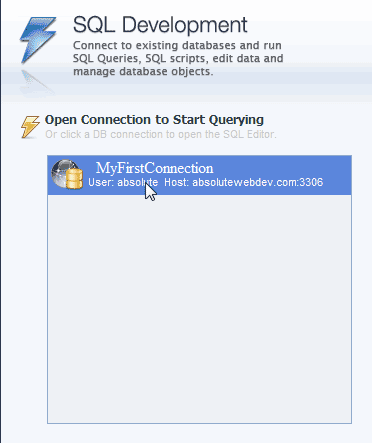
Now it shows you the list of connections available under the SQL development section, where you will find you just created a new connection as well, so click on your newly formed connection.
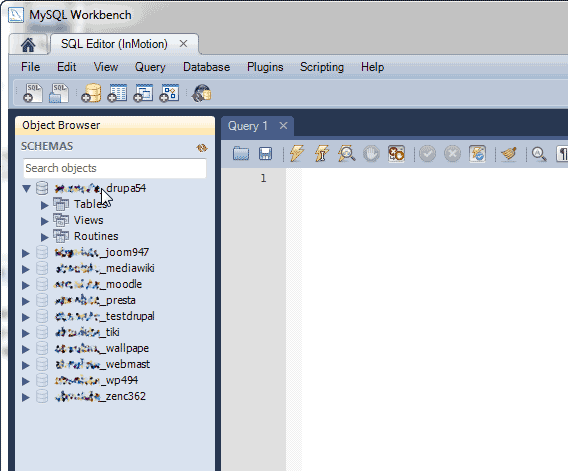
Now it opens the connection with the object browser and the query editor. The object browser shows you the list of a database. Once you click on the database further, you can see the list of all the tables available in that particular database, view available and routines, and so all. The query editor window uses to write the query and execute it on the database, so for this, you need to select the query and click on the run command.
The alternative way to connect to the MySQL database is through the command line, so next, we will see how to connect the database to MySQL.
We need to perform the following steps to connect to the MySQL database –
First, log in to your account A2 Hosting using SSH. Then open the command line. To open the command line, click the start button from the keyboard, then type cmd and press enter to open the black wind.
Next, type the following command.
mysql -u name –pReplace your name with your username and click enter; it shows a Password prompt, so type your password. Now the mysql>prompt appears once you type the correct password, so now you are connected to the MySQL database.
Next, if you want to see a list of all available databases, type the following command at the mysql> prompt.
show databases;After knowing all the available databases, if you want to access a specific database, then at the mysql> prompt, type the following command.
use database name;Replace the database name with your accesses database name.
Now you are inside the database; you can run the SQL query on the database, like creating a table, accessing the table, creating the view, and so on.
For example, consider the query to create a table:
CREATE TABLE employee (
id INT(6) PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(20) )Farther, if you need a list of commands and syntax, you can take the help at the mysql> prompt by typing help and exit the MySQL program at the mysql> prompt \q type.
Conclusion
1. Download and install MySQL workbench from this URL https://www.mysql.com/products/workbench/.
2. Start MySQL Workbench by double click on it, providing the connection name, and clicking ok.
3. Click on your connection name and write the query in the query editor.
4. The command line is an alternative way to connect the database to MySQL. Type the following command in sequence at the command prompt.
mysql -u name –p
mysql> show databases;
use database name;Then type and run the required SQL queries.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “How to Connect Database to MySQL?” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.