Updated May 15, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Server
The following article provides an outline for MySQL Server. Many RDBMS (systems) are available in the market for managing databases. The most popular among them is MySQL. MySQL is an open-source Relational Database Management System(RDBMS). It is based on Structured Query Language (SQL – a language to manage the database and perform CRUD operations such as create, read, etc., update and delete.).
MySQL Brief Journey
- It was first created and owned by a Swedish company named MySQL AB, with its first initial release in 1995 on May 23.
- In 2008, MySQL AB was acquired by Sun Microsystems in a 1 billion deal.
- In 2010, Sun Microsystems was further acquired by Oracle.
The latest version of the MySQL server is 8.0, which was released on April 19, 2018. - It can virtually run on any platform, such as Linux, Solaris, and Windows. It is the most popular RDBMS because it is an open-source and freeware DB server providing much-advanced database functionalities.
Examples
- Google, Facebook, Yahoo, and other Tech giants have employed MySQL to enhance their data processing capabilities.
- MySQL is essential for LAMP, a web development platform with the Linux operating system, Apache as the web server, MySQL as RDBMS, and PHP as a programming language. Nevertheless, Python or Perl can be used instead of PHP as the programming or scripting language.
- It can be used everywhere where the Data needs to be stored relationally, i.e., in a tabular format. Every table has a primary key, and rows can relate to each other using this primary key.
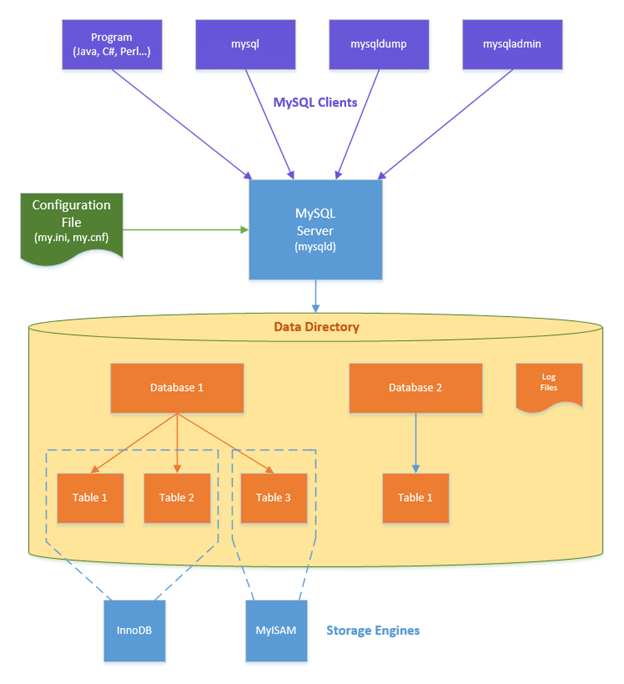
Architecture of MySQL Server
The architecture of MySQL mainly consists of the following components:
- MySQL Server
- MySQL Clients
- Data Directory
- Storage Engine
MySQL is based on a Client-Server Model.
1. MySQL Server
It is a MySQL instance where the actual data is stored and processed. This component is responsible for processing the incoming queries from MySQL clients and manipulating the database tables. It is also responsible for accepting database connections that are coming from MySQL Clients.
Important Programs of MySQL Server component are:
- MySQL: It is a MySQL server daemon program. It runs in the background and manages requests from MySQL clients.
- mysqld_safe: A program restarts the server whenever an error occurs. This was one safety feature of this program; the other one is that it maintains the logs for the runtime information in an error log.
- mysql.server: A MySQL utility has been provided to start the mysqld_safe script.
- mysqld_multi: This program is used to manage many mysqld processes that listen for connections on different connections channels like TCP/IP, UNIX Sockets, etc.
2. MySQL Clients
The MySQL clients use utilities for communicating with the MySQL server. In other words, these programs communicate with the MySQL server. MySQL clients include programs like Perl, PHP, Java, MySQL, mysqladmin, and tools such as MySQL dump, mysqlcheck, and myisamchk.
Important programs under MySQL clients are:
- MySQL is an SQL shell where one can write and execute SQL statements. It can be interactive or non-interactive. When you use it interactively, it returns results in a tabular format, while non-interactive usage returns the result in a tab-separated form.
- mysqladmin is a client for administrating MySQL servers. You can use it to check configuration files, update the server’s current status, create and drop databases, etc.
- mysqldump is a client utility and a database backup program that performs logical backups.
- mysqlcheck and myisamchk are clients that perform maintenance on Database tables, like repairing, optimizing, and analyzing the tables.
3. Data Directory
The Data Directory contains stored data due to ongoing operations over applications/software or servers. It includes Databases, tables, log files, stored procedures, etc.
- The default location for datadir in Linux is: /var/lib/mysql.
- The default location for datadir in Windows is C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.8
- The name of the configuration file which contains the path for datadir is mysqld.cnf.
- cnf can be found at /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf.
- It is possible to change the storage location for datadir in case someone runs out of allocated space.
4. Storage Engine
A storage engine is a software module RDBMS uses to perform CRUD operations (Create, read, update, and delete).
The storage engines are of two types in MySQL:
- Transactional
- Non-Transactional
The main difference between the Transactional and Non Transactional storage engines is that the transactional tables will record all the database operations in a log file. Even if MySQL crashes, you can still get your data back. At the same time, this is not the case with Non-Transactional Engines. Nevertheless, to point out, non-transactional engines are much faster, and they also have lower disk space requirements.
Below are some of the Storage Engines that MySQL is using; the most widely used among them is InnoDB.
MySQL-supported storage engines:
- InnoDB
- MyISAM
- Memory
- CSV
- Merge
- Archive
- Federated
- Blackhole
Advantages
These are the mentioned advantages:
- Portable: It can run on many platforms like UNIX, Solaris, Windows, OS/2, etc.
- Open Source: Most importantly, MySQL is open-source software available to everyone for free, provided they agree to its terms and conditions.
- Security: MySQL Data Bases are very secure, and they use complex algorithms to encrypt passwords, making it difficult to breach them.
- Connectivity: There are a good number of mechanisms available to connect with MySQL servers, such as TCP/IP, UNIX Sockets, and named pipes.
- Regular Updates and Continuous Development: Being an open-source platform, MySQL has a huge developer community that releases patches and updates for MySQL regularly.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Server” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.