Updated November 18, 2023
Working Capital Formula
The excess of current assets over current liability is known as working capital. Liabilities and assets which are short-term in nature are required in day-to-day business activities. The procedure is a working capital cycle when a business managers short-term liability from short-term assets.
Here’s the Working Capital Formula –
From working capital, we can get away with an idea regarding the scenery of the business or, in other words, how effectively the particular business is going. So, it reflects the short-term liquidity of the particular company and the degree of operational efficiency we can measure based on a higher current asset over current liabilities.
Constituents of Current Assets
- Current investments
- Cash
- Inventories
- Trade receivables
- Bank balance
- Short-term loans and advances
- Other current assets
Constituents of Current Liabilities
- Short-term borrowings
- Trade payables
- Other current liabilities
- Short-term provisions.
Example of Working Capital Formula
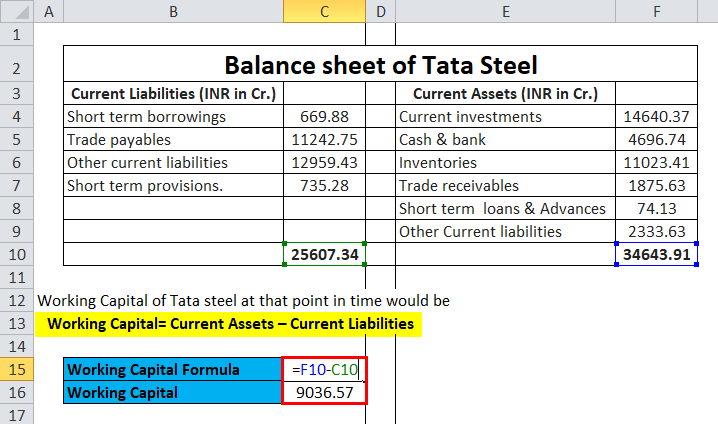
The Balance Sheet of Tata Steel is presented as follows:
|
The Balance Sheet of Tata Steel |
||||
|
Current Liabilities (INR in Cr.) |
Current Assets (INR in Cr.) |
|||
| Short-term borrowings | 669.88 | Current investments | 14640.37 | |
| Trade payables | 11242.75 | Cash & bank | 4696.74 | |
| Other current liabilities | 12959.43 | Inventories | 11023.41 | |
| Short-term provisions. | 735.28 | Trade receivables | 1875.63 | |
| Short-term loans and advances | 74.13 | |||
| Other Current liabilities | 2333.63 | |||
| 25607.34 | 34643.91 | |||
The Working Capital of Tata Steel at that point in time would be
- Working Capital= Current Assets – Current Liabilities
- Working Capital = INR (34643.91 – 25607.34)
- Working Capital = INR 9036.57
Explanation of Working Capital Formula
- A working capital formula is extensively used in a business to meet short-term financial obligations or short-term liabilities.
- Positive net working capital results when a company has enough assets over its current dues. On the other hand, if the company cannot produce positive working capital, it has to take its excess liabilities, such as higher short-term borrowings, higher accounts payable, etc.
- Another striking formula each analyst inspects is the operating working capital, which is accounts receivable class inventory minus accounts payable.
- Thus, despite each current asset, one may look at the accounts receivable, inventory value, and accounts payable. Thus, the financial health of the particular company can be fairly understood when it shows a positive value.
- Having a positive working capital indicates a healthy sign of the short-term financial health of the particular business as it has enough liquid assets after repairing its short-term bills, and internally, the financial health of the particular company would help to grow its business and its assets.
- Without additional working capital, a company has to borrow additional funds from a bank loan or a financial institution. Then, it will hinder the working capital as the current borrowings will come under current liabilities, reducing the net working capital.
- So, in other words, it can be integrated that a business is not strong enough to meet its short-term liabilities from its short-term assets. Thus, there is always a requirement for short-term borrowings from a third party, which can be interpreted as a negative sign for the business. Short-term borrowings would lead to higher interest costs, affecting profitability and margin. So, most capital-intensive businesses have negative working capital or very low working capital, and the profitability and the margin are very low compared to assets-light businesses.
- Negative working capital suggests that the assets of the particular business are not effectively used, and it may lead to a liquidity crisis.
- If a company has used fixed assets such as Land properties and buildings for long-term investments, but there is a cash crunch because of higher short-term liabilities. Also, the company will face a liquidity crisis, forcing it to take short-term borrowings.
- A late payment to creditors will result in higher accounts payable, and a delay in the entire process will result in lower working capital, ultimately hindering the corporate credit rating of the particular business.
Significance and Use of Working Capital Formula
Working capital is extensively used in analyzing different companies within the same sector.
An FMCG business would have relatively Lee higher working capital compared to a steel manufacturing business because of steel manufacturing request plants and machinery, which are relatively more costly than the manufacturing plants of FMCG. So, despite having higher assets, the business would require borrowing from banks and other financial institutions, creating higher interest costs.
Show that the margin of a steel plant business is generally lesser than that of an FMCG company.
From working capital, one can have a fair idea about a particular business’s current assets and liabilities.
If a business generates enough cash flows, then a part of that cash flow will be invested in current investments, which are short-term and long-term investments for long-term investing purposes.
Short-term investments can be utilized when there is a requirement for additional liquidity within the business due to a spike in current liabilities.
Cash and Bank balances generally don’t contain any interest receipt due to being short-term. Trade receivables generally happen to be a certain portion of the Revenue. So, higher trade receivable suggests there is a chance of a bed date in the future if the business scenario is not favored for the company. On the other hand, trade payables r generally credit given by the supplier.
Working Capital Calculator
You can use the following Working Capital Calculator
| Current Assets | |
| Current Liabilities | |
| Working Capital Formula | |
| Working Capital Formula = | Current Assets – Current Liabilities |
| = | 0 – 0 |
| = | 0 |
Working Capital Formula in Excel (With Excel Template)
Here, we will do the same example of the Working Capital formula in Excel. It is very easy and simple. You need to provide the two inputs i.e. Current Assets and Current Liabilities
You can easily calculate the Working Capital using the Formula in the template provided.
We need to calculate Working Capital using Formula, i.e. Working Capital= Current Assets – Current Liabilities.
Conclusion
A working capital formula determines the business’s financial health and suggests how the profitability can be increased through the current ratio, which we get by dividing current assets by current liabilities. The ideal ratio should be 2 to 1 for manufacturing companies. However, a capital-intensive company will have a different ratio, and in the case of negative working capital, the ratio might reverse in most cases. The working capital formula can determine the day-to-day operations, i.e. the excess of Current Assets over Current Liabilities.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to a Working Capital formula. Here, we discuss its uses along with practical examples. We also provide a Working Capital Calculator with a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –