Updated July 26, 2023
Definition of Working Capital Example
The company requires working capital to meet its day-to-day expenses and represents an investment in short-term assets. An example of working capital in active voice is when the company exceeds its current liabilities with its current assets.
It helps determine the company’s liquidity and performance. Gross working capital represents the investment in current assets, while net working capital is the difference between current assets and liabilities. It can be positive or negative.
Examples of Working Capital (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of Working Capital in a better manner.
Working Capital Example – #1
Let us look at a simple example that uses the balance sheet of Wells Fargo to calculate working capital
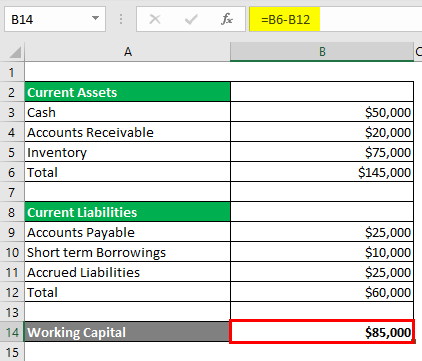
Working Capital is calculated as
Working Capital = Total Current Assets + Total Current Liabilities
- Working Capital = $1,45,000 + $60,000
- Working Capital = $85,000
The total current assets are $1,45,000, while the total current assets are $60,000. Subtracting both of these gives us a working capital of $85,000. The company has a good amount of cash after it has paid all of its obligations. This means that the company is in a good financial position
In this example, as we can see, the working capital is positive. This means that the company can pay off its short-term liabilities immediately. While negative working capital indicates the opposite.
We have here calculated working capital for one year, but it is also possible to calculate working capital for a month or a quarter
Working Capital Example – #2
Let us look at an example of Negative working capital. It is mainly possible in the retail sector. Let us look at one example of a major retail giant in the US, Walmart. Let us assume that Walmart buys 200,000 DVDs and is expected to pay the movie studio in the next 30 days. But Walmart will not wait 30 days to put those DVDs on its shelf. It will put these DVDs on the shelf once they receive the delivery.
Assume that they sold all the DVDs by the 15th of the month. They have sold all the DVDs and made a considerable amount of profit. They did all before they paid the studio for the inventory
Now imagine that if Walmart can pull this off for one product, it can do it for all its products. In this case, it does not need cash to pay for its accounts payable as new cash is constantly generated at various levels to cover the dues. But an important point to note here is that the timing of the cash flows is crucial. This helps in maximizing its efficiency
One way to determine if the company uses this strategy is to check inventory with accounts payable. If the amount of accounts payable is high and working capital is high, this might be it.
Working Capital Example – #3
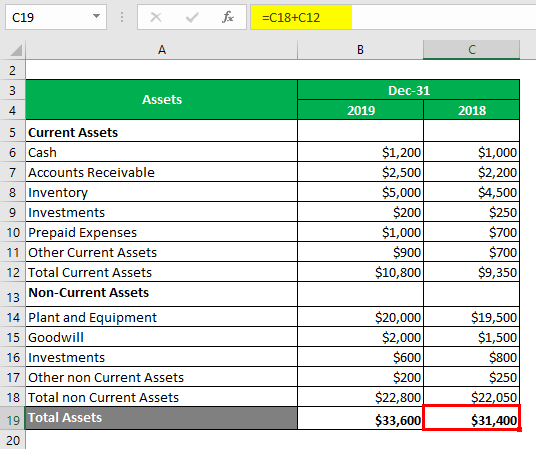
Below is the Balance sheet for a US-based organization. The balance sheet provided is for 2019 and 2018
Total Assets = Total Current Assets + Total non-Current Assets
For 2018
- Total Assets = $9,350 + $22,050
- Total Assets = $31,400
For 2019
- Total Assets = $10,800 + $22,800
- Total Assets = $33,600
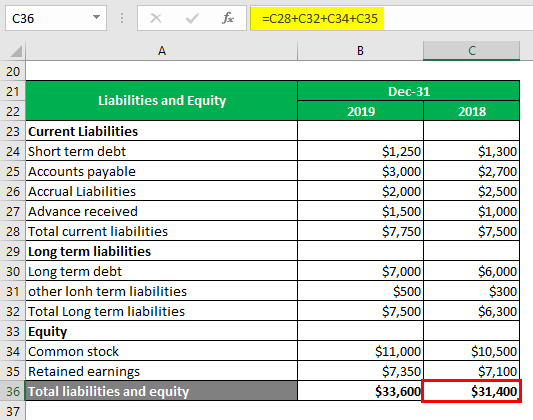
Total Liabilities and Equity is calculated as
Total Liabilities and Equity= Total current liabilities + Total Long term liabilities + Common stock + Retained earnings
For 2018
- Total Liabilities and Equity= $7,500 + $6,300+ $10,500 + $7,100
- Total Liabilities and Equity= $31,400
For 2019
- Total Assets = $7,750 + $7,500 + $11000 + $7,350
- Total Assets = $33,600
Let us now calculate working capital for both years –
Working Capital is calculated as
For 2018 & 2019
- Working Capital 2018 = $9350 – $7500 = $1850
- Working Capital 2019 = $10,800 – $7750 = $3050
Average Value of Working Capital is calculated as
- Average Value of Working Capital = ($3050 + $1850) /2
- Average Value of Working Capital = $2450
The large difference in working capital is mainly due to the significant increase in current assets. Days in payables and receivables can be calculated using these statements and working capital
Working Capital Example – #4
Examples of real working capital companies are listed below
- Amazon: The main reason Amazon is surviving with this strategy is that customers pay upfront and have no difficulty raising money
- Dell Computers: This is also a classic case of maintaining minimum inventory and extremely low working capital. Dell computers demand upfront payments from customers. This has not only reduced the working capital but also given it an edge against its competitors
- McDonald’s: It is very common for any restaurant business to have negative working capital. McDonald’s has been running on negative working capital for over a decade, from 1992 to 2000. It had negative working capital of as much as $698.5 million in this period
Looking at the above examples, it can be said that negative working capital is a sign of effective business management
Conclusion
Positive working capital is a sign of good short-term financial health and liquidity. It means that the company has a sufficient amount of funds to cover its short-term obligations. If the working capital is increasing, it might lead to more borrowing and the need to raise more money
On the other hand, negative working capital may mean that assets are not being used effectively, and the organization might be going through a liquidity crisis. However, having negative working capital is not always a bad sign. Huge companies, as seen above, like Walmart have negative working capital because of the continuous and fast inflow of cash
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Working Capital Example. Here we discuss the definition and practical example of working capital with a detailed explanation and downloadable Excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –