Updated March 17, 2023
What is XPath?
XPath is a word that describes how objects can be identified and processed by using a syntax addressing a path through the logical structure or hierarchy of the document in Extensive Markup Language (XML) documents. It makes it easier to write programming phrases than to understand the XML-style and sequence of each word in a document. XPath can also allow the programmer in a higher level of abstraction to handle the text. XPath is a language that both Extensible Language Transformations (XSLT), as well as XPointer, uses and defines. XPath is an extensible language. The abstraction of information defined in the XML Information Set is used.
Linking in XML is divided into two parts: XLink and XPointer. XLink and XPointer define a standard way of creating hyperlinks in XML documents.
Expression of XPath
XPath allows different types of expressions to retrieve relevant information from the XML document. XPath addresses a specific part of document. It models an XML document as a tree of nodes. An expression of XPath is a technique for navigating through and selecting nodes from the document.
XPath expressions can be used in C, C++, Python, Java, JavaScript, PHP, XML Schema and many other languages. An XPath expression refers to a pattern to select a set of nodes. XPointer use these patterns for addressing purpose or to perform transformations by XSLT. The XPath expression specifies seven types of nodes which can be the result of execution.
1. Root
Root element of an XML document. Using the following ways root elements can be found.
- Use Wildcard (/*): To select the root node
- Use Name (/class): To select the root node by name
- Use Name with a wildcard (/class/*): To select all elements under the root node
Code:
<!—-Using Wildcard-->
<p><xsl:value-of select = “name(/*)”/></p>
<!—-Using Name-->
<p><xsl:value-of select = “name(/class”/></p>
<!—-Using Both-->
<p><xsl:value-of select = “name(/class/*)”/></p>
2. Element
Element node of an XML document. Below are the ways to find element
- /class/*: used to select all elements under the root node.
- /class/library: used to select all the library elements from the root node.
- //library: used to select the entire library element from the document.
Code:
<!—-Using /class/*-->
<xsl:for-each select = "/class/*">
<!—-all library element from root node -->
<xsl:for-each select = "/class/library">
<!—entire library element from document-->
<xsl:for-each select = "//library">
3. Attributes
An attribute of an element node in the XML document retrieved and checked by using the @attribute-name of an element.
Code:
<!—To get value of attribute Book ID -->
<td><xsl:value-of select = "@bookId"/></td>
4. Text
Text of an element node in the XML document, retrieved and checked by name of an element.
Code:
<!—To get text value of Book Name -->
<td><xsl:value-of select = "bookname"/></td>
5. Comment
Example of comment
Code:
<!-- Comment: Library contains below books. -->
Node or List of the node from XML
Following are the list of useful expressions to select a node or list of the node from an XML document.
- ‘/’: Using this selection start from the root node.
- ‘//’: Using this selection starts from the current node which matches selection
- ‘.’: To select current this expression used.
- ‘..’: To select the parent node of the current node.
- ‘@’: To select attributes.
Example
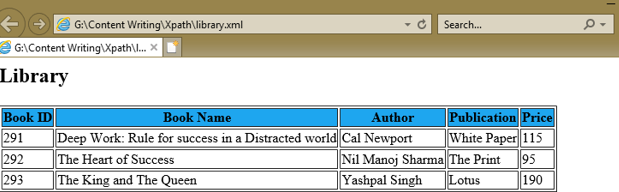
To understand an XPath expression, we’ve created an XML document, library.xml, and its style sheet document library.xsl which uses the XPath expressions under the select attribute of various XSL tags to get the values of book id, book name, author, publication, and price of each book node.
1. library.xml
Code:
<?xml version = "1.0"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type = "text/xsl" href = "library.xsl"?>
<class>
<!-- Comment: Library contains below books. -->
<library bookid = "291">
<bookname>Deep Work: Rule for success in a Distracted world</bookname>
<author>Cal Newport</author>
<publication>White Paper</publication>
<price>115</price>
</library>
<library bookid = "292">
<bookname>The Heart of Success</bookname>
<author>Nil Manoj Sharma </author>
<publication>The Print</publication>
<price>95</price>
</library>
<library bookid = "293">
<bookname>The King and The Queen</bookname>
<author>Yashpal Singh</author>
<publication>Lotus</publication>
<price>190</price>
</library>
</class>
2. library.xsl
Code:
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version = "1.0"
xmlns:xsl = "http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<!-- Declaration -->
<xsl:template match = "/">
<html>
<body>
<h2>Library</h2>
<table border = "2">
<tr bgcolor = "#afafaf">
<th>Book ID</th>
<th>Book Name</th>
<th>Author</th>
<th>Publication</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
<!—For Loop -->
<xsl:for-each select = "class/library">
<tr>
<!—Table Details -->
<td> <xsl:value-of select = "@bookid"/></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select = "bookname"/></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select = "author"/></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select = "publication"/></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select = "price"/></td>
</tr>
</xsl:for-each>
<!—End of loop -->
</table>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Output:
Benefits of XPath
Below are the benefits :
- XPath queries are simple to type and read and also are compact.
- XPath syntax is easy for the common and simple cases.
- The query strings are embedded in scripts, programs, & HTML or XML attributes easily.
- The XPath queries are easily analyzed.
- Any node can uniquely recognize in an XML document.
- In an XML document, the occurrence of any path or any set of conditions for the nodes in path can be specified.
- Queries return any number of results, including zero.
- In an XML document, query conditions can be calculated at any level and are not supposed to traverse from the top node of an XML document.
- The queries return unique nodes, not repeated nodes.
- In many contexts, it is used, to provide links to nodes, for finding repositories & many other applications.
- For the programmers, the queries are not procedural but more declarative. They define how elements should be traversed. To get efficient results, indexes and other structures must be used free by a query optimizer.
Conclusion
XPath is a query language used to traverse elements, attributes, text through an XML document. XPath is used widely to find particular elements or attribute with matching patterns. When a query is defined, then that XML data can be represented as a tree. The hierarchical representation of XML data is called a tree. The top of the tree is a root node. In a tree, each attribute, elements, text, comments, string, and processing instruction corresponds to one node. The relationships between the nodes can be represented by the tree.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to What is XPath?. Here we discuss expression, list, examples, and benefits of Xpath. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more-