Updated August 19, 2023
Introduction to SSL
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is an encryption-based internet security protocol for establishing authenticated, encrypted links between networked computers to provide privacy and integrity to internet communications. It has been everywhere used to get the trust from the parties; for example, when you search on google, various websites have been open, each content lock sign at the left corner, this lock sign indicates that the particular site is secure to use. Many online businesses used this SSL concept to get the users’ trust.
What is SSL?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer, and it is a protocol that is being used to provide secure communications to a computer network. The protocol’s official name is now changed and replaced; it is known as TLS, which stands for Transport Layer Security. While SSL was the foundation for TLS, it came as a replacement for the vulnerabilities that were discovered in SSL.
There is personal and secure information in today’s world, and that needs to be protected against hackers and criminals. Exchange of information can happen between a server and a client (e.g. a browser and a website) and also can happen with a network of servers.
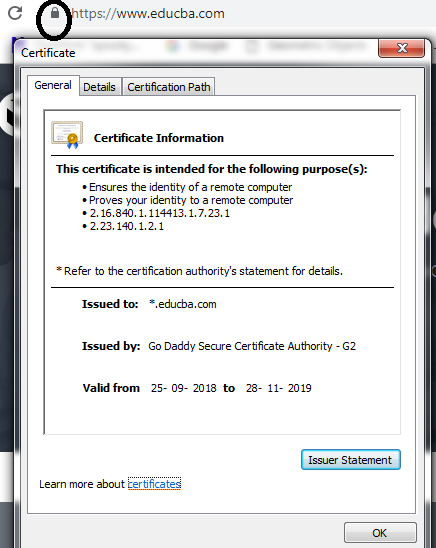
Whenever SSL secures a network or a website, HTTPS appears in the URL. HTTPS stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure. Also, one can see many more details about the issuing authority of the SSL certificate and the corporate name of the website owner by clicking on the top left lock symbol that appears on the browser bar.
Working of SSL (How a Secure Connection is Established?)
The basic approach that is being used behind the SSL is when you enable and install an SSL certificate on a server and when a client, say the web browser tries to connect with it, the SSL certificate triggers an SSL protocol which encrypts all the data between the client and the server. An SSL handshake happens between the client and the browser, which is invisible to the users. In order to set up the SSL connection, three keys are required: the private key, the public key, and the session keys.
The rule is:
The private key and vice versa can only decrypt anything which is encrypted with the help of a public key. Once the connection is established, the session key is being used to encrypt all the data.
Different algorithms are used for encrypting the data in SSL, and Symmetric algorithms supported in SSL are Camellia, DES, 3DES, RC2, ARCFOUR, AES, IDEA, SEED, NULL (i.e. no encryption).
What are the Steps involved in Establishing a Secure Connection via SSL?
Following are the steps that are involved in establishing a secure connection via SSL:
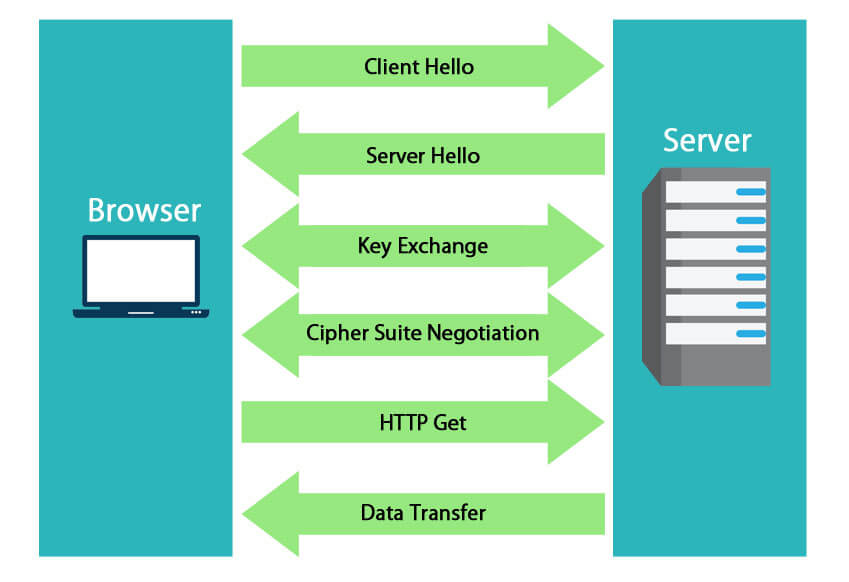
- The web browser, i.e. the client, connects to the server that is secured with an SSL. The browser/client requests for server identification.
- Next, the server sends the SSL certificate that CA issues to the client. Along with the certificate, the server also sends its public key.
- The client, i.e. the browser, receives the copy of the certificate, and then it verifies the different properties, i.e. checks for expiry, revokes, and validity. If the resulting check is trusted, a symmetric session key is sent back to the client, which is encrypted using the server’s public key.
- The server then decrypts the symmetric session key using its private key. An acknowledgment is also sent back, which is encrypted with the session key.
- Once the secure connection is established, all the transmitted data is encrypted with the help of a session key.
Features of SSL and Security Provided
SSL/TLS provides features for data encryption, authentication, and the integrity of data.
When a data is encrypted with SSL, that basically means:
- Nobody reads the sent data/message.
- Nobody modifies the message/data.
- The message/data is sent to the intended recipient.
To make sure that the message has reached the recipient and no one has modified it, SSL encrypts this and signs it.
Both the process requires the use of keys.
Public, Private, and Symmetrical Keys
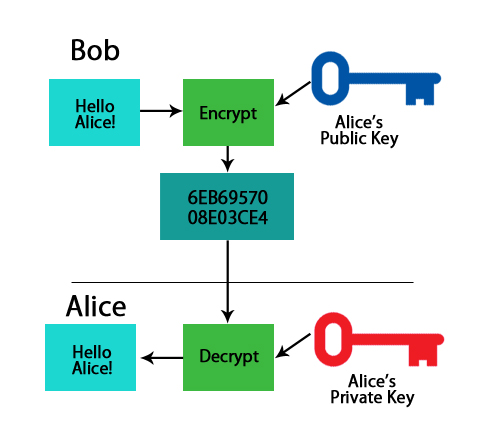
- Public Key: A public key converts a message into an unreadable format using algorithms, and only the person who is having the public key can encrypt the message. On the other end, the receiver has a private key, with the help of which he can decrypt the message.
- Private Key: The private key is being used to decrypt the message, which was encrypted using the public key.
Example:
As the name suggests, the public key is available to everyone who is having access to the repository.
A public key more or less, could look like below:
1048 0141 03C9 18FA CA8D EB2D EKD5 FD37 89B9 M069 EA97 FC20 5E35 F577 EE31 C4FB C6B4 4811 7A86 BC8F BAFA 362F 922B F01B 2K40 C744 2654 C0DD 2881 D673 CA2B 4013 C266 E2ED CB02 0201 0011.
Going with the most famous example, if Bob wants to send sensitive information to Alice, he will encrypt the data with Alice’s public key. By doing this, he would make sure that only Alice should be able to read it. While on the other side, only Alice has access to the corresponding Private Key. So only the person with the private key has the capability to decrypt the encrypted data.
Keys and Certificates
In public/private key cryptography, how do we know that the public key belongs to the entity that has claimed it?
The digital certificate is the answer to this.
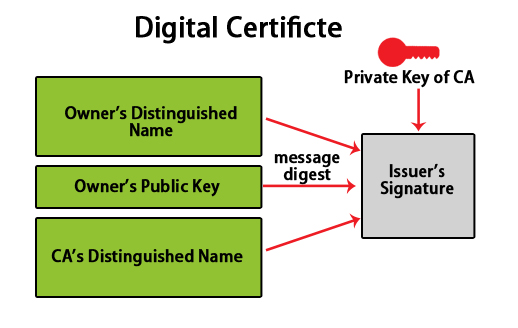
A digital key is like an electronic password that provides a link between the public key and entity (like the company, business), which is verified. Digital certificates are the preferred way of distributing public encryption keys that are trusted.
How are Digital Certificates Obtained?
Digital certificates can be obtained from any of the recognized Certificate Authority or CA.
Some of the popular certificate authorities companies are:
- Comodo SSL.
- DigiCert.
- Entrust Datacard.
- GeoTrust.
- GlobalSign.
- GoDaddy.
- Network Solutions.
- RapidSSL
To get the certificate, the business of the entity is required to fill out the form, add public keys, and be sent to the Certificate Authority. In turn, the certificate authority will run some checks, and they will send back the key, which will be enclosed in the certificate.
The certificate which comes is signed by CA (Certificate Authority).
Types of Digital Certificates
Digital certificates are mainly of two types:
- Extended Validated Certificates (EV)
The EV or the extended validated certificates are used for HTTPS websites and also for the software. The EV provides a legal entity for controlling the software package and the website.
- Domain Validated Certificates (DV)
In the case of DV or the domain validates certificates, the business’s identity or the entity is validated by putting some control over the DNS domain. The DV is a typical X.509 digital certificate.
Steps for Determining a Valid SSL Certificate
In order to determine if the website is having an SSL certificate or the valid SSL certificate (Which means trusted and not expired), below are a few of the checks that can be done:
- The major difference is the “HTTP” (i.e. HyperText Transfer Protocol) and the “HTTPS” (i.e. HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure), which says which connection is secured by SSL. An HTTP will always be displayed before any website address if it is SSL secured. While if the website doesn’t have any security, its address will be displayed with HTTP.
- A padlock symbol can be seen if the website is SSL secured.
- Also, one can see many more details about the issuing authority of the SSL certificate and the corporate name of the website owner by clicking on the top left lock (i.e. padlock) symbol that appears on the browser bar.
Where should one use SSL?
The SSL should be used everywhere to transmit data or information over a network, especially if the information is a sensitive one.
Examples:
- Intranet communication – To secure information that is exchanged within the organization’s intranet.
- Internet – To secure information that is exchanged over the internet. For e.g. the communication between a web browser and a server.
- For securing the exchange of information between server to server or over a network of servers.
- Cloud Computing.
- Securing information that is sent over mobile, tablets, etc.
- Email communications and many more.
Advantages and Benefits of SSL Certificates
As we have seen, SSL is a protocol that is being used to provide secure communications to a computer network.
Following are the advantages of using SSL:
1. To wipe out all attempts made by the bad guys, the “Hackers”
There is a number of phishing sites that are available today and are being created, so we need to be very much cautious about phishing sites. In many cases, you might see the exact replica of the original website that is being made available to you in order to fake you. But as far as SSL certificates are concerned, they will make sure that no such thing happens as fake websites can’t get an SSL certificate approved and signed by CA. Along with this, SSL will also protect you from other threats such as “man in the middle attack” and eavesdropping.
2. Search engines ranking and increase of users presence
Many of the search engines, such as Google, have updated their algorithm to a rank website to appear in the search result based on certain parameters, and one of them is an SSL secured website. Any website with SSL security will get ranked before the website which is not having any security, which means, when uses will search for information, SSL secured website will be displayed at first in search results while NoNSSL websites will be displayed in the last. Another big advantage is of gaining users’ and customers’ trust. A website secured with SSL gains users’ trust, and they are less worried about the website’s security aspect, and they do not fear while browsing through the website.
3. Secure payments gateway and safe shopping
Any business site must obtain an SSL certificate. When it comes to money and cash transfers, it becomes utmost to provide a secure tunnel between the buying entity and the selling entity whosoever is involved in the business. A business operating without an SSL certificate is almost targeted for attacks by hackers. Without a secure connection, no user will ever gain the confidence of submitting their credit card numbers for the sake of a transaction.
4. More security and extended authentication
With increasing cyber-attacks across the world, customers and Ethical hackers are also becoming more and more secure in their role to prevent any mishappening. There is a lot of sensitive information exchanged over a network, such as passwords, personal details, business deals, etc. So a secure authentication must be provided to ensure communication is well protected. This added security is achieved by issuing a server certificate along with the SSL certificate.
5. More robust encryption for secure of the information
All the information that is transferred over an SSL connection is encrypted with robust and complex algorithms. It is almost impossible to decipher them. The encryption algorithms that are mostly used by certificate authorities are RSA, DSA, and ECC. Any sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card numbers, when sent over a network will be secured with robust encryption, and that will not allow the hackers to crack it.
Conclusion
In this article, we have gained a good understanding of SSL and how it works. We also learned about the public and private keys that are being used in the encryption algorithm of SSL, and then we learned where we could use SSL. Finally, we wrapped up our article by seeing the benefits of SSL.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is SSL? Here we discussed the key concept, features, working, benefits, and steps for determining a valid SSL certificate. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –