What are Mergers and Acquisitions?
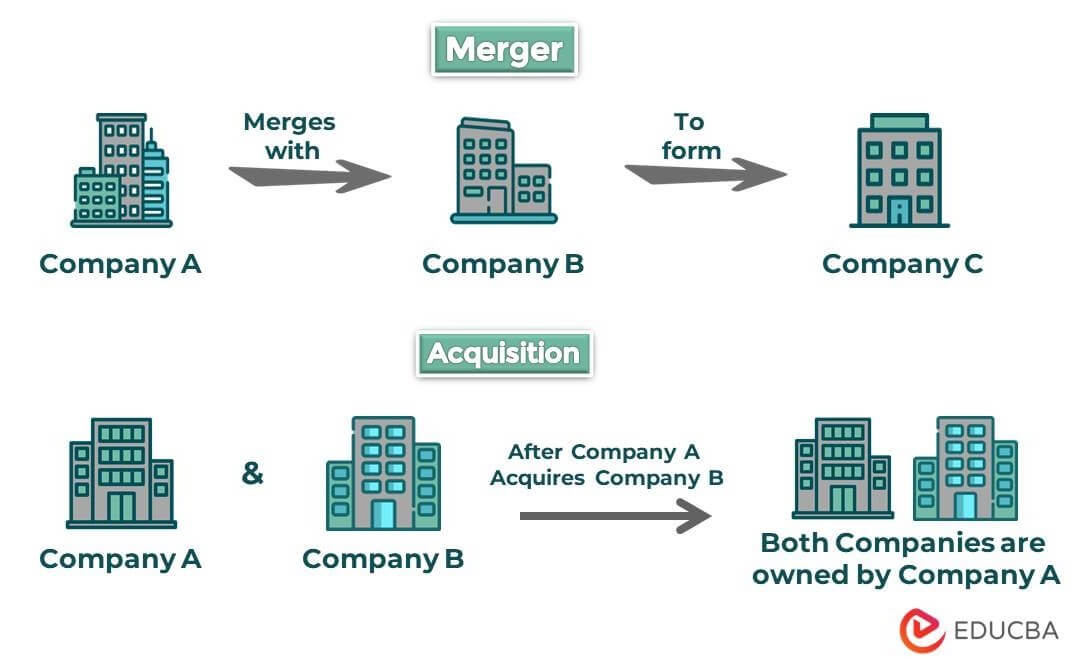
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are when two or more companies combine their entire businesses or core activities together to form a new business entity. In a merger, two independent companies come together in a mutual agreement. On the other hand, in an acquisition, one company (acquirer) buys another company (target or acquiree) either with its approval or as a hostile takeover.
The acquiring firm can buy some or all of its significant assets, make an offer for its shares, or execute a hostile takeover. One of the main reasons why a company chooses an acquisition or merger is the vast growth potential. By taking over the assets of another company, the company increases its market share, increasing sales and profitability. Ideally, the acquiring company will also get the entire customer base of the target company. However, if it doesn’t happen, the customer base will grow significantly. An adequately managed acquisition or merger can be beneficial in retaining existing customers and acquiring many new ones.
Reasons for Mergers and Acquisitions
Companies merge with or buy other companies for many reasons, including:
Synergy Benefits:
- Merging or acquiring a business can increase the value of the new business entity.
- Simply put, synergy means the new entity’s value will be comparatively more than both companies’ total value before the merger/acquisition.
- The two synergies are revenue (improved profitability) and cost synergy (reduced costs).
Diversification:
- It can help firms diversify their business by moving into new markets or offering new products or services.
- In addition, spread the risks associated with the company’s operations.
Acquisition of assets:
- Companies may also merge to acquire certain assets they cannot acquire in any other way.
- Commonly they want to gain unique assets or assets that take a long time to develop, like new technologies.
Growth:
- It increases the new company’s financial capacity to fund business development processes.
- Moreover, mergers can allow the company to increase market share without significant difficulty.
- Companies can also quickly eliminate their competition in the market by merging or acquiring them.
Tax purposes:
- If a company generates significant tax revenue, it can merge with a company with a greater tax loss.
- Thus, the company’s total tax liability will be much less than the tax liability of the standalone company.
Increase supply chain pricing power:
- By purchasing one of its suppliers or distributors, the company can save margins that the supplier previously added to its costs.
- Moreover, by purchasing a distributor, the company can provide products at a lower price.
The M&A Process
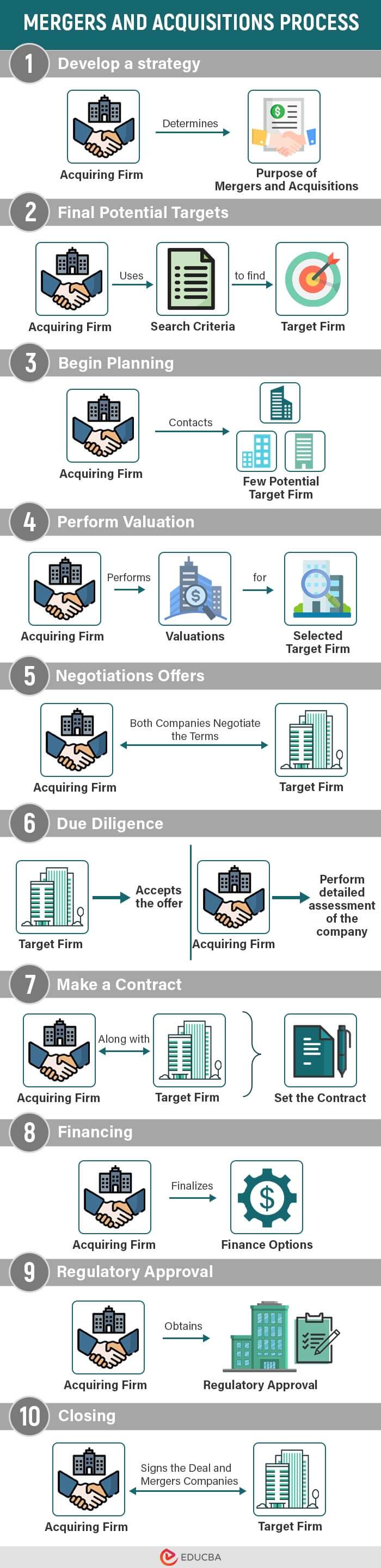
A typical 10-step M&A deal process includes:
1. Develop a Strategy
Firstly, the acquirer must have a practical and clear purpose for acquiring or merging with the target company. For example, the business may want to explore new products or sell to new markets.
2. Search for Potential Targets
Before looking for the target company, businesses must determine a list of search criteria. They should decide on which basis they will choose the target company, like profitability, location, etc. The acquirer can then use these criteria to find companies to acquire or merge with.
3. Begin Planning
Once the acquirer identifies a few potential target companies, they initiate contact and present an attractive offer. The primary objective of this is to gather additional information and assess the willingness of the target company to engage in a merger or acquisition.
4. Perform Valuation
If the initial discussions are successful, the acquirer will request the target company to provide significant information, such as current financial statements, to comprehensively evaluate the target’s potential as a business and its suitability as an acquisition target. It can help perform valuations and determine the feasibility of the acquisition.
5. Negotiations
Upon creating multiple valuation models of the target company, the acquirer will possess adequate information to formulate a justifiable offer. Following this, the two companies can engage in more in-depth negotiations to finalize the terms of the offer.
6. Due Diligence
After the target company accepts the offer, the acquiring firm conducts a thorough examination called due diligence, which involves a comprehensive analysis of the target company’s financial metrics, assets, liabilities, customers, human resources, and other aspects. Due diligence aims to verify or revise the acquirer’s initial valuation.
7. Contract
If the due diligence process finishes without significant issues or concerns, the next step involves finalizing a contract for sale. At this stage, the parties involved would make a conclusive determination regarding the type of agreement, such as whether it would be an asset purchase or a share purchase.
8. Financing
Although the acquirer may have already explored financing options for the acquisition beforehand, the specific details of the financing plan typically come together after the purchase and sale agreement is signed.
9. Regulatory Approval
The acquiring company obtains regulatory approvals, such as antitrust clearances, necessary to complete the acquisition or merger.
10. Closing
Once they get all necessary approvals and sign the purchase and sale agreement, the deal is considered closed. Following this, the management teams of both the target and acquiring companies collaborate to merge the two firms.
Mergers and Acquisitions Examples
#1 The Merger of Disney and Pixar
The $7.4 billion merger of Disney and Pixar in 2006 allowed Disney to tap into Pixar’s innovative storytelling and animation technology while giving Pixar access to Disney’s marketing and distribution channels. Since the merger, Disney and Pixar have produced blockbuster hits such as Toy Story 3, The Incredibles 2, and Frozen.
#2 The Merger of Heinz and Kraft
In 2015, Heinz and Kraft merged to create the world’s fifth-largest food and beverage company, Kraft Heinz. 3G Capital and Berkshire Hathaway orchestrated the merger.
#3 Acquisition of MGM Studios by Amazon
In March 2022, Amazon acquired MGM Studios, one of the world’s oldest and most iconic film studios, for $8.45 billion. The acquisition gave Amazon access to MGM’s vast library of movies and TV shows, which allowed it to expand its Prime Video streaming service to compete with rivals such as Netflix and Disney+.
#4 Acquisition of Giphy by Facebook
Facebook acquired Giphy for $400 million in May 2020. Giphy was a popular search engine for GIFs. Thus, Facebook took the chance to integrate Giphy’s animated images into its apps like Instagram, Messenger, and WhatsApp.
Types of Mergers and Acquisitions
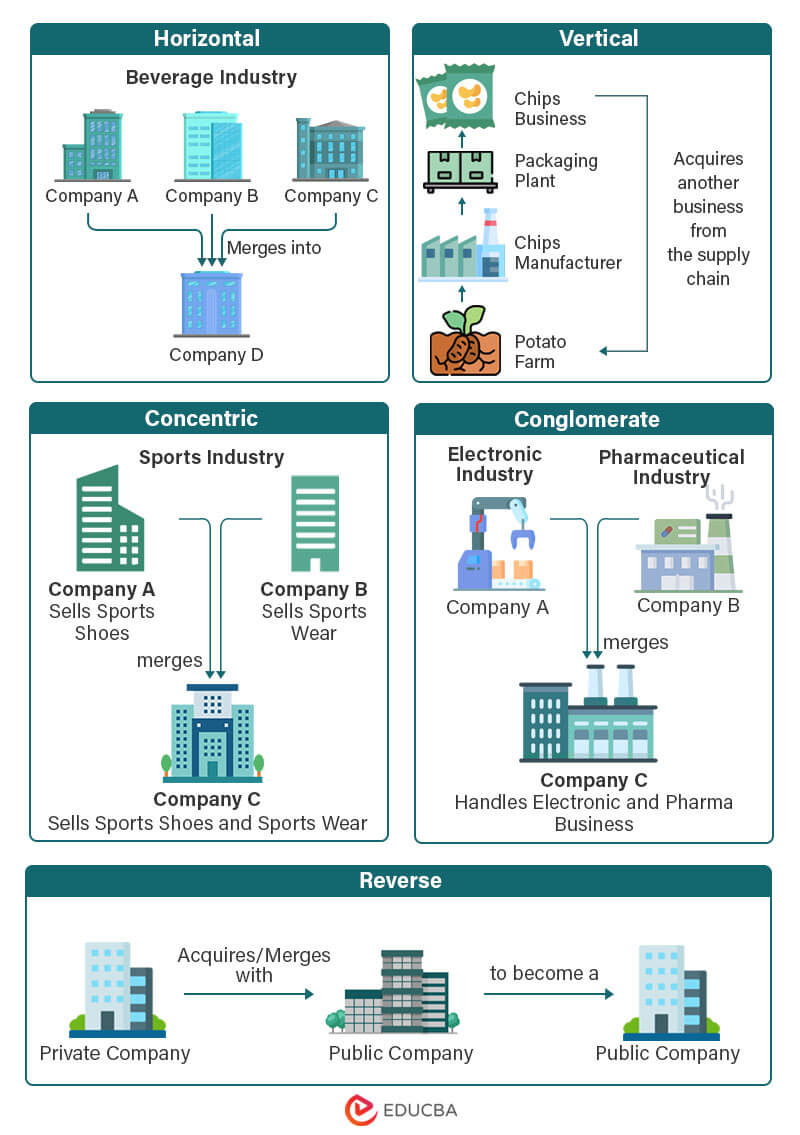
1. Horizontal
- It is when a company acquires or merges with another company operating in the same industry.
- It does not necessarily mean that the two companies are direct competitors.
- Its main advantage is that it allows a company to grow by joining forces with another company in the same industry, leading to more customers and a bigger market share.
2. Vertical
- It is where a company acquires another company that operates in a different position in the supply chain.
- For instance, the buyer may acquire a company that supplies the raw materials or distributes its products to customers.
- The main benefits are the potential to create new revenue streams, lower production costs, and make operations more efficient.
3. Conglomerate
- It is when the acquiring company and the target company are in independent industries or engage in unrelated activities.
- For example, a real estate company acquires an insurance company.
- The main reason for this type of merger/acquisition is diversification, which helps create stability for the company.
- If one product or service is struggling, the hope is that other products or services will perform well and balance out any losses.
4. Concentric
- It is where the acquiring and target companies have different products or services but sell to the same customers.
- It helps the company increase its market share and expand its product lines.
- Expanding its product lineup and gaining market share, enables a business to develop.
5. Reverse
- A reverse merger is a type of acquisition where a private company acquires a publicly traded company, which then becomes a public company through the merger.
- It allows the private company to go public without the lengthy and expensive process of an initial public offering.
Difference Between Mergers and Acquisitions
|
Basis |
Mergers |
Acquisitions |
| Definition | It is when two or more companies combine to form a new, single entity. | It is when one company takes over another company, either through a purchase or a merger. |
| Legal Status | After the merger, the new legal entity is distinct from the pre-existing companies. | After an acquisition, the acquiring company may choose to keep the acquired company as a separate legal entity or merge it with an existing entity. |
| Control | Both merging companies have equally distributed control. | In an acquisition, the acquiring company has control over the acquired company. |
| Purpose | Its strategic or financial motivations include creating economies of scale, expanding into new markets, or diversifying the company’s offerings. | The main motive is to gain access to new markets or technologies quickly. |
| Process | Mergers typically require mutual agreement and approval by both company boards and regulatory approval. | Acquisitions can be one-sided by the acquiring company’s board but may require regulatory approval. |
| Financing | Stock swaps or a combination of cash and stock are commonly used for financing. | Financing can be by cash, stock, debt, or combining these methods. |
| Employee Impact | As a brand-new company is formed, employee retention and reorganization are essential. | Employee layoffs and restructuring may not be necessary if the acquirer keeps both companies separate. |
| Legal Requirements | Mergers are subject to regulatory approval and can take longer to complete. | Acquisitions are also subject to regulatory approval but can complete more quickly in some cases. |
M&A Synergies
Synergies are the benefits that companies can gain from combining their businesses. They are one of the primary drivers behind mergers and acquisitions (M&As). However, realizing them can be challenging, as they require significant integration efforts and changes to the combined company’s operations and culture.
These benefits can come in several forms, including:
1. Cost synergies: The companies can save significant costs due to combining the operations of the two companies.
For example, the merged company can eliminate redundancies of personnel, facilities, or supply chain. Cost synergies can also come from economies of scale, where the merged company can achieve lower costs per unit by producing larger quantities.
2. Revenue synergies: These are revenue increases resulting from combining the two companies’ operations.
For example, the merged company can cross-sell products or services to each other’s customers or leverage each other’s distribution networks to expand into new markets. The merged company can charge higher prices or negotiate better terms with suppliers or customers.
3. Financial synergies: When the two companies combine their financial sources, the merged company can access cheaper financing or improve its credit rating. This way, it can reduce its cost of capital and increase its financial flexibility.
4. Strategic synergies: As the two companies combine their strategic strengths, the new entity can use each other’s technology, patents, or intellectual property and develop new products/services.
Strategic synergies can also come from combining complementary business models or capabilities, such as combining a manufacturing company with a distribution company.
Mergers and Acquisitions Valuation
Here are some standard valuation methods that companies can use to value target firms before proceeding with the merger or acquisition:
1. Comparable company analysis (CCA): It involves comparing the target company to similar companies in the same industry. The acquirer analyzes critical financial metrics such as revenue, EBITDA, and price-to-earnings ratios to determine a valuation multiple. They then apply the multiple to the target company to estimate its value.
2. Discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis: In this method, the acquiring firm estimates the future cash flows the target company may generate and discounts them back to their present value using a discount rate. It is a widespread and popular method in M&A valuation.
3. Leveraged buyout (LBO) analysis: This method involves analyzing the cash flows that the company can generate to service the debt taken on to finance the M&A transaction. This method is more common for private equity transactions.
4. Relative valuation: It is a method of valuing a company based on the value of similar companies in the same industry. It can be more straightforward than other methods but has limitations and should be used with other factors to make investment decisions.
Top 10 Banks Facilitating Mergers and Acquisitions Activities
Here are the top 10 banks that advise and help companies with mergers and acquisitions. We have mentioned their ranking, headquarters, total deal value in 2021, and total deals.
|
Rank |
Bank Name | Headquarters | 2021 M&A Deal Value (USD billions) |
Total Deals 2021 |
|
1 |
JPMorgan Chase & Co. |
US | 1,138.8 | 303 |
|
2 |
Goldman Sachs |
US | 1,032.6 | 262 |
|
3 |
Morgan Stanley |
US |
998.9 |
298 |
|
4 |
Bank of America |
US |
693.6 |
214 |
| 5 | Rothschild | France | 644.3 |
358 |
|
6 |
Credit Suisse |
Switzerland |
635.4 |
296 |
|
7 |
Citigroup |
US |
617.4 |
246 |
|
8 |
Barclays |
UK |
541.8 |
171 |
|
9 |
Evercore |
US |
422.7 |
197 |
| 10 | Lazard | US | 382.2 |
235 |
M&A Jobs
Investment Bankers: They provide advice on mergers, acquisitions, and other strategic transactions. They are responsible for identifying potential M&A targets, conducting due diligence, valuing companies, negotiating deal terms, and raising financing.
Financial Analyst: They perform financial analysis, create financial models, make valuations, and structure deals. They also develop financial projections, analyze financial statements, and assess the impact of potential transactions on a company’s financial performance.
Due Diligence Specialist: They conduct detailed investigations of companies targeted for acquisition. They assess the target’s financial, legal, and operational risks, identify potential issues, and provide deal structure and pricing recommendations.
Corporate Development Officer: They are responsible for identifying and evaluating M&A opportunities for their companies. They work closely with senior management to develop and execute strategic plans, identify potential acquisition targets, and assess the feasibility of proposed transactions.
Integration Manager: They plan and execute the integration of the companies into the new company’s operations. They develop integration plans, coordinate cross-functional teams, and oversee the implementation of integration initiatives.
M&A Consultant: They provide strategic advice and guidance to clients on M&A transactions. They help clients develop and implement M&A strategies, identify potential targets, conduct due diligence, and negotiate deal terms.
M&A Lawyer: Lawyers play a critical role in M&A transactions by providing legal advice and guidance on deal structure, regulatory compliance, and contractual matters. They draft and negotiate legal agreements, conduct due diligence, and advise clients on legal issues.
Mergers and Acquisitions Salary
The salaries for each role in the M&A field differ by location, firm, expertise level, and more. The table below shows the salary range and average salaries for the roles in the US. The data is from Comparably and Payscale:
|
Job Title |
Range |
Average |
| Investment Banker |
$56,000 – $250,000 |
$118,000 |
| Financial Analyst |
$50,000 – $86,000 |
$64,000 |
| Due Diligence Specialist |
$56,000 – $105,000 |
$64,000 |
| Corporate Development Officer |
$70,000 – $93,000 |
$81,000 |
| Integration Manager |
$99,000 – $185,000 |
$110,000 |
| Consultant |
$55,000 – $187,000 |
$121,000 |
| M&A Lawyer |
$28,035 – $245,129 |
$145,000 |
M&A Strategy
- The first and foremost M&A strategy is to practically identify potential target companies and conduct thorough research on their business operations, expected growth, and associated risks.
- After that, performing market research is also a crucial component of the strategy. It helps us understand the market’s growth factors, opportunities, trends, and customer demands.
- In addition to research and market analysis, the companies must also study the plans and strategies, including personal processes, work environment, and information and knowledge collection.
M&A Laws
Antitrust Laws
- Antitrust laws prevent M&A transactions that may lead to anti-competitive practices, such as monopolies, price-fixing, and market domination.
- Parties to M&A transactions must comply with pre-merger notification requirements and obtain approval from antitrust agencies before completing the transaction.
- These laws ensure fair competition in an open market economy. These laws are necessary for consumers to have various choices in the market and would have to pay a higher price for products and services.
- Companies that violate these laws may face significant fines, penalties, and other legal consequences.
Securities Laws
- Securities laws are essential in M&A transactions that involve public companies.
- Public companies must follow these regulations by disclosing all material information to protect investors from fraud, insider trading, and proxy solicitations.
- These laws require companies to provide accurate and timely information to shareholders, such as financial statements, management’s discussion and analysis, and disclosures related to the transaction.
- Violations of securities laws can result in legal action, fines, and penalties.
Tax laws
- Tax laws play a significant role in M&A transactions, as they govern the tax implications of asset transfers, ownership changes, and income recognition.
- Companies involved in M&A must be aware of potential tax liabilities and obligations, including capital gains tax, deductions, and credits.
- Parties can use various strategies to minimize tax liabilities, such as structuring the deal as a stock purchase or asset purchase.
- They can also make tax-free reorganizations and use net operating losses.
Labor laws
- During M&A transactions, companies have to follow specific procedures regarding changes in ownership and personnel.
- Labor laws protect employees’ rights in common labor issues like employee layoffs, severance pay, and benefits.
- Companies must comply with laws regarding worker protection, anti-discrimination, and collective bargaining agreements.
- Failure to follow labor laws can result in legal action and reputational damage.
Types of Financing in M&As
1. Equity Financing: It is when companies raise capital by selling a part of their ownership in the company. In equity financing, businesses issue new shares of stock to fund the merger/acquisition.
2. Debt Financing: It is when the acquiring firm borrows money from lenders to fund the merger/acquisition. Debt financing may include bank loans, bonds, or other types of debt securities.
3. Mezzanine Financing: It is a combination of equity and debt financing. It typically involves issuing debt that can convert into equity later.
4. Private Equity Financing: It involves raising capital from institutional investors to buy and take over companies specifically. Private equity firms typically use a combination of debt and equity financing to fund their acquisitions.
5. Asset-based Financing: It is where businesses use assets, like inventory or accounts receivable, as collateral for a loan. It is to fund the working capital needed to complete an acquisition.
Role of Investment Banking in Mergers and Acquisitions
Investment banks play a crucial role in M&A by providing financial and strategic advice to acquiring and target companies. Here are some of the critical roles that investment banks play in M&A:
Advisory services: Investment banks can advise on potential M&A transactions, including identifying potential targets or merger partners, evaluating the deal, etc.
Negotiation: Investment bankers can help clients negotiate an M&A deal, including the transaction price, payment structure, etc.
Structuring: They can structure deals to maximize value for their clients. It may include identifying the best financing option and any possible tax implications.
Due diligence: Investment banks can help conduct the due diligence on target firms or merger partners by reviewing financial statements, performing market research, and identifying legal or regulatory issues.
Financing: Investment banks can help firms secure debt, equity, or a combination of both the financings for the M&A transaction.
Regulatory approvals: Clients can obtain the necessary regulatory approvals for the M&A transaction with the help of investment banks.
Accounting for M&As
To account for a merger or acquisition, you can follow the following steps:
1. Identify the acquirer and the acquiree: The acquirer is the company that initiates the M&A transaction, and the acquiree is the company being acquired.
2. Determine the purchase price: It is the amount the acquirer pays to acquire the target company. The purchase price is as per the fair value of the acquiree’s assets and liabilities. The transaction may include cash, stock, or other assets.
3. Record the acquisition: The acquirer records the merger/acquisition date and purchase price in their books.
4. Recognize and measure the assets and liabilities of the acquiree: The acquirer must recognize and measure the assets and liabilities of the acquiree at their fair value on the acquisition date. It also involves valuing intangible assets such as goodwill, customer relationships, and patents.
5. Account for transaction costs: Transaction costs, such as investment banks or legal fees, must be accounted for separately from the purchase price and added as an expense.
6. Record goodwill: Goodwill is an intangible asset representing the business’s brand value, reputation, customer base, etc. It is also the excess value after subtracting the value of all tangible assets from the business’s fair market value. The acquirer recognizes it as an asset on their balance sheet.
7. Consolidate the financial statements: The acquirer must consolidate the target company’s financial statements into its own financial statements. It combines the company’s revenues, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
8. Disclose information about the acquisition: Finally, the acquirer must disclose information about the acquisition in its financial statements, including the purchase price, the assets and liabilities acquired, and any significant assumptions or estimates made in valuing the acquiree.
Reasons for Failure of Mergers and Acquisitions (With Examples)
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) transactions can frequently fail for various reasons. Here are some common reasons why M&A deals fail, along with examples:
Culture Clash: When companies with different cultures merge, the employees and management may have distinct values, which can lead to conflict, hindering their productivity and success. In this case, the merger/acquisition can fail.
Example: Daimler-Benz and Chrysler’s merger in 1998 was a failure, partly due to the two companies’ cultural differences. They had an overlap in decision-making, salary structure, management structure, and more.
Overpayment: When a company pays too much to acquire another company or merge with another firm, it can lead to financial difficulties and a lack of profitability.
Example: In 2015, Nokia acquired Alcatel-Lucent for $17 billion, which turned out to be too high a price for the company to pay, resulting in a loss of revenue for Nokia.
Integration Difficulties: Integrating two companies after a merger or acquisition can be complex and challenging. If the integration process is not well-planned and executed, it can result in disruptions to operations and a loss of revenue.
Example: Time Warner and AOL have different business models; thus, their merger in 2001 failed due to the difficulties of integrating the two companies.
Regulatory issues: It is essential for companies looking to merge or acquire to comply with the legal authority and obtain regulatory approval. The deal can stay intact only if the companies get the necessary permissions.
Example: In 2017, the US Department of Justice blocked the proposed merger between AT&T and Time Warner due to antitrust concerns.
Lack of due diligence: Due diligence is a thorough investigation of a company before a merger/acquisition. Thus, if inaccurate, it can result in unexpected problems arising after completing the deal.
Example: In 2015, after four years of acquiring Autonomy, Hewlett-Packard had to take an $8.8 billion write-down due to its poor due diligence process.
Cross-Border Mergers and Acquisitions
Cross-border M&A is the merger or acquisition of businesses that operate in separate nations. Companies wanting to broaden their customer bases, diversify their business models, and get access to new technology and expertise, choose this transaction. However, it also provides certain risks and difficulties.
Worldwide M&A Trends:
- Technology-driven M&A transactions increase as companies seek cutting-edge technology, business strategies, and digital capabilities.
- ESG factors, such as sustainability and ethical business practices, are becoming more critical in M&A deals. Thus, businesses evaluate the target companies’ ESG (environmental, social, and governance) risks and implement sustainability objectives into post-merger integration plans.
- Developing markets are becoming more attractive due to their expansion potential and undiscovered customer niches.
Issues with Cross-Border M&A:
- Regulatory concerns are a significant obstacle, requiring negotiation of the rules and laws of both the home country and the target firm’s nation.
- It can cause delays and increase transaction expenses, legal repercussions, and reputational harm.
- Companies should also thoroughly research the regulatory environment, retain local legal and accounting specialists, and create a complete regulatory compliance strategy to reduce risks.
Cultural and Language Differences in Cross-Border M&A
- Cultural and language differences are significant challenges in cross-border M&A transactions, leading to communication gaps, misunderstandings, and cultural clashes.
- To address these challenges, companies can engage local consultants, create cross-cultural integration teams, and invest in language training and translation services.
- These strategies can facilitate effective collaboration and alignment of values and culture between both companies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Mergers and Acquisitions
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Better Economies of Scale: The new company can place high-quantity bulk orders, i.e., purchase supplies and materials in larger quantities to negotiate easily, leading to cost efficiency to improve its scale. | Job losses: When two companies in the same business merge, there might be internal duplication of roles and departments, leading to layoffs. |
| Better distribution power: A merger or acquisition can lead to the geographic expansion of a company, increasing the company’s ability to distribute goods or services to more people. | Higher prices: When a company has less competition and a larger market share, it can set product prices as they wish. Thus, consumers will have to pay more for products or services. |
| Increased market share: When two firms in the same industry merge or buy another firm in the same industry, the new or more significant firm gains more market share. | Lost opportunities: The time, energy, and money that mergers or acquisitions require could have been beneficial if invested in other options that the company might have to forgo. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is M&A risk?
Answer: M&A risks are a merger or acquisition’s potential negative consequences and uncertainties. These risks can arise from various factors such as financial, legal, regulatory, operational, cultural, and strategic differences. Thus, proper due diligence, risk assessment, and mitigation strategies can help manage M&A risks.
Q2. Who usually loses in a merger?
Answer: Usually, the acquired company is the one who loses the most. Moreover, employees of both companies may face job losses in case of merger and acquisition. However, if the merger/acquisition fails, both parties may lose significantly in finances, goodwill, and more.
Q3. What factors affect mergers?
Answer: Several factors can affect mergers, including if the target and acquiring firm are a perfect fit, strategically and culturally. Their financial performance, operational activities, management conditions, and capital structure can also be significant factors. Moreover, the companies must also look for regulatory issues and other risks and uncertainties.
Q4. Are mergers and acquisitions permanent?
Answer: Yes, usually, mergers and acquisitions are a permanent commitment. However, for some reason, mergers and acquisitions can fail, leading to losses for both companies. A merged entity may be broken up or spun into separate companies for strategic reasons or external pressures such as regulatory requirements. It is known as a demerger or spin-off, and it involves the separation of the merged entity into two or more independent companies.
Recommended Articles
We hope that EDUCBA’s comprehensive article on Mergers and Acquisitions was helpful and informative. For further knowledge, refer to EDUCBA’s recommended articles.