What is HDFS?
The storage system in the Hadoop framework that comprises a collection of open-source software applications to solve various Big Data problems is known as Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). HDFS has a primary name node, and the nodes are organized in the same space as the data center. Data is broken down into smaller units and distributed to different nodes for storage. This primary storage system is in Java language and provides high-performance access to data.
Key Features
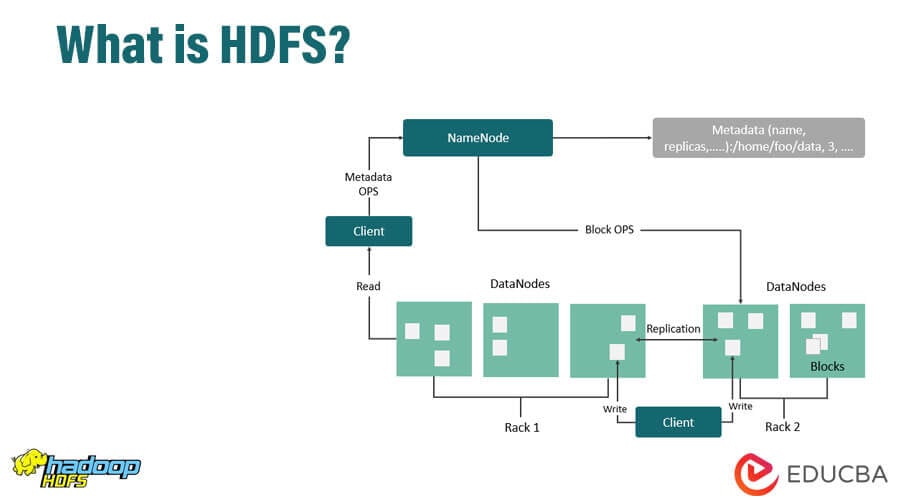
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) comprises several services, including NameNode, DataNode, Job Tracker, Task Tracker, and Secondary NameNode. By default, HDFS replicates data across the cluster three times to ensure data availability in case of node failures. For example, one can store a 100 MB file across three replications, taking up a total of 300 MB with two backup files. NameNode and Job Tracker are the Master Nodes, while DataNode and Task Tracker are the Slave Nodes.
The metadata, which contains information about the file system, directories, and files, is stored on the NameNode. The actual data is stored in blocks on different DataNodes, based on the availability of free space in the cluster. For the system to function, the NameNode must have highly reliable hardware to prevent loss of metadata. The Secondary NameNode serves as a standby node in case of NameNode failure. If a DataNode fails, then the metadata of that DataNode is removed from the NameNode, and the NameNode takes the metadata of the newly allocated DataNode instead.
How does HDFS make work easy?
HDFS allows for data replication among DataNodes, which makes it easy to keep data safe and available in case of node failures. Additionally, it can operate on a cluster of inexpensive hardware, and only one highly reliable NameNode storing metadata is necessary.
What can one do with HDFS?
Using HDFS, one can build a robust system to store massive amounts of data that is easy to retrieve, provides fault tolerance, and scalability. Furthermore, it is easy to add inexpensive hardware and can be easily monitored through one of the slave services. It is the backbone of Hadoop and provides many features to suit the Big Data environment’s needs. With HDFS, it is easy to handle and maintain large clusters and achieve scalability and fault tolerance as well.
Advantages
One of the advantages of HDFS is its cost-effectiveness, allowing organizations to build reliable storage systems with inexpensive hardware. It works seamlessly with MapReduce, which is the processing model of Hadoop. Moreover, it performs efficiently in sequential read and write operations, which are the primary access patterns in MapReduce jobs.
Required Skills
A good understanding of Hadoop Architecture is crucial because HDFS has been designed for the Hadoop Framework. Furthermore, understanding Java programming is also important, as the Hadoop Framework is in Java. Knowledge of the MapReduce model is also beneficial since HDFS works in conjunction with it. Furthermore, practical knowledge of Hive Query Language and database management, coupled with problem-solving and analytical skills in a Big Data environment, are necessary for working with HDFS.
Why use HDFS?
With the ever-increasing volume of data, storing huge amounts of data that can be terabytes in size and having a fault-tolerant system has made HDFS popular for many organizations. HDFS stores files in blocks and provides replication. The unused space in a block can help in storing other data. The NameNode stores the metadata, so it has to be highly reliable. However, the DataNodes storing the actual data are inexpensive hardware. Therefore, due to these two prominent advantages, it is of high recommendation and trust.
The amount of data generated from numerous sources is enormous, making its analysis and storage even more difficult. To address these Big Data problems, Hadoop has become immensely popular, offering two key components: HDFS and MapReduce. As data continues to grow at an exponential rate, the need for technologies like HDFS becomes more critical, as organizations cannot afford to ignore the massive amount of data being produced.
Why do we need HDFS?
The ever-increasing importance of data in organizations has led to a growing need for reliable storage solutions. HDFS provides a distributed file system capable of storing and processing large volumes of data from various sources. As a result, it is a suitable solution for managing the diverse data sets generated by businesses on a daily basis. By adopting HDFS, organizations can benefit from a model that meets their needs for reliability and scalability, ensuring that their data remains accessible and protected.
Who is the right audience for learning HDFS Technologies?
Anyone who deals with the analysis or storage of a large amount of data can find HDFS very helpful. Even those who have used databases before and understand the growing need in the market for a robust system can benefit from learning about the new approach to managing Big Data.
How will this technology help in career growth?
The adoption of Big Data technologies by organizations for storing and analyzing data has created career growth opportunities for individuals skilled in these technologies, such as Hadoop. Working with Hadoop’s reliable models, like HDFS, can provide outstanding career opportunities in data management and analysis.
Conclusion
HDFS has become a popular choice among some of the largest companies due to its fault-tolerant architecture and cost-effectiveness. With the continuous growth of data, the need for efficient storage solutions has become increasingly important for organizations that rely on data and its analysis. HDFS provides a reliable platform for data storage, ensuring the prevention of data loss in case of any disruptions.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further related articles: