Updated March 20, 2023
Introduction to TypeScript Operators
Every language has some operators. You may be known the operators in other programming languages. Operators are the ones with whom we can perform some operations something similar to arithmetic addition subtraction etc.ing to use that functionality. Of course, it is very helpful. We can say that there are some functions that are predefined by the language. In this topic, we are going to learn about different typeScript operators.
Different Operators in TypeScript
We all know that Typescript is a superset of JavaScript. In the end, whatever code in Javascript is going to compile in JavaScript only. Let’s see the operators one by one.
1. Assignment Operators
The assignment operator (=) is equal to sign in arithmetic. We can concat this operator with other operators. This Assignment operator assigns a value from left to right.
Example:
a =10;
Here in the above example, we are assigning 10 value to the variable a. Same as in algebra. The following are some combinations of assignment operators with arithmetic operators. Suppose we have x and y
x =10 and y=20
x+=y => this gives the addition of x and y
this is the shorthand syntax of x = x + y.
you can,
console.log(x);
do it for all four subtraction, multiplication, and division.
x – = y; // x = x-y
x * = y; // x = x*y
x / = y; //x = x/y
Do practice it, because shorthand syntax for assignment is a bit confusing for many programmers.
2. Arithmetic Operators
- Now, this comes to an important one. We know arithmetic operators from school. The first thing in math we introduced and that is arithmetic operators.
- These operators are + (plus),-(minus),* (multiplication),/ (division)
- In the below example, we simply applying methods to work the functionality the same as algebra.
- We have two variables with some value and with the help of arithmetic operators we are performing different tasks.
Example:
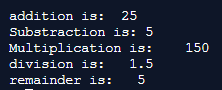
let a:number = 15;
let b:number = 10;
let result:number = 0;
result = a + b
console.log("addition is: "+result);
result = a - b;
console.log("Substraction is: "+result);
result = a*b
console.log("Multiplication is:"+result);
result = a/b
console.log("division is:"+result);
result = a%b
console.log("remainder is:"+result);Output:
3. Logical Operators
- Logical operators works as the name suggest those are logical in nature. These are more useful in conditional statements like if..else.
- Logical operators are && (and) ,||(or), ! (NOT).
- If we are familiar with the truth tables then the working of these operators will be so easy. If not don’t worry we will see it.
- Just remember with the AND operator if both the condition are true then only final output will be true.
- With OR ( || ) operator if any one of the conditions out of two is true then the output will be true.
- NOT operator is the simplest one. It will give the opposite value. If its true then it will make it false.
Example:
let a:number = 100;
let b:number = 450;
var result:boolean = ((a>10)&&(b>50));
console.log("The result of Logical AND is: ",+result);
var result:boolean = ((a>10)||(b>300));
console.log("The result of Logical OR is: ",+result);
var result:boolean=!((a>10)&&(b>100));
console.log("The result of Logical NOT is : ",+result);Output:
4. Relational Operators
These operators always provide Boolean vale like true and false. Relational operators are >(Greater than), <(Less than), >= (Greater than or equal to) ,<=( Lesser than or equal to), ==( Equality), != (Not equal) etc.
Example:
let a:number = 5;
let b:number = 9;
console.log("Value ofa: "+a);
console.log("Value of b :"+b);
let result =a>b
console.log("a greater than b: "+result)
result =a>=b
console.log("a greater than or equal to b: "+result)
result =a==b
console.log("a is equal to b: "+result)
result =a!=b
console.log("num1 is not equal to b: "+result)
result =a<=b
console.log("a lesser than or equal to b: "+result)
result =a<b
console.log("a lesser than b: "+result)Output:
5. Bitwise Operators
This is the operators works on each bit. We have bitwise AND (&), or (|),XOR( ^ ), NOT( ~ ), << Left Shift (<<), Right Shift( >> ), Right shift with Zero(>>>).
Example:
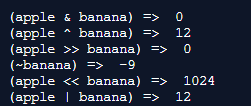
let apple:number = 4;
let banana:number = 8;
let value;
value = (apple & banana);
console.log("(apple & banana) => ",value)
value = (apple ^ banana);
console.log("(apple ^ banana) => ",value);
value = (apple >> banana);
console.log("(apple >> banana) => ",value);
value = (~banana);
console.log("(~banana) => ",value);
value = (apple << banana);
console.log("(apple << banana) => ",value);
value = (apple | banana);
console.log("(apple | banana) => ",value)Output:
6. String Operator
This operator is also known as concatenation. This is defined by a plus (+) sign.
Example:
let greet:string = "Welcome"+"Bob"
console.log(greet);Output:
In the above example, we are concatenating two values with the help of a plus operator. We can combine string types in this way.
7. Type Operator
This is very helpful in typescript because it shows the type of the given operand.
Example:
let num = 12
console.log(typeof num);Output:
As per the value assigned to the particular variable type of operator shows the result. If t value is a string then it will show string as a type of it.
8. Ternary / Conditional Operator
If you are familiar with the if.. else statement in programming then you will get an idea about this quickly. It works the same as for conditional statements in programming.
This has three goals first is condition. second is expression if the condition is true. And the third one again is the expression if a condition is false.
Example:
let toffies:number = 7
let count = toffies > 5 ?"TOffies are enough":"Need to buy more toffies"
console.log(count)Output:
Look at the above example carefully. When you try it yourself, you’ll get to know an idea.
Conclusion
To understand operators in any programming language fully you need to practice these operators with different examples. Once you cover it in one language applies to all. So one basic section in programming id=s gets covered already. So try to get it done in the initial phase of learning any programming language.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the TypeScript Operators. Here we discuss the introduction and various operators in typescript which includes, assignment, arithmetic, logical, relational operators, etc. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –