Updated March 27, 2023
Overview of SQL Full Join
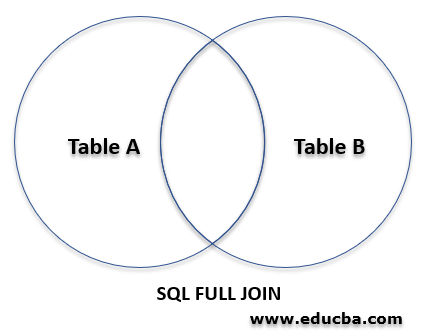
A SQL FULL join is a structured query language (SQL) statement in which when two tables are joined together, the statement returns all the rows from the joined tables even if all the rows do not meet the specified conditions, however, the non-matched rows in any of the tables are displayed as NULL, that is a FULL JOIN can be considered something similar to a combination of LEFT AND RIGHT JOINS in SQL.
Syntax:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name1
FULL JOIN table_name2
ON table_name1.column_name = table_name2.column_name
WHERE condition;</codeParameters:
The different parameters used in the syntax are :
- SELECT column_name(s): It is used to select the required data from the database. Here, column_name(s) is the name of the columns from the joined tables.
- FROM table_name1 FULL JOIN table_name2: It is used to specify the source from which data has to be fetched. Here, table_name1 is the name of the left table and table_name2 is the name of the right table. FULL JOIN will fetch all records when there is a match in the left or right table records.
- ON table_name1.column_name = table_name2.column_name: It is used to specify the common conditions on which the two tables will be joined. It can be a pair of primary and foreign keys.
- WHERE condition: It is used to specify any other conditions that the records should satisfy to make to the resultant records.
Of the above-mentioned parameters, all the parameters except the WHERE clause are mandatory. You may use GROUP BY, ORDER BY and HAVING clauses based on your requirement.
How does SQL Full Join work?
A SQL FULL join is typically used in visualizing exception reports or ETL or any other peculiar situations where both sides have data you are trying to combine.
The following Venn diagram explains how a SQL full join works.
Going ahead we will be discussing the above-mentioned self join in great detail.
In order to demonstrate and explain the FULL join in SQL effectively, we will be using the following tables. These tables are made for an e-commerce website. The first table “customers ”contains customer id, names, city to which they belong. The second table “cities” contains the id, city, and country to which they belong.
The schema for the above mentioned “customers” table is:
Number of records: 15
| Customers |
| ID(primary key) |
| Customer |
| City |
Let’s have a look at the records in the customer’s table. So that later, we can understand how self-join is helpful:
| ID | Customer | City | Items_purchased | Amount_paid |
| 1 | Peter King | Manchester | Books | 120 |
| 2 | Priya Krishna | New Delhi | pen | 50 |
| 3 | Jim Halpert | Manchester | pencil | 43 |
| 4 | Michael Scott | New York | Books | 250 |
| 5 | Harvey Spector | Birmingham | pencil | 100 |
| 6 | Deepa Kamat | Mumbai | Books | 370 |
| 7 | Anita Desai | London | pencil | 50 |
| 8 | Rachel Zane | Michigan | pen | 70 |
| 9 | Pretoria John | Canberra | pen | 190 |
| 10 | John L | Budapest | Books | 540 |
| 11 | Justin Green | Ottawa City | pen | 65 |
| 12 | Babita Ghosh | Kolkata | pencil | 75 |
| 13 | Krish Pratt | London | eraser | 30 |
| 14 | Elizabeth Blunt | London | pencil | 340 |
| 15 | Nina Debrov | Amsterdam | Books | 452 |
The schema for “cities” table is:
Number of Records: 10
| Customers |
| ID(primary key) |
| city_name |
| country |
Let’s have a look at the records in the cities table.
| ID |
City_Name |
Country |
| 1 |
New Delhi |
India |
| 2 |
Mumbai |
India |
|
3 |
Kolkata |
India |
|
4 |
London |
England |
| 5 |
Manchester |
England |
|
6 |
Ottawa City |
Canada |
| 7 |
Ontario |
Canada |
|
8 |
Pune |
India |
Examples to Implement SQL Full Join
Some of the examples are given below:
Example #1
Find the names of customers whose resident cities are not present in the cities table.
Code:
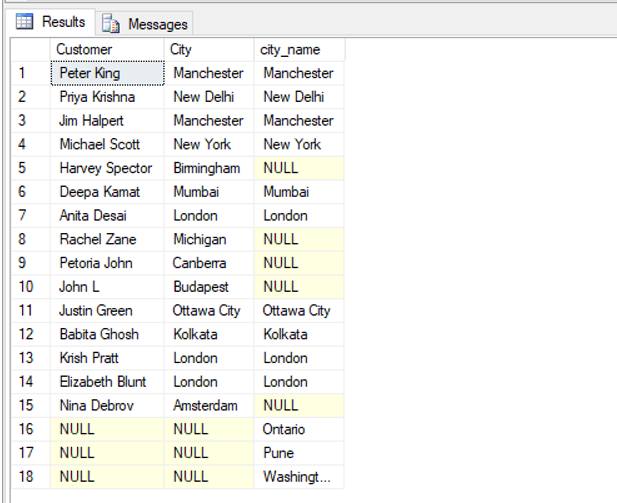
SELECT t1.Customer, t1.City, t2.city_name
FROM customers as t1 FULL JOIN cities as t2
ON t1.City = t2.city_name;Output:
In the above example, we can notice that cities like Birmingham, Michigan, Canberra, Budapest, and Amsterdam are not present in the cities table but they are still shown on FULL join with NULL values. Similarly, cities like Ontario, Pune and Washington D.C are not present in customers but were present in the cities table are also displayed with NULL values for not matching records.
Example #2
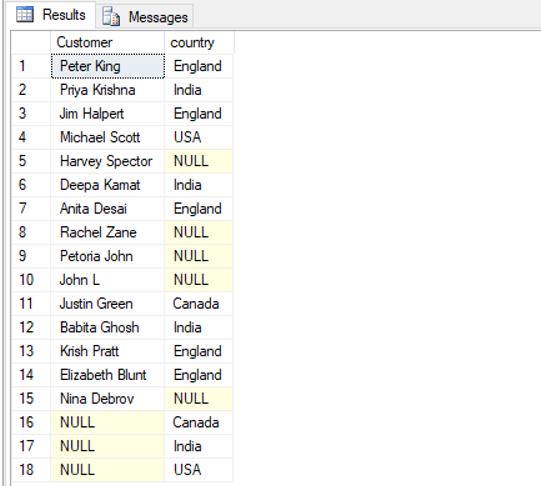
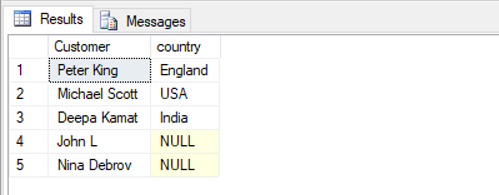
Find the names of customers along with the country to which they belong.
Code:
SELECT t1.Customer, t2.country
FROM customers as t1 FULL JOIN cities as t2
ON t1.City = t2.city_name;Output:
Example #3
Find the names of customers who purchased items in the books category, along with the country to which they belong.
Code:
SELECT t1.Customer, t2.country
FROM customers as t1 FULL JOIN cities as t2
ON t1.City = t2.city_name
WHERE Items_purchased = 'Books';Output:
Example #4
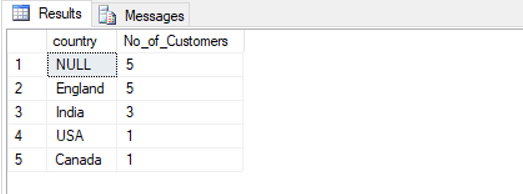
Find the number of customers per country ordered in descending order.
Code:
SELECT t2.country, count(t1.Customer) as No_of_Customers
FROM customers as t1 FULL JOIN cities as t2
ON t1.City = t2.city_name
GROUP BY t2.country
ORDER BY 2 DESC;Output:
Example #5
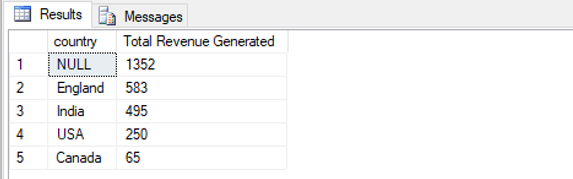
Find the total revenue generated by the e-commerce company across different countries ordered from highest to lowest.
Code:
SELECT t2.country, sum(t1.Amount_paid ) as "Total Revenue Generated"
FROM customers as t1 FULL JOIN cities as t2
ON t1.City = t2.city_name
GROUP BY t2.country
ORDER BY 2 DESC;Output:
Example #6
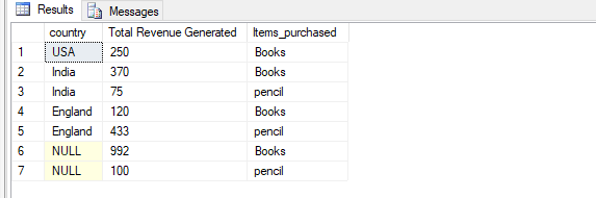
Find the total revenue generated by the e-commerce company in the Books and pencils category across different countries ordered from highest to lowest.
Code:
SELECT t2.country, sum(t1.Amount_paid ) as "Total Revenue Generated", t1.Items_purchased
FROM customers as t1 FULL JOIN cities as t2
ON t1.City = t2.city_name
WHERE t1.Items_purchased = 'Books' OR t1.Items_purchased = 'pencil'
GROUP BY t2.country, t1.Items_purchased
ORDER BY 1 DESC;Output:
When performing joins in SQL, we should always try to use table aliases which are abbreviations of the given tables. This helps in writing beautiful pieces of code.
Conclusion
SQL full join is a statement that returns all the records from both the joined tables. We should use it when we want to check for missing information in the database.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Full Join” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.