Updated May 10, 2023
Introduction to MySQL MIN() Function
MySQL MIN() function is an SQL query that returns the minimum value from a set of values recorded in a database table. Usually, MIN() is an aggregate function that can be used to calculate over a range of values returned by the SELECT query statement to find the minimum record from those separated rows in the table. MIN() function receives a conditional expression that can be a column name or valid term involving columns. The function returns a NULL value if no condition matches. Suppose we can use this function to find out the least population of a city from a list of cities.
Syntax with Explanation:
MIN ( [DISTINCT] Expression)The term ‘Expression’ requires a numeric value that can either be a field in a table or a formula. This keyword allows for removing the duplicate values from the list of records in the database table. But almost it will be the same result without distinct keywords, too; it has not much effect on MIN () like on other SUM (), COUNT (), or AVG () aggregate functions.
Also,
MIN([DISTINCT] expression) [over_clause]The over_clause is not compulsory but can be associated with window tasks. So, over_clause is used only if we don’t add the DISTINCT keyword in the MIN() function.
How Does MIN() Function Work in MySQL?
As we know that MIN() function is used to find the minimum value from the total rows selected by the select statement, we can now easily get the benefits in our business or product management. For example, it will allow getting the low-selling product of your company, a less expensive item, or a minimum quantity of the product in your store consumed by the customers.
We can apply this SQL query in our Databases which returns the result. MySQL MIN() SQL statement is shown below:
SELECT MIN ([Column_Name]) FROM [Source]A database table as a source can return the minimum value present in the specified column by using the MIN() function.
Examples to Implement MIN() in MySQL
Given below are the examples of MIN() in MySQL:
Example #1 – Get minimum value in a column
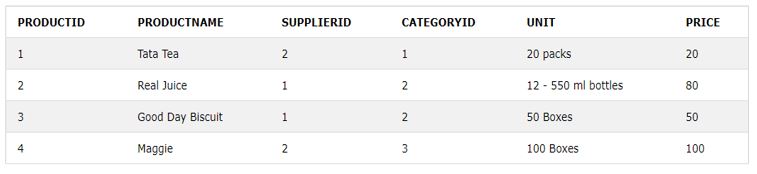
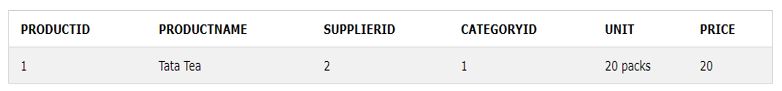
Let us take the below-shown screenshot of records from a table of Products.
After inspection of all product prices, we applied the MIN() to get the product whose price is lower than others.
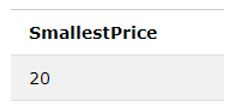
SELECT MIN(Price) AS SmallestPrice FROM Products;Output:
Example #2 – With WHERE clause
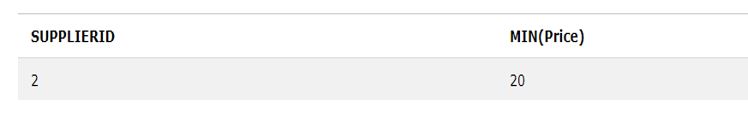
Here we use MIN() to return the smallest value from a particular condition using the WHERE keyword with the SELECT statement.
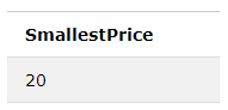
SELECT MIN(Price) AS SmallestPrice FROM Products WHERE SupplierID=2;Output:
We have the smallest value for the only price whose SupplierID is two from the Products table. We can also use any multi-word alias (like SmallestPrice) to define the lowest value, as in the above query.
Example #3 – Sub-query statement
To provide not only the minimum price from the products table but also to show the row information, including other fields, we have used MIN() in a subquery form as follows:
SELECT * From Products WHERE Price = (SELECT MIN(Price) AS SmallestPrice FROM Products);Output:
The inner query returns the lowest price, and the outer query provides the row information of the lowest price field in the products table.
Example #4 – With GROUP BY Clause
This function with the GROUP BY clause helps find the minimum value for every group based on the criteria.
SELECT SupplierID , MIN(Price) FROM Products GROUP BY SupplierID;Output:
SupplierID groups the product fields from the Products table, but the minimum prices are arranged randomly, not ascending or descending.
Example #5 – With ORDER BY clause
This function with the ORDER BY clause helps to specify the column with which we can order by the minimum value for every group based on the criteria.
SELECT SupplierID , MIN(Price) FROM Products
GROUP BY SupplierID
ORDER BY MIN(price);Output:
Now, the fields are grouped by SupplierID, and the result set is ordered based on MIN(Price) in ascending order, where the first small minimum value is set first and the next greater minimum at last.
Example #6 – With HAVING clause
We use the HAVING clause with MIN() function to filter these groups based on a certain condition.
SELECT SupplierID , MIN(Price) FROM Products
GROUP BY SupplierID
HAVING MIN(Price) <50
ORDER BY MIN(price);Output:
In the above query, firstly, we have used MIN() to get the lowest price from a group of Products with GROUP BY clause association, and again, based on the HAVING clause, we have applied the MIN function to get the lowest prices which are less than 50 in the table.
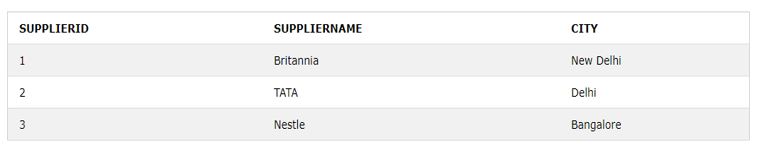
Next, suppose we want names of suppliers instead of supplier ids; then, we can even use the JOIN clause with the above query. We need to apply INNER JOIN for both the tables, Products, and Suppliers.
The example uses the Suppliers table data for supplier ID 1, 2, and 3.
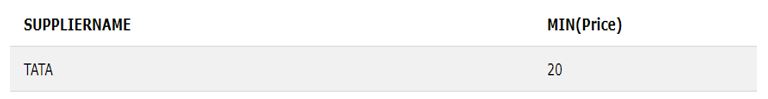
Now the SQL statement for this is as follows:
SELECT SupplierName, MIN(Price) FROM Products
INNER JOIN Suppliers
USING (SupplierID)
GROUP BY SupplierName
HAVING MIN(Price) <50
ORDER BY MIN(price);Output:
Example #7 – Find the Minimum Character Length
With MIN(), we can find the minimum value from numeric data in the column field and implement it in other areas. We can combine MySQL MIN() function with other functions like CHAR_LENGTH.
For example, taking the same Products table, we can write the following query and find the minimum number of characters in the ProductName column:
SELECT MIN(CHAR_LENGTH(ProductName)) AS 'Min Char Length'
FROM Products;Output:
Conclusion
So, MIN() function helps deal with many cases, such as getting the lowest number, the cheapest item, the least expensive product, the lowest credit limit, and the smallest payment from consumers. Hence, in this article, you all might have discovered some important usages of the MIN() function in MySQL with syntaxes and examples that will help you to treat the functional queries related to databases and tables with the areas of business or any industry with massive data stored.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MIN() in MySQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.