Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to SQL Clauses
MySQL queries are SQL functions that help us to access a particular set of records from a database table. We can request any information or data from the database using the clauses or, let’s say, SQL statements. For example, SQL Clauses receives a conditional expression that can be a column name or valid term involving columns where this supports the MySQL functions to calculate the result values for a table in the database.
There are generally five kinds of SQL Clauses in MySQL Server. They are listed as follows:
- WHERE Clause
- ORDER BY clause
- HAVING Clause
- TOP Clause
- GROUP BY Clause
List of SQL Clauses
Various SQL clauses are given below to execute the statement:
1. SQL WHERE Clause
In MySQL, we use the SQL SELECT statement to select data from a table in the database. Here, the WHERE clause allows filtering certain records that exactly match a specified condition. Thus, it helps us to fetch only the necessary data from the database that satisfies the given expressional conditions. The WHERE clause is used with SELECT statement as well as with UPDATE, DELETE type statements and aggregate functions to restrict the no. of records to be retrieved by the table. We can also use logical or comparison operators such as LIKE,<,>,=, etc. with WHERE clause to fulfill certain conditions.
Query:
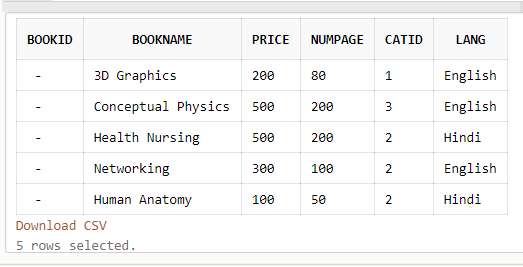
SELECT Column1,….ColumnN From Table_name WHERE [condition];For example, we are considering a table named Books as the demo:
The query to get records from this table:
Query:
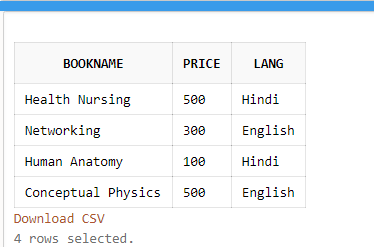
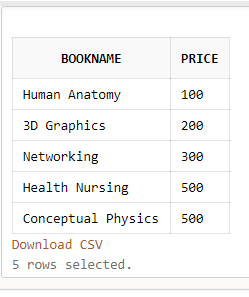
SELECT BookName, Price, Lang From Books WHERE CatID >1;Output:
In the above example, we have fetched the rows from a table using WHERE clause where CatID is greater than 1.
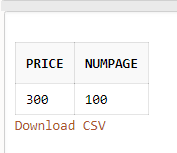
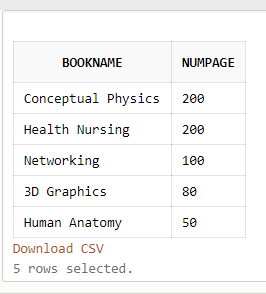
Query:
SELECT Price, NumPage From Books WHERE BookName='Networking';Output:
2. SQL ORDER BY Clause
The ORDER BY clause is used in SQL for sorting records. It is used to arrange the result set either in ascending or descending order. When we query using SELECT statement the result is not in an ordered form. Hence, the result rows can be sorted when we combine the SELECT statement with the ORDER BY clause.
Query:
SELECT column1, …,columnN FROM TableName ORDER BY column1,...,column ASC|DESC;We add ASC for ascending and DSC for descending with the column name in the query to display the result rows in an ordered form.
Query:
SELECT BookName, Price From Books ORDER BY Price ASC;Output:
The result table is retrieved with columns that are sorted in ascending order and the below table is returned in descending.
SELECT BookName, NumPage From Books ORDER BY NumPage DESC;Output:
3. SQL GROUP BY Clause
The GROUP BY clause is used to group rows that have the same values in the result set. Like if we find the names of books from the table grouped by CatID.
Query:
SELECT Column FROM Table WHERE condition GROUP BY Column [ORDER BY Column];This clause is generally used with aggregate functions that allow grouping the query result rows by multiple columns. The aggregate functions are COUNT, MAX, MIN, SUM, AVG, etc.
We have the following example:
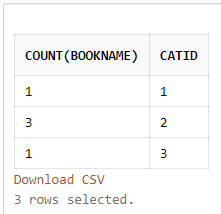
SELECT COUNT(BookName), CatID From Books GROUP BY CatID;Output:
The SQL GROUP BY clause returns the aggregated value applying the functions on the columns of the table. The above screenshot shows that the result is returned grouped by CatID where no. of BookName present in those CatID is fetched.
4. SQL HAVING Clause
Actually, this clause is introduced to apply functions in the query with the WHERE clause. In SQL, the HAVING clause was added because the WHERE clause could not be applied with aggregate functions.
Query:
SELECT Column FROM Table WHERE condition GROUP BY Column HAVING condition [ORDER BY Column];We can also use the HAVING clause with logical operators such as OR and AND.
Let us consider the SQL statement below to learn the clause:
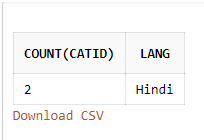
SELECT COUNT (CatID), Lang From Books GROUP BY Lang HAVING COUNT(CATID) <3;Output:
Here the result table is returned where the columns are grouped by Lang and no. of rows is restricted by the HAVING clause by providing a condition that CatID should be less than 3.
5. SQL TOP Clause
The TOP clause is used to determine the number of record rows to be shown in the result. This TOP clause is used with SELECT statement specially implemented on large tables with many records. But the clause is not supported in many database systems, like MySQL supports the LIMIT clause to select limited no. of rows and in Oracle ROWNUM is used.
For SQL Server / MS Access Query:
SELECT TOP no|percentage ColumName(s) FROM TableName WHERE condition;MySQL Query:
SELECT ColumnName(s) FROM TableName WHERE condition LIMIT no;Oracle Query:
SELECT ColumnName(s) FROM TableName WHERE ROWNUM <= no;For example, we can explain this clause by these SQL statements where we can return the rows using TOP Clause with SELECT and WHERE for different database platforms:
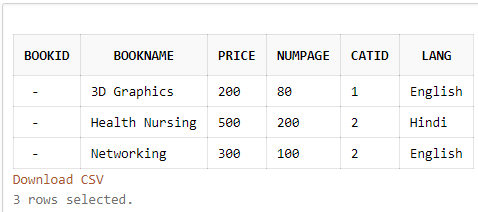
SELECT TOP 3 * FROM Books;
SELECT * FROM Books LIMIT 3;
SELECT * FROM Books WHERE ROWNUM <= 3;Output:
Conclusion
These SQL Clauses support in many ways for MySQL database access and data extraction by applying any filter which describes the conditions and if the conditions qualify for satisfying it then we get the particular result rows. Here, the information from a table that does not satisfy the conditions is not used. We have to deal with many big database that is used today in many fields like in Ecommerce shopping, Banking sector, Management, Education and other digital fields where a large number of information are stored and need to be retrieved time to time. So, by SQL statements, functions, operators and keywords in combination to SQL clauses makes the info access proper and manageable to deal with different tables in a database.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Clauses” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.