Updated July 5, 2023
Introduction to SQL Outer Join
In SQL, outer join refers to the fact that contents that are common to both the tables along with those which are uncommon are extracted as the final output. Such a join between two or more tables facilitating data extraction in such a fashion is referred to as an outer join.
Types of Outer Join
In SQL, we have three types of outer joins.
These are:
- Left Outer Join,
- Right Outer Join
- Full Outer Join.
Full Outer Join works like a set in mathematics. The following section throws more light on the concept of SQL outer join.
Syntax
The syntax of a left outer join, right outer join, and full outer join are as follows.
1. Left outer join
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column_a, table1.column_b…., table2.column_a, table2.column_b,….
FROM
table1 LEFT JOIN table2
ON
table1.common_field = table2.common_field2. Right outer join
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column_a, table1.column_b…., table2.column_a, table2.column_b,….
FROM
Table1 RIGHT JOIN table2
ON
table1.common_field = table2.common_field3. Full Outer Join
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column_a, table1.column_b…., table2.column_a, table2.column_b,….
FROM
table1 LEFT JOIN table2
ON
table1.common_field = table2.common_field
UNION
SELECT table1.column_a, table1.column_b…., table2.column_a, table2.column_b,….
FROM
Table1 RIGHT JOIN table2
ON
table1.common_field = table2.common_fieldHow SQL Outer Join Work?
To understand the working of outer joins, we must first understand what table is specified at what position. Like in the left outer join, the output is determined by the position of the table on the left-hand side, and in the case of a right outer join, the output is determined by the position of the table on the right-hand side.
‘Let’s go through the following examples to understand how exactly the joins work.
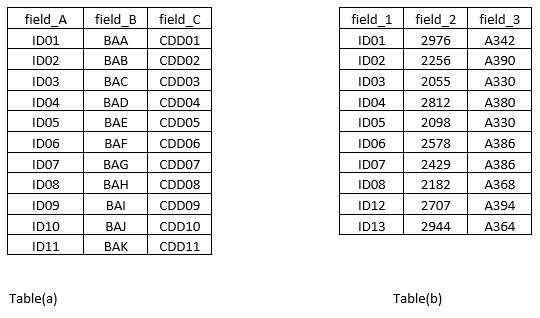
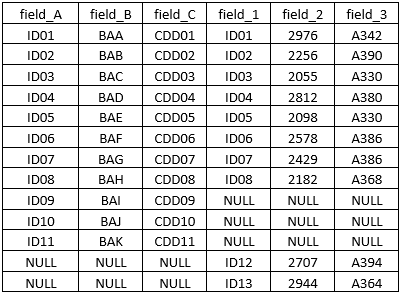
As shown below, we have two tables, table (a) and table (b).
Let’s have a look at both these tables:
Here, one field is common in the two tables. It is named as field_A in the first table, while it has been named as field_1 in the second table. Using the above two tables, we will demonstrate the working of the left, right, and full outer joins.
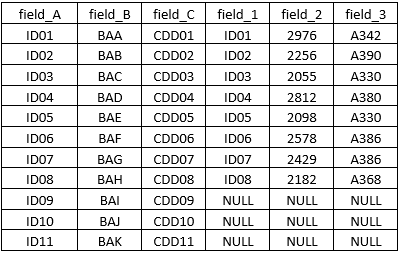
Let’s see what output we get when we perform the left outer join over the common field. When the left outer join is applied over the two tables, keeping table (a) as the left table, all the contents from the left table are returned along with only those contents from the right table present in both tables. So, the left table gets precedence. The output table would look like as shown below.
We can see that we have a NULL value for certain entries. This is because those particular IDs are not present in table (b).
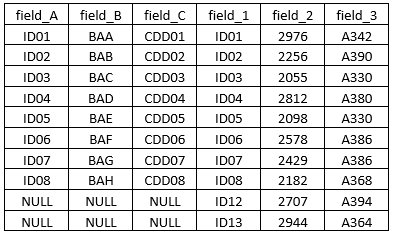
Let’s see what happens when we perform the right outer join. In this case, the right table gets the precedence. The output table would look as follows.
In the case of a full outer join, contents from both tables are brought together. The output table would look as follows.
Examples of SQL Outer Join
We’ll now implement outer joins in SQL. For the illustrations, we use two tables: employees and salaries. emp_no is the common field in the two tables. Let’s implement the joins and see the query’s output in each situation.
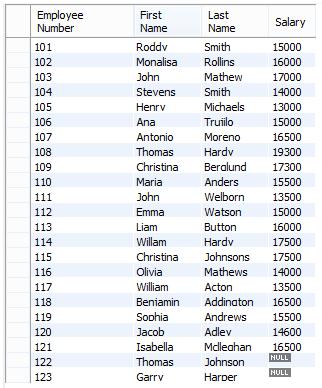
1. Left Outer Join
Code:
select e.emp_no 'Employee Number', e.first_name 'First Name', e.last_name 'Last Name', s.salary 'Salary'
from employees e
LEFT JOIN salaries s
on
e.emp_no = s.emp_noOutput:
We got NULL in the Salary column, as salaries for those employees might have still not been updated in the salaries table.
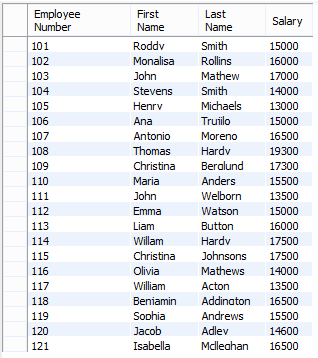
2. Right Outer Join
Code:
select e.emp_no 'Employee Number', e.first_name 'First Name', e.last_name 'Last Name', s.salary 'Salary'
from employees e
RIGHT JOIN salaries s
on
e.emp_no = s.emp_no;Output:
Observe carefully the difference between the two outputs. It will give an idea as to how the left and right outer join work.
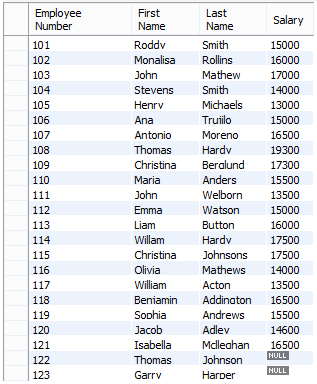
3. Full Outer Join
Code:
select e.emp_no 'Employee Number', e.first_name 'First Name', e.last_name 'Last Name', s.salary 'Salary'
from employees e
LEFT JOIN salaries s
on
e.emp_no = s.emp_no
UNION
select e.emp_no 'Employee Number', e.first_name 'First Name', e.last_name 'Last Name', s.salary 'Salary'
from employees e
RIGHT JOIN salaries s
on
e.emp_no = s.emp_no;Output:
Conclusion
Join is a very useful concept in SQL. The concept allows regulation of data extraction from multiple tables as required. The concept’s usefulness is quite evident in situations involving the vast number of records from which particular records must be extracted.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Outer Join” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.