Updated October 18, 2023
Introduction to SQL DELETE ROW
The SQL DELETE statement is a powerful command to remove one or more rows from a database table. It allows you to selectively delete specific rows based on certain conditions or all rows in a table. Deleting rows is a fundamental operation in SQL, as it helps manage and maintain a database’s data integrity.
Removing a row using the DELETE statement permanently erases the data from the table and makes it difficult to retrieve. Therefore, it is crucial to exercise caution and ensure that you have a clear understanding of the delete operation you want to perform.
Deleting rows can be useful in various scenarios, such as removing outdated or irrelevant data, correcting errors, or removing duplicate entries from a table. Understanding the syntax and proper usage of the DELETE statement is essential to ensure accurate and efficient deletion of rows while preserving the integrity of the database.
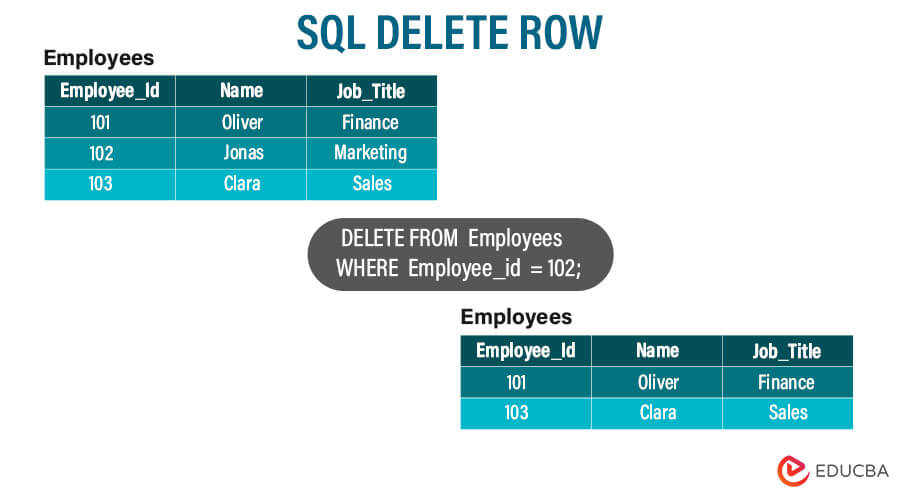
Table of Content
Syntax of SQL DELETE Statement
The syntax of the SQL DELETE statement is as follows:
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;Parameters
Let’s break down the different components of the syntax:
- DELETE FROM: This clause indicates that you want to delete rows from a specific table.
- table_name: Specifies the name of the table from which you want to delete rows.
- WHERE: An optional clause that allows you to specify conditions to determine which rows should be deleted. All rows in the table will be deleted if the WHERE Clause is omitted.
- Condition: This is the condition that determines which rows will be deleted. It can consist of one or more expressions using logical operators such as equals (=), not equals (!=), greater than (>), less than (<), etc. The condition is evaluated for each row; if it evaluates to true, the row will be deleted.
Key Takeaways
- A table in a database can have one or more rows removed using the DELETE statement.
- The WHERE clause allows you to employ a variety of conditions, including equality, comparison operators, logical operators (AND, OR), and functions.
- The DELETE statement permanently deletes data from the table, so use caution. Before executing the DELETE statement, ensure you have a backup or have checked the condition.
- Use the DROP TABLE statement to remove a table in its entirety. This command deletes the table from the database and all related data and structures.
How to DELETE ROW in SQL?
Having discussed the syntax and parameters used in the DELETE statement, let’s go ahead and try some examples to delete rows in SQL.
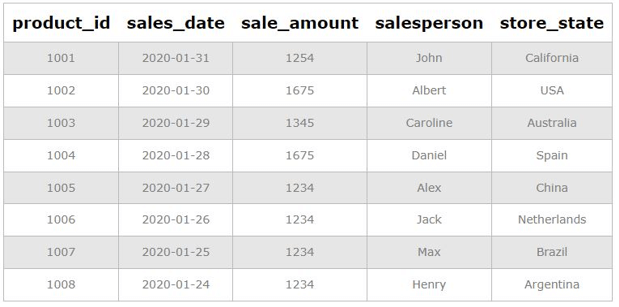
To understand the examples, consider the following table called “daily_sales”. This table contains details such as product_id, the salesperson who sold them, date of sale, amount, etc.
Code:
Let us create a table named daily_sales using the following create table statements and insert some values in it using insert statement.
CREATE TABLE daily_sales(product_id int, sales_date int, sale_amount int, salesperson varchar(100), store_state varchar(100));
INSERT INTO daily_sales(product_id, sales_date, sale_amount, salesperson, store_state)
VALUES ('1001', '2020-01-31', '1254', 'John', 'California');
INSERT INTO daily_sales(product_id, sales_date, sale_amount, salesperson, store_state)
VALUES ('1002', '2020-01-30', '1675', 'Albert', 'USA');
INSERT INTO daily_sales(product_id, sales_date, sale_amount, salesperson, store_state)
VALUES ('1003', '2020-01-29', '1345', 'Caroline', 'Australia');
INSERT INTO daily_sales(product_id, sales_date, sale_amount, salesperson, store_state)
VALUES ('1004', '2020-01-28', '1675', 'Daniel', 'Spain');
INSERT INTO daily_sales(product_id, sales_date, sale_amount, salesperson, store_state)
VALUES ('1005', '2020-01-27', '1234', 'Alex', 'China');
INSERT INTO daily_sales(product_id, sales_date, sale_amount, salesperson, store_state)
VALUES ('1006', '2020-01-26', '1234', 'Jack', 'Netherlands');
INSERT INTO daily_sales(product_id, sales_date, sale_amount, salesperson, store_state)
VALUES ('1007', '2020-01-25', '1234', 'Max', 'Brazil');
INSERT INTO daily_sales(product_id, sales_date, sale_amount, salesperson, store_state)
VALUES ('1008', '2020-01-24', '1234', 'Henry', 'Argentina');
select * from daily_sales;Output:
Example #1 – Delete Specific row
Suppose the store_state California store has been closed, and we have to remove all the records pertaining to it from our daily sales table.
Code:
DELETE FROM daily_sales
WHERE store_state = 'California';We can check it using a simple SELECT statement for those wondering if we have deleted the correct rows.
Select * from daily_sales;Output:
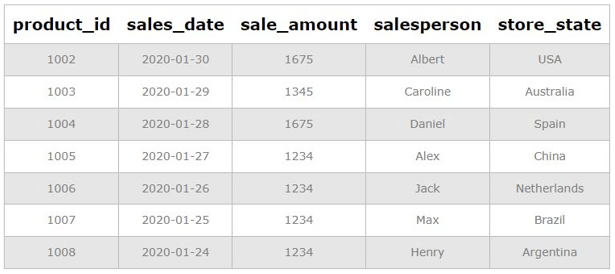
Explanation: To remove details of the California store, we have used a WHERE clause in our DELETE statement to filter rows where store_state is California. As we can see in the image above, the SQL query we just wrote has successfully removed all rows where store_state is California. It can be seen that all rows pertaining to the California store have been removed successfully.
Example #2 – Delete Multiple Rows
Suppose all the Product_id entries ranging from 1006 to 1008 are entered erroneously by a data entry specialist, and we have been tasked to remove all such rows from the daily_sales table.
Code:
DELETE FROM daily_sales
WHERE product_id BETWEEN 1006 AND 1008;We can see that all rows pertaining to sale_amount between 500 and 1500 have been removed from the table.
Select * from daily_sales;Output:
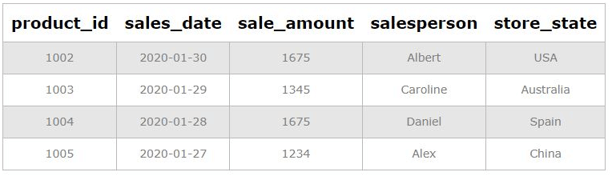
Explanation: We have successfully deleted all rows with any erroneous entry, i.e., product_id between 1006 and 1008. Next, we can check if the required rows have been deleted from the daily_sales table. For the uninitiated, we can use a SELECT statement to fetch all records in the table.
Example #3 – Delete using IN Clause
Suppose all the entries made on a day on which ‘Daniel’ made sales are wrong, and we have been tasked to remove all such rows from the daily_sales table.
Code:
DELETE FROM daily_sales
WHERE sale_amount IN (SELECT sale_amount
FROM daily_sales
WHERE salesperson = 'Daniel');We can check it using a simple SELECT statement for those wondering if we have deleted the correct rows.
Select * FROM daily_sales;Output:
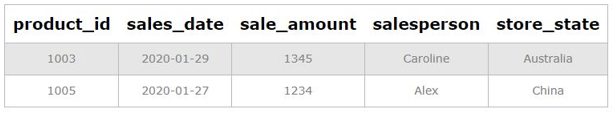
Explanation: This example has been purposely written to illustrate the use of subqueries as a part of the WHERE clause in DELETE statements. And, of course, the query must have done its take to remove all the desired rows from the table.
Example #4 – Deleting all rows in the table
Deleting all rows in a table can be done by using the SQL DELETE statement without specifying a WHERE clause. When the WHERE clause is omitted, the DELETE statement removes all rows from the specified table. Here’s an example of how to delete all rows from a table:
Let’s say we want to delete all rows from the “daily_sales” table. We can use the following SQL DELETE statement:
DELETE FROM daily_sales;After executing this query, all rows from the “daily_sales” table will be deleted. The resulting table will be empty.
However, after executing the DELETE statement, we can check if the “daily_sales” table is empty. You can use the following SQL query to check if the table is empty:
Select * FROM daily_sales;Strategies to Optimize ROW DELETION in SQL
Below are the different strategies to optimize delete row in SQL:
| Strategy | Description |
| Small Batch Deletes | Instead of deleting all rows in one large transaction, delete them in smaller batches. |
| Analyze and Optimize Query Execution Plan | Use database query optimization tools and techniques to analyze the execution plan for deleting queries. |
| Use Proper Indexing | Efficient indexing enhances the speed of searching and removing records. |
| Minimize Logging | While using bulk operations, use minimal logging to optimize deletions. |
| Partitioning | Delete an entire partition instead of deleting numerous rows from an unpartitioned table. |
Difference Between DELETE and TRUNCATE
| Aspect | DELETE | TRUNCATE |
| Definition | Use the DELETE command to DELETE specific records from a table. | Use the TRUNCATE command to delete the complete data from the table. |
| Language Type | DML Command | DDL Command |
| WHERE Clause | It works with the WHERE Clause. | It does not work with the WHERE Clause. |
| Indexed View | It works with indexed views. | It does not work with an indexed view. |
| Speed | The DELETE Command is slower than the TRUNCATE Command. | TRUNCATE Command is faster than DELETE Command. |
Precautions When Using SQL DELETE statement
To avoid unintended data loss and maintain data integrity, it’s essential to follow these precautions when using the DELETE statement:
- Use a WHERE clause: Always include a WHERE clause in the DELETE statement to specify the condition for row deletion. Without a WHERE clause, all rows in the table will be deleted. Double-check the condition to ensure it targets the correct rows.
- Backup data: Before performing any DELETE operation, create a data backup, especially if working with critical or production databases. Backups provide a safety net in case of accidental data deletion.
- Limit testing in production: Avoid testing DELETE statements directly in the production environment. Instead, use a testing or development environment to verify your queries.
- Use transactions: Wrap your DELETE statements in a transaction to ensure data consistency. Transactions allow you to roll back changes if any issues occur during the deletion process.
- Use constraints: Utilize foreign key constraints or triggers to maintain referential integrity between tables. This helps prevent orphaned records and ensures data consistency after deletions.
- Review conditions carefully: Double-check the conditions specified in the WHERE clause to ensure they match the intended rows for deletion. An incorrect condition can lead to data loss.
- Limit user privileges: Grant DELETE permissions only to users who require this operation. Restrict access to DELETE statements to prevent unauthorized or accidental deletions.
- Test with caution: Before executing a DELETE statement, test it with a SELECT query using the same condition to see which rows will be affected. This helps avoid unintended deletions.
- Monitor and log: Regularly monitor database activities and maintain comprehensive logs. This allows you to track and identify any suspicious or accidental deletions.
- Use safe DELETE methods: For large-scale deletions or data purging, consider using safe DELETE methods like soft deletion (setting a flag to indicate deletion) or archiving data instead of permanently deleting it.
Conclusion
In this discussion, we covered the basic syntax of the SQL DELETE statement, including specifying the table name, using the WHERE clause to define conditions, and providing examples of deleting specific rows, multiple rows, and all rows in a table.
We also highlighted the importance of taking precautions when using the DELETE statement. These precautions include backing up data, using transactions, testing queries in a safe environment, and carefully reviewing conditions to ensure the correct rows are targeted for deletion. Monitoring and logging database activities can help track and identify any unexpected deletions.
By implementing these precautions and following best practices, you can effectively and safely utilize the SQL DELETE statement to manage and maintain your database’s data.
FAQs
1. What happens if I use the DELETE statement without a WHERE clause?
All rows in the specified table will be deleted if you use the DELETE statement without a WHERE clause. This can result in the complete removal of data from the table, so using this form of DELETE with extreme caution is crucial.
2. Can I use the DELETE statement to remove rows with references in other tables?
Deleting rows with foreign key references in other tables can be challenging. First, remove or update the related rows in the referencing tables or use cascading DELETE options if supported by your database engine.
3. Please explain the distinction between the DELETE and TRUNCATE statements.
You should use the DELETE statement to remove specific rows from a table. On the other hand, if you want to remove all rows from the table, use the TRUNCATE statement. Still, it also resets the identity column, if applicable. TRUNCATE is usually faster than DELETE when deleting all rows.
4. Are there alternatives to physically deleting data using DELETE?
Some alternatives include soft deletion (adding a flag to indicate deletion), archiving data to a separate table, or using a logical delete approach instead of physically removing rows.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on SQL DELETE ROW was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

