Updated March 14, 2023

Overview of Triggers in SQL
A SQL trigger is a special type of stored procedure in a database which gets executed automatically whenever special events like any data manipulation (INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE), definition (CREATE, ALTER and DROP) or logon event occurs in the database, usually to protect the integrity of the database or fulfill some business requirements, more like a programmed SQL constraint.
Types of Triggers in SQL
While working with relational databases you will come across the following types of Triggers:
| SQL Trigger | Functions |
| DML Triggers | DML trigger is a stored procedure in SQL that gets executed automatically whenever a data manipulation language event occurs. |
| DDL Triggers | DDL trigger is a stored procedure in SQL that gets executed automatically whenever a data definition language event occurs. |
| Logon Triggers | Logon trigger is a stored procedure in SQL that gets executed automatically whenever a logon event occurs but before the beginning of a user session. |
Going ahead, we will be discussing the above-mentioned triggers in great detail.
1. DML Triggers
DML trigger is a stored procedure in SQL that gets executed automatically whenever a data manipulation language event occurs. Data manipulation(DML) events can be an INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE query.
DML triggers help in the prevention of malicious attacks and protect the integrity and security of the database when incorrect DML statements are being performed on the database. They can also be used to perform some complex SQL queries. They are more or less similar to constraints but they are more complex.
There are two types of DML triggers :
1. AFTER Triggers: AFTER Triggers are executed after an insert, delete or update query has been performed. Hence, their primary purpose is not to check constraint violations.
2. INSTEAD OF Triggers: INSTEAD OF Triggers are executed before an insert, delete or update query has been performed. Hence, they can be used for constraint processing.
The basic syntax for writing DML Triggers is as follows :
CREATE [ OR ALTER ] TRIGGER trigger_name
ON table_name
[BEFORE | AFTER] {INSERT , UPDATE, DELETE}
AS
Trigger_bodyThe parameters used in the above-mentioned syntax are :
- CREATE [ OR ALTER ] TRIGGER trigger_name: This statement creates a trigger with the provided name or alters the mentioned trigger.
- ON table_name: Specify the name of the table on which trigger has to be created.
- [BEFORE | AFTER]: Specify the kind of trigger you want to create: before the execution of a statement or after the execution.
- {INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE}: Specify the DML event after which trigger will get fired automatically. You may choose any one or all of them.
- AS Trigger_body: Specify the trigger operation in this section.
Theoretical explanations can be very overpowering sometimes. Let’s take the help of a few examples to understand DML triggers better.
Example: SQL statements to illustrate DML triggers.
In this example, we are trying to create a reminder for the data entry expert to enter a unique customer_id, every time he enters some data.
Code:
CREATE TRIGGER reminder1
ON dbo.customers_dec
AFTER INSERT
AS
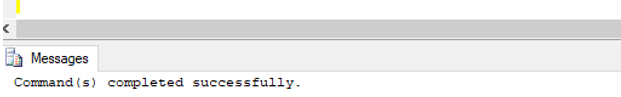
RAISERROR ('Please do not forget to mention a unique customer_id !!', 16,10);Output:
Now let’s check if the trigger has been created or not by trying an insert query on customers_dec table.
Try this query to check :
INSERT INTO customers_dec([customer_id],[name],[city])
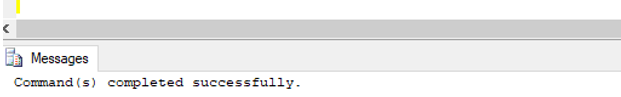
VALUES(1,'Mike Cole', 'Alberta');Output:
As you can see in the above DML trigger has been created successfully.
2. DDL Triggers
DDL trigger is a stored procedure in SQL that gets executed automatically whenever a data definition language event occurs. Data definition language(DDL) events that are used more commonly are CREATE, ALTER, GRANT, and DROP.
DDL triggers are mostly used for recording the list of DDL events that have been performed on the database in order to ensure its integrity or to prevent changes in the database.
The simplified syntax for writing DDL Triggers is as follows :
CREATE [ OR ALTER ] TRIGGER trigger_name
ON database_name
FOR {CREATE_TABLE,DROP_TABLE, ALTER_TABLE, ...}
AS
Trigger_bodyThe parameters used in the above-mentioned syntax are :
- CREATE [ OR ALTER ] TRIGGER trigger_name: This statement creates a trigger with the provided name or alters the mentioned trigger.
- ON database_name: Specify the name of the database on which trigger has to be created.
- FOR: FOR is used to specify the DDL statement for which trigger will be applied.
- {CREATE_TABLE, DROP_TABLE, ALTER_TABLE, …}: Specify the DDL statement before which trigger will get fired automatically. You may choose any one or all of them.
- AS Trigger_body: Specify the trigger operation in this section.
Now let’s take the help of an example to understand DDL triggers better.
Example: SQL statements to illustrate DDL triggers.
In this example, we are trying to create a DDL trigger which will automatically fire up every time we perform a CREATE, DROP or ALTER event in the “practice_art” (it’s a dummy database).
Code:
CREATE TRIGGER security
ON DATABASE
FOR CREATE_TABLE,ALTER_TABLE,DROP_TABLE
AS
PRINT 'Please disable the "security" trigger to perform Data Definition operations!'
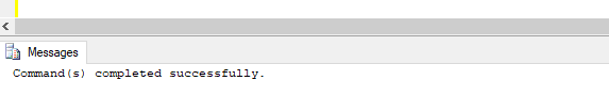
ROLLBACK;Output:
Now let’s check if the trigger has been created or not by trying to create a table in the practice_art database.
Try this query to check :
CREATE TABLE new_table(
Column_1 int,
Column_2 varchar(255)
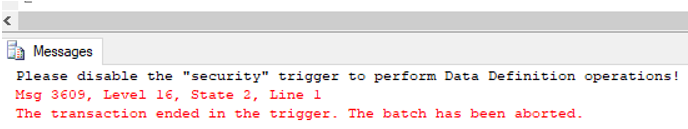
);Output:
As you can see in the above DDL trigger has been created successfully.
3. Logon Triggers
Logon trigger is a stored procedure in SQL that gets executed automatically whenever a logon event occurs but before the beginning of a user session.
These triggers are created to prevent unauthorized access to the database and hence enhance its security.
The simplified syntax for writing Logon Triggers is as follows :
CREATE [ OR ALTER ] TRIGGER trigger_name
ON ALL SERVER
WITH logon_trigger_options
{FOR | AFTER} LOGON
AS
Trigger_bodyThe parameters used in the above-mentioned syntax are:
- CREATE [ OR ALTER ] TRIGGER trigger_name: This statement creates a trigger with the provided name or alters the mentioned trigger.
- ON ALL SERVER: The logon trigger by default gets applied to all the currently supported SQL servers (for eg. SQL Server 2008 and above in MS SQL server).
- WITH logon_trigger_options: Specify the type of trigger you want, for example, if it has to be encrypted or not. This is an optional statement.
- { FOR |AFTER } LOGON: Specify the sequence of execution of trigger with respect to logon event.
- AS Trigger_body: Specify the trigger operation in this section.
Now let’s take the help of an example to understand logon triggers better.
Example: SQL statements to illustrate logon triggers.
Code:
CREATE TRIGGER logon_message
ON ALL SERVER
AFTER LOGON
AS
PRINT 'You have successfully logged in!'
ROLLBACK;Output:
In the above example, we have simply printed a message after login. But we can use logon triggers to perform more complex operations such it can be used to limit the number of login events a user can perform, keeping a count of the number of logins on a daily basis, etc.
Conclusion
SQL triggers are scheduled procedures that get triggered or executed when a specified event occurs. They are primarily used to enhance the security and integrity of databases.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Triggers in SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.