Updated March 28, 2023
What is SQL Subquery?
SQL subquery is a nested inner query enclosed within the main SQL query usually consisting of INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and SELECT statements, generally embedded within a WHERE, HAVING or FROM clause along with the expression operators such as =, NOT IN, <, >, >=, <=, IN, EXISTS, BETWEEN, etc., used primarily for solving complex use cases and increasing the performance or speed of a DBMS operation.
Syntax
The basic syntax for writing SQL subqueries depends upon the part of the main query where you want to embed it. It can be embedded within HAVING, WHERE or FROM clauses. We will be learning about all of them shortly one by one.
Syntax #1 – Subquery in FROM Clause
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM (SELECT column_name(s) from table_name) as table_alias
WHERE condition;Syntax #2 – Subquery in WHERE Clause
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name_1
WHERE column_name expression_operator{=,NOT IN,IN, <,>, etc}(SELECT
column_name(s) from table_name_2);Syntax #3 – Subquery in HAVING Clause
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name_1
WHERE condition
GROUP BY column_name(s)
HAVING Aggregate_function(column_name)expression_operator{=,
<,>}(SELECT column_name(s) from table_name_2);Parameters in SQL Subquery
The parameters used in the above syntaxes are:
- SELECT column_name(s): It is used to select the required data from the database. Mention the column name(s) which you want in the result set.
- FROM: It is used to specify the source from which data has to be fetched. In the first case, the result of the subquery will act as the source. In the second case, data will be fetched from table_name_1.
- WHERE condition: It is used to specify the conditions to filter records. In the second case, the rows will be filtered according to the comparison between the results of the subquery and the mentioned column.
- GROUP BY column_name(s): It is used to group rows, having similar values into summary rows.
- HAVING condition: It is used to filter groups based on the specified condition. In the third case, the filtering of groups is done based on the result of the subquery.
Subquery in FROM Clause
Subqueries in the FROM clause create a derived or intermediate table that can be used directly to fetch results for the main SELECT query or joined with other tables and then used subsequently. In order to understand the concept better, we will take the help of two tables, Employees (this contains personal details of all the employees) and departments (it contains details like department id, name, and its hod).
The data in the departments’ table look something like this:
| departmentid | departmentname | head |
| 4001 | Sales & Marketing | 10024 |
| 4002 | Products | 10023 |
| 4003 | Human Resources | 10022 |
The data in the employees’ table is as follows:
| employeeid | lastname | firstname | departmentid | address | city |
| 10028 | Becker | Todd | 4001 | 27 street | Oslo |
| 10029 | Rebecca | Ginny | 4001 | 27 street | Manhattan |
| 10027 | Tobby | Riya | 4002 | 31 street | Manhattan |
| 10026 | Sharma | Deepak | 4002 | 10th street | New Delhi |
| 10024 | Krishna | Lina | 4001 | 27 street | Oslo |
| 10023 | Jackson | David | 4002 | 27 street | Manhattan |
| 10022 | Mayers | David | 4003 | 27 street | Manhattan |
Here are a few examples to understand subqueries in the FROM clause.
Example #1
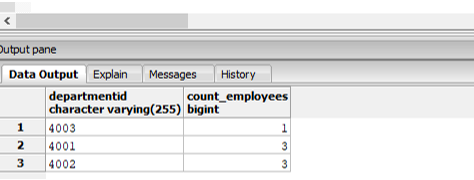
Find the number of employees in each department.
Code:
SELECT departmentid, count_employees
FROM (SELECT count(DISTINCT employeeid) AS "count_employees",departmentid
FROM employees GROUP BY departmentid) AS employee_summary
ORDER BY count_employees;Output:
Explanation: In the above example, we have first created a derived table “employee_summary” and used it to fetch departmentid and count of employees working in that department.
Example #2
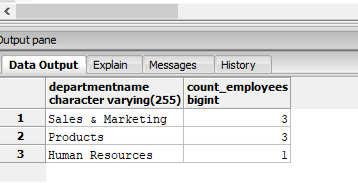
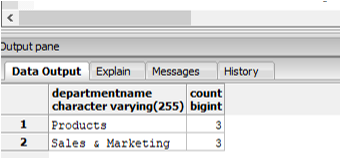
Find the number of employees in each department, but with department names in the final result.
Code:
SELECT dept.departmentname, employee_summary.count_employees
FROM (SELECT count(DISTINCT employeeid) AS "count_employees",departmentid
FROM employees GROUP BY departmentid) AS employee_summary
INNER JOIN
department as dept
ON dept.departmentid::varchar = employee_summary.departmentid
ORDER BY employee_summary.count_employees DESC;Output:
Explanation: In the above example, we have first created a derived table “employee_summary” and then joined it with the “department” table to get department names.
Subquery in WHERE Clause
A subquery in the WHERE clause helps in filtering the rows for the result set, by comparing a column in the main table with the results of the subquery. Here is an example to understand subqueries in the WHERE clause.
Example #1
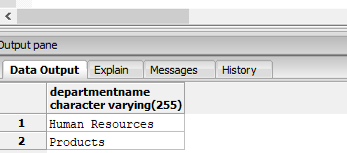
Find the name of departments where the head of the department is from “Manhattan”.
Code:
SELECT departmentname
FROM department
WHERE head IN (SELECT employeeid::varchar
FROM employees
WHERE city = 'Manhattan');Output:
Explanation: In the above example, we have created a condition in the WHERE clause which compares if the head of the department is from Manhattan. But since we have all the information pertaining to cities in the “employees” table, we had to create a subquery that selects employeeid from the “employees” table who are from “Manhattan” and then compares it with employee ids of the head in “department” table.
Subquery in HAVING Clause
A subquery in the HAVING clause helps in filtering the groups for the result set, by comparing a column in the main table with the results of the subquery. Here is an example to understand subqueries in the HAVING clause.
Example #1
Find the departments where the total number of employees is more than the total number of employees in New Delhi.
Code:
SELECT d.departmentname,count(e.employeeid)
FROM department as d INNER JOIN employees as e
ON d.departmentid::varchar = e.departmentid
GROUP BY d.departmentname
HAVING count(e.employeeid)>(SELECT count(employeeid) FROM employees WHERE city = 'New Delhi');Output:
Explanation: In the above example, we have created a subquery in the HAVING clause. The result of this subquery will fetch the total number of employees from New Delhi and then compare it with the number of employees in each department. Hence, it will help us in arriving at the final result.
Conclusion – SQL Subquery
SQL subqueries are nested inner queries written within the main query. They help in solving complex problems. Subqueries are a good alternative to SQL joins as they increase efficiency or speed.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Subquery” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.