Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to SQL IN Operator
IN is a logical operator in Structured Query Language (SQL) that allows for specifying multiple values in the WHERE clause of a SQL INSERT, SELECT, DELETE and UPDATE query for filtering records based on a specific condition, more or less like a shortcut for using multiple ‘OR’ operators. IN operator can be used to specify multiple values at once. It can even be used to hold results of a SELECT subquery.
IN Operator checks the membership of a value in a given set of values or list. It is immensely helpful as it helps in writing all the values together instead of clubbing them together using an ‘OR’ operator.
Syntax
Below are the syntax and parameter for SQL IN Operator:
Syntax #1
The basic syntax for using IN logical operator in SQL is as follows:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE test_expression IN (value1, value2, ...);Syntax #2
You may even use a SELECT query in place of multiple values, using the following syntax:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE test_expression IN (SELECT subquery);Parameters
The parameters used in the above syntax is as follows :
- SELECT column_name(s): It is used to select required data from the database. Mention the
column names that you want in the result set. - FROM table_name: Mention the table name or source from which the columns will be fetched.
- WHERE: It is used to specify the conditions to filter records.
- Test_expression: It is the expression for which we want to perform the test or the column name for which we want to check its membership in a given set using the IN logical operator .
- IN: IN is a logical operator that lets us specify more than one value.
- (value1, value2, …) OR SELECT subquery: SET of values to which the test_expression will be compared for ensuring its membership.
BETWEEN Operator
Going ahead we will be discussing the above mentioned BETWEEN operator in great detail.
In order to understand the concept better, we will take help of the employees table ( this contains personal details of all the employees) and department table (this contains details of department id, name, hod etc).
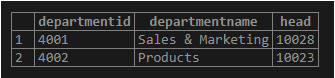
The data in the “department” table look something like this:
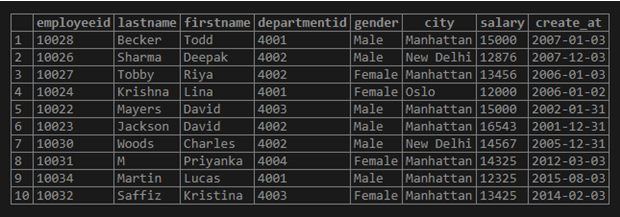
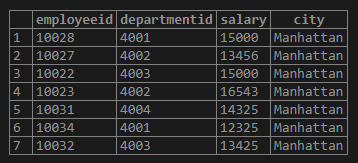
The data in the “employees” table is as follows:
Examples to Implement SQL IN Operator
Below are the examples mentioned:
1. Understanding the basic function of IN operator
Let us see some basic functions:
Example #1
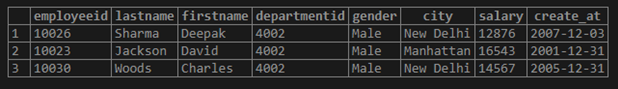
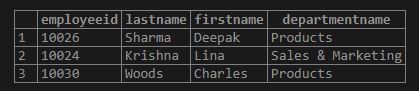
Find the details of employees having employee ids as 10023, 10030 and 10026.
Code:
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE employeeid IN (10023,10030,10026);Output:
Example #2
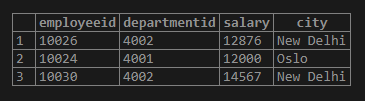
Find the employeeid, department_id, salary and city of employees from Oslo and New Delhi.
Code:
SELECT employeeid,departmentid, salary,city
FROM employees
WHERE CITY IN ('OSLO','NEW DELHI');Output:
Example #3
Find the employeeid, department_id, salary and city of employees who are not from Oslo and New Delhi.
Code:
SELECT employeeid,departmentid, salary,city
FROM employees
WHERE CITY NOT IN ('OSLO','NEW DELHI');Output:
2. Using IN with BETWEEN expression operator
IN expression operator is very frequently used along with BETWEEN operator in the WHERE clause. It is used to specify an additional condition in the query. IN filters only those rows/records which are present in the mentioned set.
Example #1
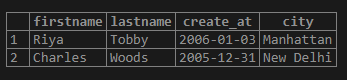
Find the names of the employees , who joined the company between 2003 and 2006 and are from Manhattan or New Delhi.
Code:
SELECT firstname,lastname, create_at, city
FROM employees
WHERE create_at BETWEEN '2003-01-01' AND '2006-12-31'
AND city IN ('Manhattan', 'New Delhi');Output:
3. Using IN operator with subqueries
IN logical operator can be used to check if a value exists/matches with the results of a sub query or not.
Example #1
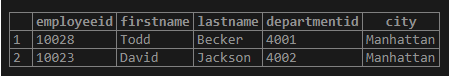
Find the names of the employees who are head of a department in the company.
Code:
SELECT employeeid, firstname, lastname, departmentid, city
FROM employees
WHERE employeeid IN (SELECT head FROM department);Output:
Example #2
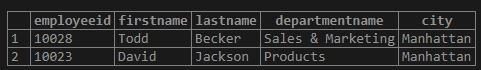
Find the names of the employees along with their department name who are also head of a department in the company.
Code:
SELECT e.employeeid, e.firstname, e.lastname,d.departmentname, e.city
FROM employees as e INNER JOIN department as d
ON e.departmentid = d.departmentid
WHERE e.employeeid IN (SELECT head FROM department);Output:
Example #3
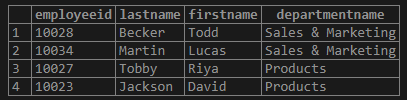
Find the names of the employees along with their department name who are from Manhattan. (Consider only those departments that have a head of department.)
Code:
SELECT e.employeeid,e.lastname, e.firstname, d.departmentname
FROM employees as e INNER JOIN department as d
ON e.departmentid = d.departmentid
WHERE e.employeeid IN (SELECT employeeid
FROM employees
WHERE city = 'Manhattan');Output:
Example #4
Find the names of the employees along with their department name who are not from Manhattan. (Consider only those departments that have a head of department.)This example is just the opposite of the above example.
Code:
SELECT e.employeeid, e.lastname, e.firstname, d.departmentname
FROM employees as e INNER JOIN department as d
ON e.departmentid = d.departmentid
WHERE e.employeeid NOT IN (SELECT employeeid
FROM employees
WHERE city = 'Manhattan');Output:
Conclusion
IN is an operator that is used to club multiple values together and then check the membership of a data value among those values. It’s application is similar to usage of an OR operator multiple times. IN helps us in writing concise SQL queries.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL IN Operator” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.