Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to SQL SELECT Query
‘Select’ queries in SQL are used to fetch one or more records from a table/ database, which can also accommodate other condition clauses, depending on the user’s needs. The resulting data set is stored temporarily on an output table set, commonly known as ‘result-set. Querying with a ‘select’ statement can return a whole table if no condition statements are included or return only intended data if filters or conditions are included in the ‘select’ query.
Syntax of SQL SELECT Query
Select is one of the basic commands of the relational database management system. We can use the SELECT keyword as a prefix to select the record(s) from a given table. The select query return set of records from the given one or more tables.
1. Selecting the required columns of a given table
SELECT <column_A>, <column_B>, ...... FROM <My_table_name>;Explanation:
- SELECT is a command itself; we can use it to select the record from the table.
- <column_A>, <column_B>, …… are the columns of the table My_table_name.
- <My_table_name> is the name of a table.
2. Selecting all the columns of a table
SELECT * FROM <My_table_name>;Explanation:
- SELECT is a command itself we can use to select the record from the table.
- * denotes all the columns of the given table.
- <My_table_name> is the name of a table.
3. Selecting the records with the WHERE clause
SELECT <column_One>, <column_Two>, ...... FROM <My_table > WHERE <column_ One > = <Column_Value>;Explanation:
- <column_One>, <column_Two>, …… are the columns of the table My_table.
- <My_table > is the name of a table.
- WHERE is a keyword we can use in the SQL select statement to select the specified condition records.
4. Selecting the number of records
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM <My_table>;Explanation:
- COUNT(*), this will give us the total number of rows of the table My_table.
- <My_table > is the name of a table.
Examples of SQL SELECT Query
In this section, we will discuss some examples, considering the syntax mentioned above so that anyone can easily understand by putting in little effort. Let’s practice some examples to understand the SQL select statement better.
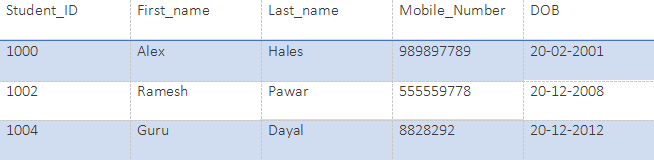
Suppose we have a database name “SCHOOL”. This database has tables, as mentioned below:
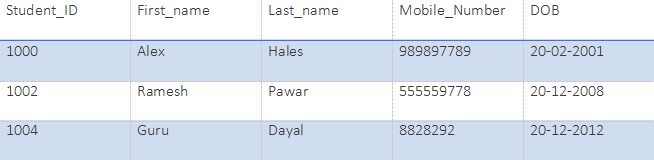
Students:
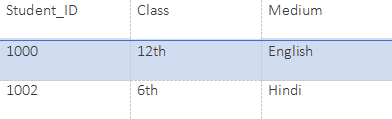
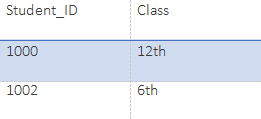
Class:
Example #1 – SELECT with Required Columns
Query:
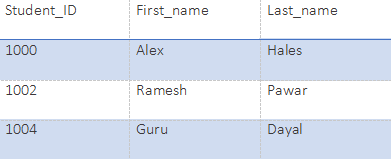
SELECT Student_ID, First_name, Last_name from Student;Output:
Query:
SELECT Student_ID, Class from Class;Output:
Example #2 – SELECT all the Columns of a Table
Query:
SELECT * from Student;Output:
Query:
SELECT * from Class;Output:
Example #3 – Selecting the Records with WHERE Clause
Query:
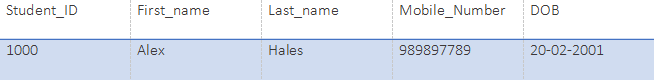
SELECT * from Student WHERE First_name="Alex";Output:
Query:
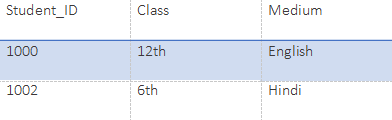
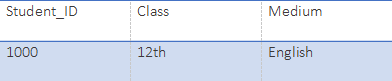
SELECT * from Class where Medium=' English ';Output:
Example #4 – Selecting the Number of Records
Query:
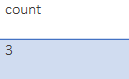
SELECT COUN(*) as count from Student;Output:
Query:
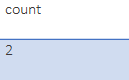
SELECT COUN(*) as count from Class;Output:
Other Facts about the SQL SELECT
The select statement mentioned above can be performed on the relational database. There are various other select statement queries we can use to select the records. The select statement always returns a result set. This result set may contain zero (0), one, or multiple records as well. There are various other things in the select statement we can use to get the desired result. We can use the JOIN keyword to select the records from two or more tables. There are various ways to use two or more select statements to get records from one or more tables. We should use a primary key to any table so that a record can be identified uniquely.
We can use the below mentioned optional clause with the SELECT statement:
- WHERE: We have already seen this with examples.
- GROUP BY: This is required before using the aggregate function.
- HAVING: We can perform an aggregate function using this over the GROUP BY statement.
- ORDER BY: We can use this with the SELECT to sort the order of the result set.
- AS: We have seen this while selecting the total records of a given table. This AS can be used to make an alias of either the selected column or the table.
Conclusion
We can use the SQL select statement to select the required columns or the records as per the business need. Almost every relational database has this SELECT command to select the record from the table. We can use select in various ways. We can select conditional-based records. The select operation can be performed on one or more tables. We can combine various other commands with the SELECT statements. MySQL, ORACLE are examples of relational database management system.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQL SELECT Query. Here we discuss the introduction, syntax, examples and some other facts about the SQL Select Query. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –