Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to SQL ROW
A row in SQL or any relational database is basically a tuple that holds implicitly structured data values in a database table. For the uninitiated, a tuple in any programming language is a set of multiple data values that forms a single record for a particular relation. Rows and columns in SQL can be considered similar to rows of a grid or matrix, where each row contains values for every column. Rows form the building blocks of any relational database.
The highlighted tuple or row forms a row in the relational database.
Creating a Row Structure
It is logical to believe that in order to create a row, we must first create a table. A row to a table is like soul to the body. Ergo, to begin with, let us create a database table called “students”. We can use the following code snippet to create the said table.
Code:
CREATE TABLE students (
roll_no int NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
student_name VARCHAR(255),
degree_major VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
degree_year VARCHAR(255)
);The given CREATE TABLE statement will create a structure where each row in the table will consist of roll_no, student_name, degree_major, and degree_year values.
Adding Rows in a Database Table
A database table is like a blank sheet without any values. Once we add values to the defined structure or outline, the rows hold a meaningful relationship for the added values. Therefore, here is how you add a row in the datatable.
1. Insert statement for adding a row
Code:
INSERT INTO students(
roll_no, student_name, degree_major, degree_year)
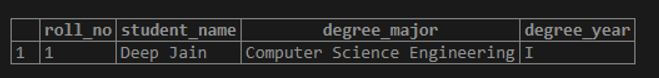
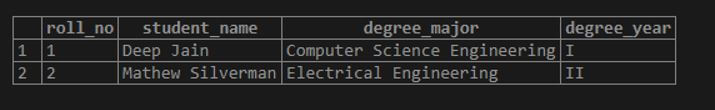
VALUES (1,'Deep Jain','Computer Science Engineering','I');The command got executed successfully, thereby creating a row in the students table. The said row can be visualized using a SELECT query. We can fetch all the rows from any table using a SELECT * or SELECT ALL statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM students;Output:
Now we have a row with data values in the student’s table.
2. Insert statement for adding multiple rows
You must be wondering how to add multiple rows in a datatable. It’s simple, we can use the same good old INSERT statement in the following manner.
Code:
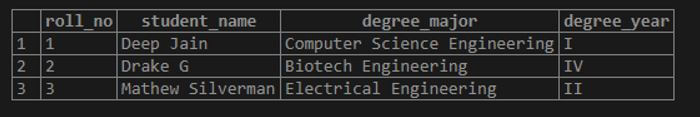
INSERT INTO public.students(
roll_no, student_name, degree_major, degree_year)
VALUES (2,'Drake G','Biotech Engineering','IV'),
(3,'Mathew Silverman','Electrical Engineering','II');The INSERT query just created two more rows in the student’s table. Have a look for yourself using the SELECT statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM students;Output:
Deleting a Row from the Database Table
When it comes to deleting/removing one or more rows from a database table, we use the DELETE statement.
1. DELETE statement for deleting a row
Code:
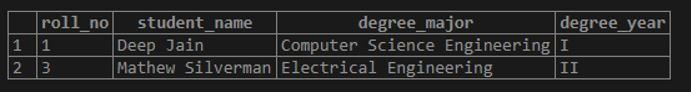
DELETE FROM students
WHERE degree_year = 'IV';We successfully removed a row where degree_year value is ‘IV’.
Now, the student’s table looks something like this.
Code:
SELECT * FROM students;Output:
2. DELETE statement for deleting all rows
In order to delete all the rows in the database table, use the DELETE statement without the WHERE clause.
Code:
DELETE FROM students;Modifying or Updating an Existing Row in the Data Table
What if you do not want to delete a row but modify some values in it. This can be achieved using an UPDATE statement.
Here is an example to update the roll_no of a student named ‘Mathew Silverman’ to 2 instead of 3.
Code:
UPDATE students
SET roll_no = 2
WHERE roll_no = 3;Command got executed successfully. Let’s check if it’s reflected in the table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM students;Output:
The row has been successfully updated.
Assigning Row Numbers to Rows in the Data Table
Suppose we want to sequentially arrange rows in the database based on a column value. We can do so by using the ROW_NUMBER function in SQL. It helps us in fetching data rows based on their row number.
Here is how you can add row numbers to existing rows in the datatable.
Code:
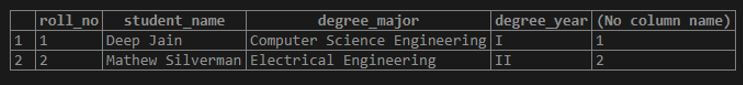
SELECT
roll_no,
student_name,
degree_major,
degree_year,
ROW_NUMBER () OVER (ORDER BY roll_no)
FROM
students;Output:
Filtering Rows for Final Result Set
When fetching rows for the final result set, we might not always want to fetch all the rows from the said table. We can filter rows using a WHERE, HAVING, LIMIT or TOP clause.
Here is how to filter rows using the WHERE clause.
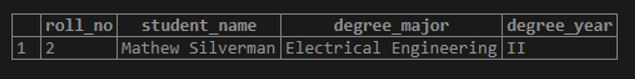
Code:
SELECT
roll_no,
student_name,
degree_major,
degree_year
FROM
students
WHERE degree_major = 'Electrical Engineering';Output:
Here is how to limit the number of rows appearing in the final result set.
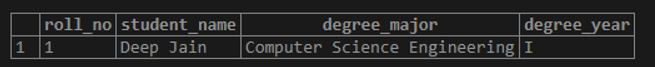
Code:
SELECT * FROM students
LIMIT 1;Output:
Adding Constraints to Row Values
We cannot directly add constraints to a row in SQL, but we can add constraints such as NOT NULL, UNIQUE, CHECK, etc. to columns which will eventually get reflected in the rows.
Here is how we can add constraints to an existing table.
Code:
ALTER TABLE students
ADD CONSTRAINT unique_class UNIQUE(degree_year);The unique_class constraint has been successfully created.
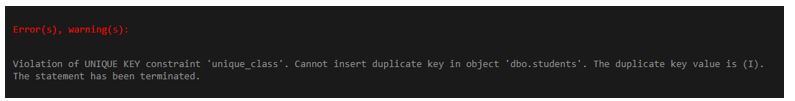
Let’s try inserting a new row with a duplicate value for degree_year.
Code:
INSERT INTO students(
roll_no, student_name, degree_major, degree_year)
VALUES (3,'Rohan Joshi','Integrated Physics','I');Output:
See the new row could not be inserted in the table. Now try this next query with a unique value for degree_year.
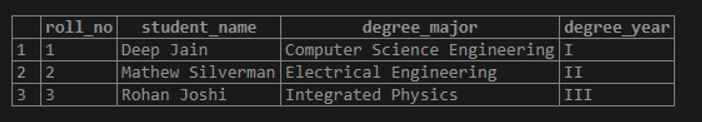
Code:
INSERT INTO students(
roll_no, student_name, degree_major, degree_year)
VALUES (3,'Rohan Joshi','Integrated Physics','III');The query returned successfully. The new row looks something as follows.
Code:
SELECT * FROM students;Output:
Conclusion – SQL ROW
A row can be considered as the building block of any relational database. It is the tuple that holds data values together for each relation in the table. If you know how to work with rows, you know how to work in any relational database.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL ROW” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.