Introduction to Spark YARN
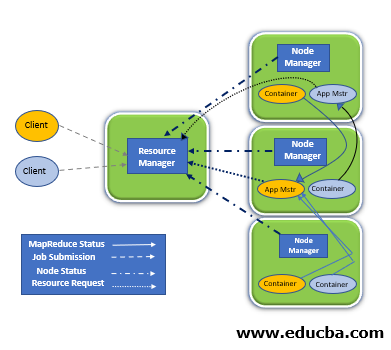
The Apache Spark YARN is either a single job ( job refers to a spark job, a hive query or anything similar to the construct ) or a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) of jobs. Apache Spark YARN is a division of functionalities of resource management into a global resource manager. And onto Application matter for per application. A unit of scheduling on a YARN cluster is called an application manager. A framework of generic resource management for distributed workloads is called a YARN. YARN supports a lot of different computed frameworks such as Spark and Tez as well as Map-reduce functions. And this is a part of the Hadoop system.
Syntax
The syntax for Apache Spark YARN::
$ ./bin/spark-submit --class path.to.your.Class --master yarn --deploy-mode cluster [options] <app jar> [app options]
How Apache Spark YARN works
Understanding cluster and client mode:
The job of Spark can run on YARN in two ways, those of which are cluster mode and client mode. Choosing apt memory location configuration is important in understanding the differences between the two modes. And also to submit the jobs as expected.
There are two parts to Spark. Spark Driver and Spark Executor.
Spark driver schedules the executors whereas Spark Executor runs the actual task.
Client mode
A small application of YARN is created. The Spark driver runs on the client mode, your pc for example. The job fails if the client is shut down. Spark executors nevertheless run on the cluster mode and also schedule all the tasks.
Cluster mode
YARN application master helps in the encapsulation of Spark Driver in cluster mode. Most of the things run inside the cluster. When you start running a job on your laptop, later even if you close your laptop, it still runs.
When SparkPi is run on YARN, it demonstrates how to sample applications, packed with Spark and SparkPi run and the value of pi approximation computation is seen.
Applications fail with the stopping of the client but client mode is well suited for interactive jobs otherwise. Cluster mode is more appropriate for long-running jobs.
How can you give Apache Spark YARN containers with maximum allowed memory?
YARN will reject the creation of the container if the memory requested is above the maximum allowed, and your application does not start.
- Below is the maximum allowed value for a single container in Megabytes.
yarn.scheduler.max-allocation-mb get the value of this in $HADOOP_CONF_DIR/yarn-site.xml.
- Make sure that values configured in the following section for Spark memory allocation, are below the maximum.
- scheduler.maximum-allocation-Mb. This guide will use a sample value of 1536 for it. Adjust the samples with your configuration, If your settings are lower.
Examples to Implement Spark YARN
Below are examples mentioned:
Example #1
This is how you launch a Spark application but in cluster mode:
Code:
$ ./bin/spark-submit --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \
--master yarn \
--deploy-mode cluster \
--driver-memory 4g \
--executor-memory 2g \
--executor-cores 1 \
--queue thequeue \
Explanation: The above starts the default Application Master in a YARN client program. Then, to Application Master, SparkPi will be run as a child thread. The Application master is periodically polled by the client for status updates and displays them in the console. Once your application has finished running. The client will exit.
Do the same to launch a Spark application in client mode, But you have to replace the cluster with the client. The below says how one can run spark-shell in client mode:
$ ./bin/spark-shell --master yarn --deploy-mode client
Example #2
How can you add Other Jars:
The driver runs on a different machine than the client In cluster mode. which is the reason why spark context.add jar doesn’t work with files that are local to the client out of the box. To the SparkContext.addjar, the files on the client need to be made available. For this, we need to include them with the option —jars in the launch command.
Code:
$ ./bin/spark-submit --class my.main.Class \
--master yarn \
--deploy-mode cluster \
--jars my-other-jar.jar,my-other-other-jar.jar \
my-main-jar.jar \
app_arg1 app_arg2
Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed the Spark resource planning principles and understood the use case performance and YARN resource configuration before doing resource tuning for the Spark application. We followed certain steps to calculate resources (executors, cores, and memory) for the Spark application. The results are as follows: Significant performance improvement in the Data Frame implementation of Spark application from 1.8 minutes to 1.3 minutes. RDD implementation of the Spark application is 2 times faster from 22 minutes to 11 minutes.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Spark YARN. Here we discuss an introduction to Spark YARN, syntax, how does it work, examples for better understanding. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –