Updated June 27, 2023
Introduction to Spark Commands
The framework of Apache Spark allows for quick computations and builds upon Hadoop. It extends the concept of MapReduce in the cluster-based scenario to efficiently run a task. Spark Command is written in Scala.
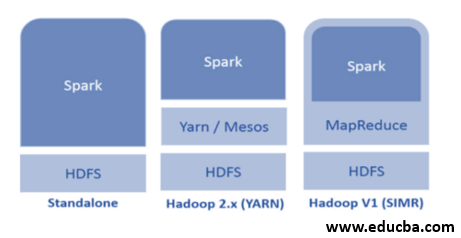
Spark can utilize Hadoop in the following ways (see below):
- Standalone: Spark is directly deployed on top of Hadoop. Spark jobs run parallelly on Hadoop and Spark.
- Hadoop YARN: Spark runs on Yarn without the need for any pre-installation.
- Spark in MapReduce (SIMR): Spark in MapReduce is used to launch the spark job and standalone deployment. With SIMR, one can start Spark and use its shell without administrative access.
Components of Spark
Spark comprises the following parts:
- Apache Spark Core
- Spark SQL
- Spark Streaming
- MLib
- GraphX
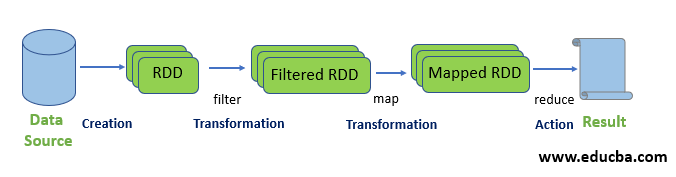
Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDD) are considered the fundamental data structure of Spark commands. RDD is immutable and read-only. RDDs perform computations through transformations and actions using Spark commands.
Spark shell provides a medium for users to interact with its functionalities. You can process data using a variety of commands offered by the interactive shell.
Basic Spark Commands
Let’s take a look at some of the basic commands which are given below:
1. To start the Spark shell
2. Read a file from the local system:
Here “sc” is the spark context. To read “data.txt” located in the home directory, you don’t need to specify the full path. However, you must provide the full path if it’s located elsewhere.
3. Create RDD through parallelizing
NewData is the RDD now.
4. Count Items in RDD
5. Collect
This function returns all RDD’s content to the driver program. This helps debug at various steps of the writing program.
6. Read the first 3 Items from RDD
7. Save output/processed data into the text file
Here “output” folder is the current path.
Intermediate Spark Commands
Here are some intermediate commands worth exploring:
1. Filter on RDD
Let’s create a new RDD for items that contain “yes.”
To apply the transformation filter to an existing RDD and generate a new list of items, you must filter for the word “yes.”
2. Chain Operation
Here filter transformation and count action acted together. This is called chain operation.
3. Read the first item from RDD
4. Count RDD Partitions
Since RDDs are composed of multiple partitions, counting the number of partitions is sometimes necessary. As it helps in tuning and troubleshooting while working with Spark commands.
By default, the minimum no. pf partition is 2.
5. join
This function joins two tables (the table element is in a pairwise fashion) based on the common key. In pairwise RDD, the first element is the key, and the second element is the value.
6. Cache a File
Caching is an optimization technique. Caching RDD means RDD will reside in memory, and all future computations will be done on those RDD in memory. It saves disk read time and improves performance. In short, it reduces the time to access the data.
However, data will not be cached if you run the above function. This can be proved by visiting the webpage:
http://localhost:4040/storage
RDD will be cached once the action is done. For example:
Persist () is another function similar to cache (). Persist allows users to specify an argument determining where the data will be cached, whether in memory, disk, or off-heap memory. Cache() and persist() both function well without any arguments.
Advanced spark commands
Here are some advanced commands worth exploring:
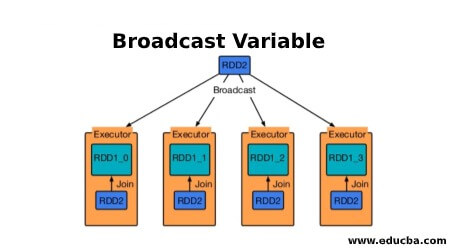
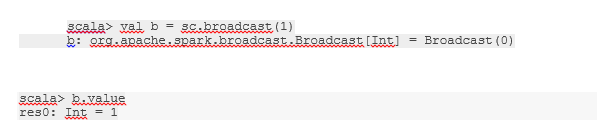
1. Broadcast a variable
Broadcast variable helps the programmer keep reading the only variable cached on every machine in the cluster rather than shipping a copy of that variable with tasks. This helps in the reduction of communication costs.
In short, there are three main features of the Broadcasted variable:
- Immutable
- Fit in memory
- Distributed over cluster
2. Accumulators
Accumulators are the variables that get added to associated operations. There are many uses for accumulators like counters, sums, etc.
The name of the accumulator in the code could also be seen in Spark UI.
3. Map
The map function helps in iterating over every line in RDD. The function used in the map applies to each element in the RDD.
For example, in RDD {1, 2, 3, 4, 6}, if we apply “rdd.map(x=>x+2),” we will get the result as (3, 4, 5, 6, 8).
4. Flatmap
Flatmap works similarly to the map, but the map returns only one element, whereas flatmap can return a list of elements. Hence, splitting sentences into words will need a flatmap.
5. Coalesce
This function helps to avoid the shuffling of data. The current partition utilizes this technique to reduce the amount of data that needs shuffling. This way, we can restrict the usage of nodes in the cluster.
Tips and Tricks to Use Spark Commands
Below are the different tips and tricks of Spark commands:
- Beginners of Spark may use Spark-shell. Since Spark is built on Scala, using Scala Spark shell is an excellent option. However, Python Spark shell is also available, which can be used by those proficient in Python.
- Spark shell has a lot of options to manage the resources of the cluster. Below Command can help you with that:
- In Spark, working with long datasets is the usual thing. But things go wrong when bad input is taken. It’s always a good idea to drop bad rows by using the filter function of Spark. A good set of input will be a great go.
- Spark chooses a good partition on its own for your data. But it’s always a good practice to keep an eye on partitions before you start your job. Trying out different partitions will help you with the parallelism of your job.
Conclusion
Spark command is a revolutionary and versatile big data engine that can work for batch processing, real-time processing, caching data, etc. Spark has a rich set of Machine Learning libraries that can enable data scientists and analytical organizations to build strong, interactive, and speedy applications.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Spark commands. Here we have discussed concepts, basic, intermediate, and advanced Spark Commands along with tips and tricks to use effectively. You may also look at the following article to learn more –