Introduction to Spark Shuffle
In Apache Spark, Spark Shuffle describes the procedure in between reduce task and map task. Shuffling refers to the shuffle of data given. This operation is considered the costliest. Parallelising effectively of the spark shuffle operation gives performance output as good for spark jobs. Spark data frames are the partitions of Shuffle operations. The original data frame partitions differ with the number of data frame partitions. The data moving from one partition to the other partition process in order to mat up, aggregate, join, or spread out in other ways is called a shuffle.
Syntax
The syntax for Shuffle in Spark Architecture:
rdd.flatMap { line => line.split(' ') }.map((_, 1)).reduceByKey((x, y) => x + y).collect()
Explanation: This is a Shuffle spark method of partition in FlatMap operation RDD where we create an application of word count where each word separated into a tuple and then gets aggregated to result.
How Spark Architecture Shuffle Works
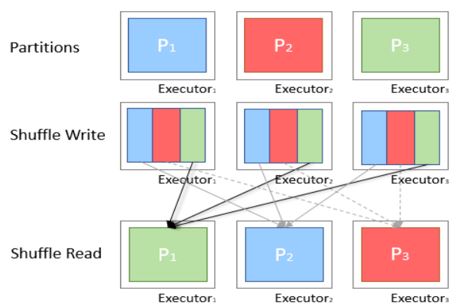
Data is returned to disk and is transferred all across the network during a shuffle. The shuffle operation number reduction is to be done or consequently reduce the amount of data being shuffled.
By default, Spark shuffle operation uses partitioning of hash to determine which key-value pair shall be sent to which machine.
More shufflings in numbers are not always bad. Memory constraints and other impossibilities can be overcome by shuffling.
In RDD, the below are a few operations and examples of shuffle:
– subtractByKey
– groupBy
– foldByKey
– reduceByKey
– aggregateByKey
– transformations of a join of any type
– distinct
– cogroup
These above Shuffle operations built in a hash table perform the grouping within each task. This is often huge or large. This can be fixed by increasing the parallelism level and the input task is so set to small.
These are a few series in Spark shuffle operation –
One partition – One executor – One core
Four partitions – One executor – Four core
Two partition – Two executor – Two core
Skewed keys.
Examples to Implement Spark Shuffle
Let us look into an example:
Example #1
( customerId: Int, destination: String, price: Double) case class CFFPurchase
Let us sat that we consist of an RDD of user purchase manual of mobile application CFF’s which has been made in the past one month.
Val purchasesRdd: RDD[CFFPurchase] = sc.textFile(…)
Goal: Let us calculate how much money has been spent by each individual person and see how many trips he has made in a month.
Code:
val buyRDD: RDD[ADD_Purchase] = sc.textFile()
// Return an array - Array[(Int, (Int, Double))]
// Pair of RDD
//group By Key returns RDD [(K, iterable[V])]
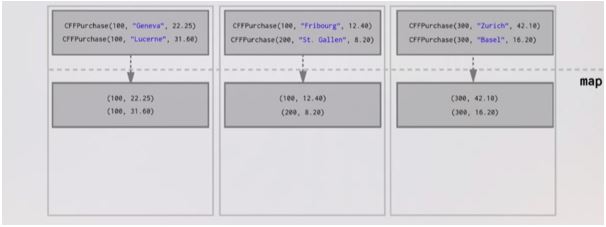
val purchasesForAmonth = buyRDD.map( a=> (a.IdOfCustomer, a.cost))
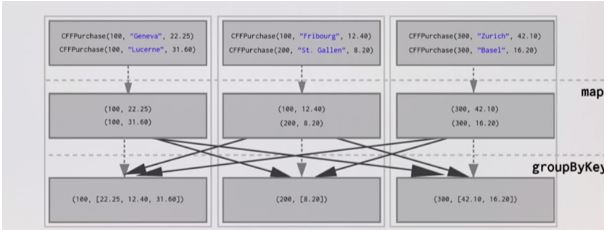
.groupByKey()
.map(p=> (a._1. (a._2.size, a._2.add)))
.collect()
sample1 – sample1.txt:
val Buy = List (ADDPurchase (100, “Lucerne”, 31.60))
(100, “Geneva”, 22.25))
(300, “Basel”, 16.20))
(200, “St. Gallen”, 8.20))
(100, “Fribourg”, 12.40))
(300, “Zurich”, 42.10))
With the data distribution given above, what must the cluster look like?
Output:
Explanation: We have concrete instances of data. To create collections of values to go with each unique key-value pair we have to move key-value pairs across the network. We have to collect all the values for each key on the node that the key is hosted on. In this example, we have assumed that three nodes, each node will be home to one single key, So we put 100, 200, 300 on each of the nodes shown below. Then we move all the key-value pairs so that all purchase by customer number 100 on the first node and purchase by customer number 200 on second node and purchase by customer number 300 on the third node and they are all in this value which is a collection together. groupByKey part is where all of the data moves around the network. This operation is considered as Shuffle in Spark Architecture.
Important points to be noted about Shuffle in Spark
1. Spark Shuffle partitions have a static number of shuffle partitions.
2. Shuffle Spark partitions do not change with the size of data.
3. 200 is an overkill for small data, which will lead to lowering the processing due to the schedule overheads.
4. 200 is smaller for large data, and it does not use all the resources effectively present in the cluster.
And to overcome such problems, the shuffling partitions in spark should be done dynamically.
Conclusion
We have seen the concept of Shuffle in Spark Architecture. Shuffle operation is pretty swift and sorting is not at all required. Sometimes no hash table is to be maintained. When included with a map, a small amount of data or files are created on the map side. Random Input-output operations, small amounts are required, most of it is sequential read and writes.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Spark Shuffle. Here we discuss introduction to Spark Shuffle, how does it work, example, and important points. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –