Updated April 6, 2023
Introduction to Scope in AngularJS
The concept of scope was introduced in AngularJS 1.xx, it is written $scope and read as SCOPE, $scope binds the view (HTML template) and controller (data to be added or rendered on the template), so it is the glue between view and controller. The data available in a controller to be rendered in view is known as the model.
The controller provides data to view, and whenever there are any updates/changes in model data, the view is rendered with updates because of $scope.
The scope is very important in angularJS as it helps to develop MVC pattern applications that is one of the core features of the angularJS framework.
- Model – in MVC pattern Model is the data available to view for rendering.
- View – View has a responsibility to display data to the user or on UI.
- Controller − Controller controls the interactions between the Model and View.
The controller is single points of the data source to view. $scope is a special Javascript object provided by AngularJS that is injected to view. $scope has properties and methods, which can be parsed in the view template of angularJS application using expression ({{}}).
Controllers and Scopes
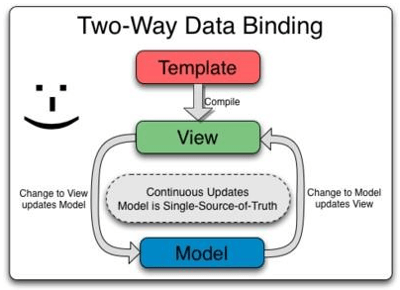
The controller is a Javascript function that is available to a part of the view; we pass the scope object to the controller as an argument, the view can render data available to it through $scope, ng-model, and ng-bind directives in AngularJS helps us to achieve two-way data binding in AngularJS application.
$scopes is a Javascript object, and controllers is a Javascript function; these two interact in the following situations:
- Controllers use the $scope object to expose controller methods to templates.
- Controllers define methods (behavior) that can mutate the model or properties on the scope.
- Controllers may have registered watches on the model.
- Each controller is attached to one corresponding $scope only but may be a child of one or more
$scope objects.
Adding Properties and methods to $scope object
ngApp.controller('firstController', function ($scope){
$scope.message = "Hello!";
$scope.name = “John”
$scope.greet = function(){
return $scope.message+“ ” + $scope.name;
});
$scopeThis is a $scope object provided by angularJS framework; here, it is injected in Controller, or in other words, passed as argument in Controller.
$scope.method
Using this, we can add properties and methods to $scope object, code here adds message and name properties, and greet method to $scope object.
$scope.message
This example illustrates the way to add a method to the $scope object.
Making scope available to view
AngularJS provides a bunch of directives; ng-controller is the directive used to specify the controller for a particular view.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html >
<head>
<title>AngularJS $scope example</title>
Include angularJS library here to include it in project
</head>
<body ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="'firstController'"> Greetings: <br />
{{message}}+‘ ‘+ {{name}}<br />
</div>
</body>
</html>Ng-app
Ng-app is the directive provided by AngularJS; from this point scope of the Angular application starts.
body ng-app=”myApp”
Including angular library to the HTML page
div ng-controller=”‘firstController'”
Ng-controller directive is used to insert a controller in a view and define its $scope.
name and message are properties of
$scope object accessed in the view template; here, we can also use $scopes methods.
AngularJS applications can have multiple scopes as per requirement; each scope is attached with a controller. Expressions in AngularJS and evaluated against scope and scope provide a context to expression evaluation; for example, {{name}} is an expression in the above code example, and this is evaluated against $scope passed in firstController.
$scope objects provide us a way to achieve two-way binding in AngularJS, with the help of build-in directive AngularJS called ng-model and $watch and $apply API.
What is $rootScope?
On the application level, there is a root scope in AngularJS Application; root scope is provided by the AngularJS framework; it is the parent of all the scopes available in the application. All controllers ($scopes) inherit properties and methods from $rootScope, so root scope also serves as a way to pass data down the controllers and makes it available for all over the application. Apart from root scope their maybe other child-parent relationship in scopes in the scopes of angularJS application, and as a general rule, child
$scope have access of all the properties and methods of the parent $scope.
$rootScope, parent and child Controller’s $scope Code example
Each controller has its own space/ scope, but the root scope can be accessed all over the application. In other words, root scope is the parent of all scopes and is for the entire application module.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>AngularJS $root Scope and Child $scope</title>
</head>
<body ng-app="ngApp">
<div ng-controller="parentController"> Controller Name: {{controllerName}} <br />
{{ greetings }} <br />
<div ng-controller="childController"> Controller Name: {{controllerName}} <br />
{{ greetings }} <br />
</div>
</div>
<div ng-controller="siblingController"> Controller Name: {{controllerName}} <br /> Message: {{message}} <br />
</div>
</body>
</html>Javascript controller and scope Code:
var ngApp = angular.module('myNgApp', []);
ngApp.controller('parentController', function ($scope, $rootScope) {
$scope.controllerName ="parent Controller at root level";
$rootScope.greetings ="Hello, I am from root scope";
});
ngApp.controller('childController', function ($scope) {
$scope.controllerName ="first child Controller";
});
ngApp.controller('siblingController', function ($scope) {
$scope.controllerName ="Second child Controller";
});
div ng-controller="parentController"
This is parent controller at top div level, it has two nested div, each having their own controller.
div ng-controller="childController"
div ng-controller="siblingController"
These two are child controllers of parent controller and siblings to each other. In first-child controller {{ greetings }} is coming from root controller$rootScope
$rootScope is available to all the controllers; here, we are inserting root scope to parent controller; this root controller can be accessed by any child controller.
At times root scope is used in AngularJS applications to store some common data and access it throughout the application uniformly.
Model Mutation and $scope
All the $scopes in angularJS has a watch API provided by AngularJS framework to observe changes in model data, watch propagates changes with the particular scope object, and UI template associated with that $scope is updated per changes in Model. Scopes also provide another API called $apply to propagate any model changes through the system into the view from outside of the “AngularJS realm” (controllers, services, and other AngularJS event handlers).
In a nutshell, $scope is very important in AngularJS frameworks that encapsulate view and model and helps us to achieve two-way data binding.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Scope in AngularJS” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.