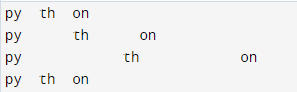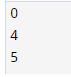Updated August 17, 2023
Introduction to Python 3 String
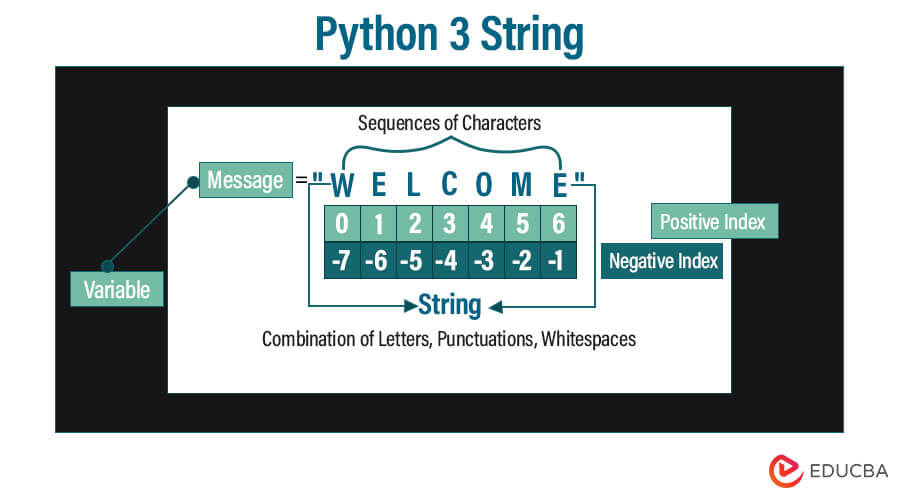
Python 3 strings are one of Python’s most common data types. Simply wrapping characters in quotations allows us to construct them. Variable value assigning is the same as creating strings. Python lacks a character type, so it handles these as one-length strings and thus considers them as substrings. To get a substring, use an index or indices. These functions make it simple to manipulate strings.
Table of Contents
What is Python 3 String?
- The string data type in Python contains several built-in functions. These functions make it simple to change and manipulate strings. Functions are actions that we do on code elements. Built-in functions are a specified language of Python programming immediately accessible to us.
- The lower and upper functions return a string with all the letters in an original string changed to upper or lower case letters.
Python 3 String Characters
- Instances and exceptions are the main built-in types. Mutable collection classes exist. Methods that don’t return a specific item but never return the collection instance itself, but instead return none.
- Several object types offer some actions; For instance, you can compare nearly all objects for equality by utilizing the repr and somewhat different str functions. The print method employs the function implicitly when writing an object.
- Below, you can find a list of non-printable or escape characters rendered with backslash notation. Both single and double-quoted strings understand the escape character.
Below is Python 3 string characters as follows.
1) \a – This character is used for alert or bell.
2) \b – This character is used for backspace.
3) \cx – This character is used for control-x
4) \C- x – This character is used for control-x
5) \e – This character is used for escape.
6) \f – This character is used for a form feed.
7) \M – \C-x – This character is used for meta control x.
8) \n – This character is used for newline.
9) \nnn – This character is used for an octal range.
10) \r – This character is used for carriage return.
11) \s – This character gives space between two characters or words.
12) \t – This character gives the tab between two characters or words.
13) \v – This character gives a vertical tab.
14) \x – This character is used for character-x.
15) \xnn – This is nothing but the hexadecimal notation. In that, n is nothing but the range from 0 to 9.
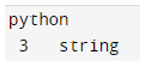
The below example shows Python 3 string characters as follows. In the below example, we have used \v, \t, and \n characters.
Code:
Py3str = "python \n 3 \t string"
print (Py3str)Output:
- When the preceding code is run, the above result is obtained. Now every single special character, right down to the final newline, has been converted to its printed form. Also, NEWLINEs appear when a line ends with the return of carriage or its escape code.
- The raw strings do not consider the backslash as a special character. They preserve every character typed into them in the same format as when they were initially typed.
- The below example demonstrates that the string preserves its original format from when we first typed it.
Code:
print ('C:\\python 3 string')Output:
Python 3 String Operators
These methods allow searching specific substrings in a number of different ways. If only start and end are supplied, the technique is applied to segment from start to end.
Below is the string operator, which was used in Python as follows.
1. Addition (+)
This string operator is used to add multiple strings. The below example shows the addition string operator as follows.
Code:
py = "Python " + "string"
print(py)Output:
2. Multiplication
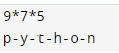
This string operator is used to repeat the string many times. The below example shows multiplication string operators as follows.
Code:
py = "python " * 5
print (py)Output:
3. Slice
This operator returns the character which was provided by the x character. The below example shows the slice string operator as follows.
Code:
py = "Python"
print(py [1])Output:
4. Range Slice
This operator returns the character provided by the x:y character.
Code:
py = "Python"
print (py [2:4])Output:
5. In
This operator returns true if x exists in the string as follows.
Code:
py = "python"
print("p" in py)
print("h" in py)
print("a" in py)Output:
6. Not In
This operator returns true if x does not exist in the string.
Code:
py = "python"
print("p" not in py)
print("h" not in py)
print("a" not in py)Output:
Formatting Operators
For percent is one of Python’s most useful tools. This operator only applies to strings, compensating for C’s lack of printf family functions.
Below is the string formatting operator used in Python as follows.
1) %c – This is the string formatting character operator.
2) %s – This is a string conversion used to format the string.
3) %i – This is nothing but the signed decimal integer.
4) %d – This is nothing but the signed decimal integer.
5) %u – This is nothing but the unsigned decimal integer.
6) %o – This is nothing but the octal integer.
7) %x – This is nothing but the hexadecimal integer in lowercase letters.
8) %X – This is nothing but the hexadecimal integer in uppercase letters.
9) %e – This is nothing but exponential notation.
10) %f – This is nothing but the floating point number.
11) %g – This is the shorter of %e and %f.
Below is the Python 3 string formatting operator example as follows. In the below example, we are using %s and %d operators.
Code:
print ("ABC %d XYZ %s PQR")Output:
These methods allow to search specific substrings in a number of different ways. If only start and end are supplied, the technique is applied to segment from start to end. Python 3 strings are one of Python’s most common data types. Simply wrapping characters in quotations allows us to construct them.
Python 3 String Methods
Below are string methods available in Python are as follows. String methods are very important in Python.
1. Capitalize
Returns a string copy with the first letter capitalized and the remainder lowercase. If we wish all words’ first letters capitalized, use the title. The below example shows capitalization string methods in Python.
Code:
py = "python 3 string methods"
print (py.capitalize ())
py = "python 3 string methods"
print (py.title())Output:
2. Casefold
Returns a string that has been case-folded. You can utilize casefolded strings for caseless matching. The below example shows casefold string methods in Python.
Code:
py = "Python String Methods"
py1 = py.casefold()
print(py1)Output:
3. Center
Returns the centered string in a length-width string. You can use the provided fill char to add padding if width equals or is less than len. The below example shows center string methods in Python.
Code:
py1 = "python"
py2 = py1.center(10, "+")
print (py2)Output:
4. Count
Non-overlapping substring occurrences in the range [start, end]. Slice notation interprets optional arguments “start” and “end.” Python will not count characters twice due to non-overlapping occurrences. The below example shows count string methods in Python as follows.
Code:
py = "Python String Methods"
print(py.count("S"))
print(py.count("o"))
print(py.count("t"))Output:
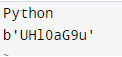
5. Encode
As a bytes object, it returns a string that has been encoded. utf-8 is the standard encoding. To set a custom error handling scheme, errors can be provided. The below example shows that encode string methods in Python are as follows.
Code:
from base64 import b64encode
py = "Python"
print(py)
py = b64encode(py.encode())
print(py)Output:
6. Endswith
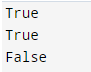
The result is True if the text concludes with the required suffix; otherwise, False is returned. The test starts at that location if the start parameter is specified. The test ends comparing at that location when we select the optional end. The below example shows endswith string methods in Python as follows.
Code:
py = "Python"
print(py.endswith("on"))
print(py.endswith("n"))
print(py.endswith("no", 1, 3))Output:
7. Expandtabs
The specified tab size returns a copy of the string with all tab characters replaced by one or more spaces. Every tabsize character has a position. The below example shows expandtabs string methods in Python as follows.
Code:
py = "py\tth\ton"
print(py)
print(py.expandtabs())
print(py.expandtabs(tabsize=14))
print(py.expandtabs(tabsize=4))Output:
8. Find
Returns the string’s lowest index where the substring sub is located within the slice. The below example shows that find string methods in Python are as follows.
Code:
py = "Python"
print(py.find("P"))
print(py.find("o"))
print(py.find("n"))Output:
9. Format
This method applies string formatting. You can invoke this method on a string containing literal text or brace-delimited replacement fields.
Code:
print("{} Python {}".format("String", "Methods"))Output:
10. Index
If we have not found any substring, this string in Python will raise an error as follows.
Code:
py = "Python"
print(py.index("P"))
print(py.index("h"))Output:
11. Isalnum
If the string has all of the characters alphanumeric, it returns True. Otherwise, it returns False.
Code:
py = "Python"
print(py.isalnum())Output:
12. Isalpha
If the string has all of the alphabetic characters, it returns True. Otherwise, it returns False.
Code:
py = "Python"
print(py.isalpha())Output:
13. Isdecimal
Returns true if the string contains all of the characters are decimal characters. Otherwise, it returns False.
Code:
py = "Python"
py1 = "752"
print(py.isdecimal())
print(py1.isdecimal())Output:
14. Isdigit
Returns true if the string contains all of the digits. Otherwise, it returns False.
Code:
py = "Python"
py1 = "752"
print(py.isdigit())
print(py1.isdigit())Output:
15. Islower
Returns true if the string contains all lowercase letters. Otherwise, it returns False.
Code:
py = "Python"
py1 = "python"
print(py.islower())
print(py1.islower ())Output:
16. Isupper
Returns true if the string contains all uppercase letters. Otherwise, it returns False.
Code:
py = "PYTHON"
py1 = "python"
print(py.isupper())
print(py1.isupper())Output:
Examples
Below are the different examples:
Example #1
The below example shows that join python string methods are as follows.
Code:
py = "*"
print(py.join("975"))
py1 = "-"
print(py1.join("python"))Output:
Example #2
The below example shows the isnumeric string method in Python, which is as follows.
Code:
py = "742"
print(py.isnumeric())
py1 = "Python3"
print(py1.isnumeric())Output:
Example #3
The below example shows isprintable methods in Python as follows.
Code:
py = "\t"
print(py.isprintable())
py1 = "Python3"
print(py1.isprintable())Output:
Example #4
The below example shows the isspace string method in Python as follows.
Code:
py = ""
print(py.isspace())
py1 = " "
print(py1.isspace())Output:
Example #5
The below example shows the istitle string method in Python as follows.
Code:
py = " Python"
print(py.istitle())
py1 = "python"
print(py1.istitle())Output:
Conclusion
In conclusion, Python 3 offers a versatile and powerful string-handling capability, empowering developers to manipulate and process textual data efficiently. With its decadent array of built-in methods, formatting options, and Unicode support, Python 3 is indispensable for many applications, from basic text processing to complex linguistic analysis and beyond.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Python 3 String” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.