Updated February 20, 2023
Introduction to Python 3 Operators
Python 3 operators are used to manipulate values and variables. In general, there are multiple types of operators available in python. Therefore, operators are very useful and important in python. Types of operators are divided into their operations, performed on the operand. There are six types of operators available in python. The arithmetic operator is mostly used in python to solve arithmetic operations.
What are Python 3 Operators?
The operator module provides a set of high-performance functions that correspond to python’s intrinsic operators. The expression py1+py2 is equal to the operator.add (py1, py2). Without the two underscores, names of functions are utilized for specific methods. Many of them have a variation with double underscores preserved for backward compatibility. For clarity’s sake, variations without double underscores are recommended. Mathematical operations and sequence operations are among the categories of functions available.
Types of Python 3 Operators
Below are the types of python 3 operators:
Python 3 operator is divided into multiple types.
1. Arithmetic Operator
An arithmetic operator is used to perform arithmetic operations. There is multiple arithmetic operator available in python. Below is the example of the arithmetic operator as follows. In the below example, we perform multiplication, addition, subtraction, and division operation as follows.
In the below example, we have used two variables, py1 and py2, to declare the value on which we have performed the arithmetic operation.
Code:
py1 = 20
py2 = 5
addition = py1 + py2
subtraction = py1 - py2
multiplication = py1 * py2
division = py1 / py2
print (addition)
print (subtraction)
print (multiplication)
print (division)Output:
2. Comparison Operator
A comparison operator is used to compare the values on the condition to either return true or false. Below is the example of a comparison operator as follows. In the example below, we perform greater than, less than, not equal to, and equal to operation.
In the below example, we have used two variables, py1 and py2, to declare the value on which we have performed a comparison operation.
Code:
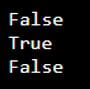
py1 = 25
py2 = 35
print (py1 > py2)
print (py1 < py2)
print (py1 == py2)
print (py1 != py2)Output:
3. Logical Operator
Below is the example of a logical operator as follows. In the below example, we are performing and, not and or operation as follows.
In the below example, we have used two variables, py1 and py2, to declare the value on which we have performed a logical operation.
Code:
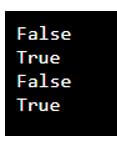
py1 = True
py2 = False
print (py1 and py2)
print (py1 or py2)
print (not py1)Output:
4. Bitwise Operator
Below is the example of the bitwise operator as follows. In the below example, we are performing bitwise or not, and xor operations are as follows. In the below example, we have used two variables, py1 and py2, to declare the value on which we have performed the bitwise operation.
Code:
py1 = 25
py2 = 15
print (py1 & py2)
print (py1 | py2)
print (~py1)
print (py1 ^ py2)Output:
5. Assignment Operator
Below is the example of assignment operators as follows. In the below example, we have performing =, +=, -=, and *= operations.
Code:
py1 = 15
py2 = py1
print (py2)
py2 += py1
print (py2)
py2 -= py1
print (py2)
py2 *= py1
print (py1)Output:
6. Identity Operator
Below is the example of an identity operator as follows. In the below example, we are performing and are not operating as follows.
Code:
py1 = 15
py2 = 25
py3 = py1
print (py1 is not py2)
print (py1 is py3)Output:
7. Membership Operator
Below is the example of a membership operator as follows. In the below example, we are performing in and not in operation.
Code:
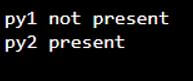
py1 = 15
py2 = 43
py_list = [27, 19, 43, 67, 84]
if (py1 not in py_list):
print ("py1 not present")
if (py2 in py_list):
print ("py2 present")Output:
Python 3 Operators Arithmetic
Below is the arithmetic operator available in python:
1. Addition
This operator is used to add two numbers.
The below example shows the addition operator.
Code:
py1 = 15
py2 = 43
print (py1+py2)Output:
2. Subtraction
This operator is used to subtract two numbers.
The below example shows the subtraction operator.
Code:
py1 = 15
py2 = 43
print (py1-py2)Output:
3. Division
This operator is used to divide two numbers.
The below example shows the division operator.
Code:
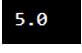
py1 = 25
py2 = 5
print (py1/py2)Output:
4. Multiplication
This operator is used to multiply two numbers.
The below example shows the multiplication operator.
Code:
py1 = 25
py2 = 5
print (py1*py2)Output:
5. Modulus
This operator is used to return the remainder.
The below example shows the modulus operator.
Code:
py1 = 37
py2 = 5
print (py1%py2)Output:
Python 3 Operators Comparison
Below is the comparison operator available in python as follows:
- Greater than (>)
- Less than (<)
- Greater than or equal to (>=)
- Less than or equal to (<=)
- Equal to (==)
- Not equal to (!=)
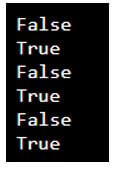
Below example shows the python 3 comparison operator as follows:
Code:
py1 = 19
py2 = 39
print(py1 > py2)
print(py1 < py2)
print(py1 == py2)
print(py1 != py2)
print(py1 >= py2)
print(py1 <= py2)Output:
Python 3 Operators Values
While using any operator in python, we need first assign a value to the variable; after assigning the value, we are doing the operation.
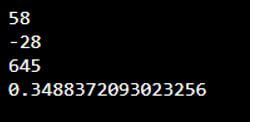
In the below example, we are declaring two-variable names as py_val1 and py_val2 as follows.
Code:
py_val1 = 15
py_val2 = 43
print (py_val1+py_val2)
print (py_val1-py_val2)
print (py_val1*py_val2)
print (py_val1/py_val2)Output:
Conclusion
The operator module provides a set of high-performance functions that correspond to python’s intrinsic operators. For example, python 3 operators are used to manipulate values and variables. There are multiple types of operators available in python. Types of operators are divided into their operations, which they perform on the operand.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python 3 Operators. Here we discuss the introduction, types of Python 3 operators, comparison, and values, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –