Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Versions
PowerShell provide a command-line powerful interface to perform various automation works. If you are aware of Linux and mac command line, PowerShell command-line is the same. PowerShell’s first release was in 2006 with its version 1.0. This version supports Windows XP SP2, Windows Server 2003 SPI, and Windows Vista. Every version comes with a few more supports and commands. So currently PowerShell version 6 is going on as stable version and 7 is about to come. PowerShell version 6 supports Windows, Mac, and Linux operating systems. So in very simple terms, the biggest change in its version is support for another platform, which means support for operating systems other than Windows. In another version, there are additions of a few more commands and syntax.
Different Versions of PowerShell
Below are the 9 Different versions of PowerShell:
1) PowerShell 1.0
PowerShell version 1.0 was the very basic version, and it supports Windows XP SP2, Windows Server 2003 SPI, and Windows Vista.
2) PowerShell 2.0
Till PowerShell 1 we were only capable to write commands for the local machine, that is, we were only able to control local machines, but in PowerShell 2 with the help of WS-management, we can write our commands for a remote machine (remote machine means accessing others computer from your computers).
New changes in PowerShell 2.0 are given below:
- Background Jobs: Here, to invoke asynchronous any job it uses a Background job, and it waits for user input, for example, you are running any script and you want that script should ask the input value than only it should execute.
- Introduction of Transactions: In this PowerShell provides the ability to write commands where a developer can roll back their changes.
- Modules: This gives PowerShell the ability to self-managed, in very simple we can write a script and this script can be a command for another script, and define our own features to be used in other scripts.
- Data Language: It allows localization, means we can write a script on one domain and when the same script will run on other domains then the local string will be imported at the runtime of script.
- Debugging of Scripts: It allows us to set any breakpoint into the script for debugging.
- Network File Transfer: With the introduction of Background Intelligent Transfer Service in PowerShell, it becomes able to asynchronous file transfer between two machines.
3) PowerShell 3.0
PowerShell 3.0 releases on 02 December 2011 and it supported Windows 7,8 including Windows Server 2012. The new improvements are given below:
- Jobs Scheduling: We can set any time for jobs to be run, for example, if you have jobs A, B, C then it can be scheduled time for execution of all these jobs.
- Session Connectivity: Control over remote sessions, When a script needs it can connect and disconnect to session.
- Support for Delegation: It can delegate a user with less permission for Administrative tasks.
- Detect Automatic Modules: It gives power to PowerShell scripts to load modules implicitly when it was needed by scripts.
New Commands and Features: There are many new commands also added in this version, like get-WmiObject, dwin32_logicaldisk, volumes, firewalls, It also includes network connectivity and also allows us to handle printers.
4) PowerShell 4.0
in this version, it starts supporting Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2. PowerShell 4.0 introduced a few new features they are.
- Save-Help: One of the important improvements in PowerShell 4.0 is it allow you to save Help for that module which is remote.
- Improved Debugging: Debugging was already there, but i PowerShell 4.0 it comes with few more debugging features like workflow support, able to execute remote debug remote machine.
- Switch Option in -PipelineVariable: To expose the current pipeline we use PipelineVariable.
- Desired State Configuration: In simple terms, this version of PowerShell allows us to configure a system where it can recognize the machine.
- Where and ForEach: Where and ForEach method syntax provides an alternate method of filtering and iterating over objects.
Example:
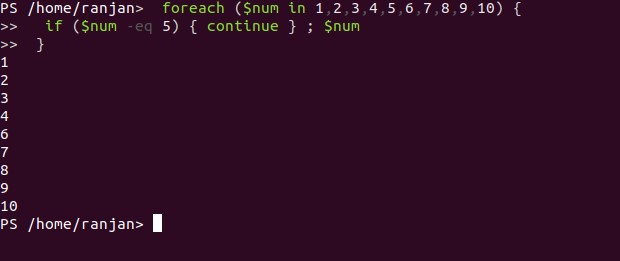
The example of foreach in the below screen, here we are displaying all numbers except number 5, this could be useful for filtering data.
foreach ($num in 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10) {
if ($num -eq 5) { continue } ; $num
}
Output:
Example:
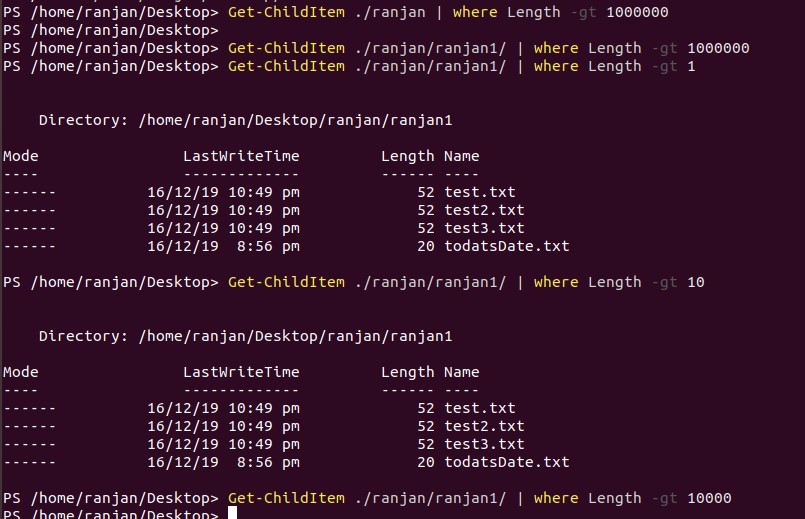
The Example of where is given below:
Get-ChildItem ./ranjan/ranjan1/ | where Length -gt 10
Output:
5) PowerShell 5.0
The main features include in PowerShell 5.0 are OneGet command which supports Chocolatey’s.
Example:
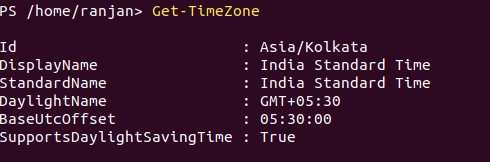
It introduced two new commands called Get-TimeZone and Set-TimeZone.
Get-TimeZone
Output:
6) PowerShell 6.0
This release was one of the measured releases, as in this release is made PowerShell as cross-platform. Cross-platform means are independent of any operating system(support, for example, macOS, Linux, and Windows). It becomes free and completely open-source. This release was achieved on 10th January 2018 and it is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
7) PowerShell Core 6.1
Some of the important features added in 6.1 are given below:
- Ability to support 1900 commands to Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019.
- It builds on .NET core 2.1.
- support all new versions of Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- There was also an improvement in performance.
8) PowerShell Core 6.2
In this release mostly bug fixing and some performance enhancements work has been done.
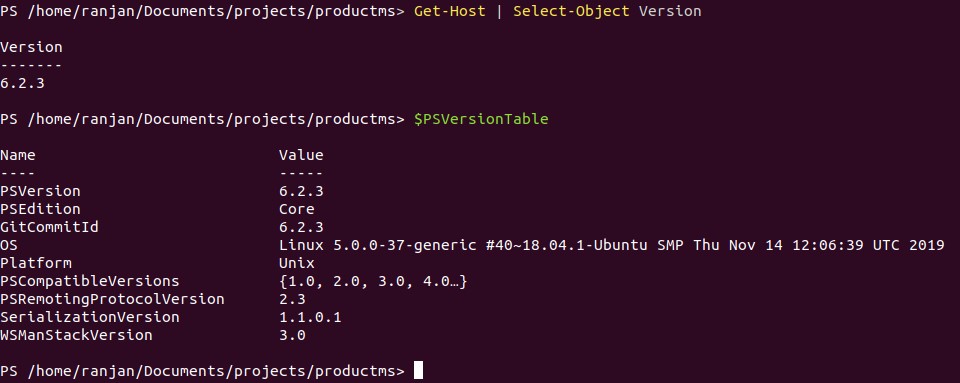
Example:
In this example, I am using PowerShell 6.2 and checking my Operating system details.
Get-Host | Select-Object Version
$PSVersionTable
Output:
The above example shows how I am able to run PowerShell on Linux with PowerShell version 6.2. If i will go with any older version than it would not work.
9) PowerShell 7
New features in PowerShell 7 include:
- It is based on the .NET Core 3.1.
- ForEach-Object -Parallel.
- Windows compatibility wrapper.
- Notification for new versions.
- Get-Error cmdlet to handle errors powerShell.
- Options for Pipeline chain operators which is && and ||.
- It includes ternary operators like (x ? y: z), so if you are using PowerShell version 7 then the only a ternary operator will work.
- Out-GridView, -ShowWindow are some new commands.
Conclusion
From version 1 to 7 every version comes with some new commands and features, but they did big architectural changes by supporting operating systems other than Windows like macOS and Linux.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Versions. Here we discuss the basic concept and top 9 different PowerShell versions along with the examples. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –