Updated March 17, 2023
How To Install PowerShell
The following article provides an outline for How To Install PowerShell. PowerShell is a task automation engine from Microsoft with a command-line shell and associated scripting language. Windows PowerShell is an open-source whose base source code is available on GitHub. It is built on a .NET framework, while the PowerShell Core is built on .NET Core. It helps administrators and IT professionals to automate system tasks, configure and manage operating systems such as Windows, Linux and macOS, and their applications and processes. Its equivalent in Linux is known as Bash Scripting. It is an object-oriented engine, i.e. it is based on objects. Commands of Windows PowerShell are called cmdlets which are .NET classes. These perform an action and, as output, returns an object that can be pipelined as an input to another command.
PowerShell functions are grouped together for managing particular tasks called PowerShell Modules. These modules allow administrators to reuse the script or code for the automation of a task. The host application for Windows PowerShell is the Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE). It can access command-line tools, .NET class libraries, and COM objects. There are many versions of PowerShell released till date. It was first made public in September 2003 at the Professional Developers Conference with the name Monad. All versions of Windows PowerShell are compatible with the previous versions of it.
Different Versions of PowerShell
Different versions of PowerShell are as follows:
1. PowerShell 1.0
This was released in November 2006 supported by Windows Server 2003 SP1, Windows XP SP2, and Windows Vista.
2. PowerShell 2.0
These released in October 2009 are integrated with Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7. Other available Windows versions that support it are Windows XP Service Pack 3, Windows Vista with Service Pack 1, and Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2. Additional features like transactions, PowerShell remoting, Steppable Pipelines, Modules, Script debugging, Eventing, Windows Powershell Integrated Scripting Environment, block comments, new cmdlets, and operators were included.
3. PowerShell 3.0
It was released in September 2012 integrated with Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012. It was made available for Windows Server 2008 with Service Pack 2, Windows 7 with Service Pack 1, and Windows Server 2008 R2 with Service Pack 1. It is a part of Windows Management Framework 3.0, which was made available to the general public in December 2012. New features like session connectivity, scheduled jobs, and Automatic module detection were added.
4. PowerShell 4.0
It was released in October 2013 integrated with Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2. It is also supported by Windows 7 with Service Pack 1, Windows Server 2012, and Windows Server 2008 R2 with Service Pack 1. The default execution Policy was made RemoteSigned, and debugging was enhanced.
5. PowerShell 5.0
It was released in February 2016 integrated with Windows 10 and was made available for Windows 8.1, Windows 7 with Service Pack 1, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012. Additional features like PowerShell .NET enumerations, Debugging for PowerShell Background Jobs, class definitions, DSC partial configurations, and many more were included.
6. PowerShell 5.1
This was released in January 2017 with the Windows 10 Anniversary Update and in Windows Server 2016. It is the first version that came with two editions of Desktop and Core.
7. PowerShell Core 6.0
It was released to the public on 10 January 2018, while it was announced on 18 August 2016. It is supported in many Windows versions like Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7 with Service Pack 1, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2016.
Steps to Install PowerShell
Now let us see how to install Windows PowerShell 3.0 on Windows 7:
If you are using versions like Windows 8, 8.1, Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2, then Windows PowerShell 3.0 would be preinstalled in your systems, but if you are working on Windows 7 or Windows Server 208 R2, then Windows PowerShell 3.0 may or may not be preinstalled. There is a possibility that you may be working with version 2.0, which come preinstalled in these versions of Windows.
You can update the version from 2.0 to 3.0. But first, you must ensure that on which version of Windows Powershell you are working. So to check the version.
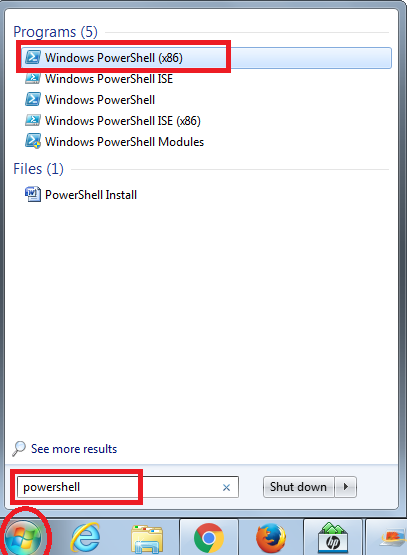
Step 1: Click on Start, type PowerShell in the search column and select PowerShell console.
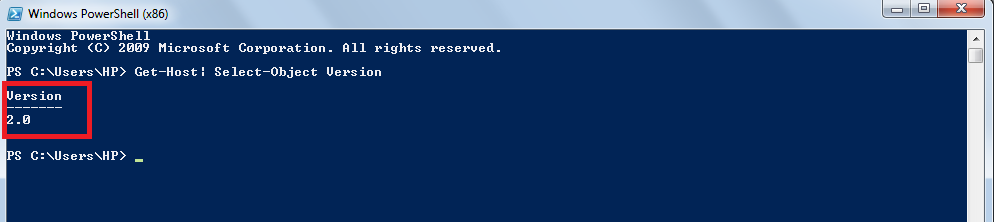
Step 2: The PowerShell console will open. Then type the command:
Get- Host | Select-Object Version
The output of that command will tell you the version.
If the version is 3.0, then you can start working, but if the version is 2.0, then you need to update it. For this, you must install Windows PowerShell 3.0.
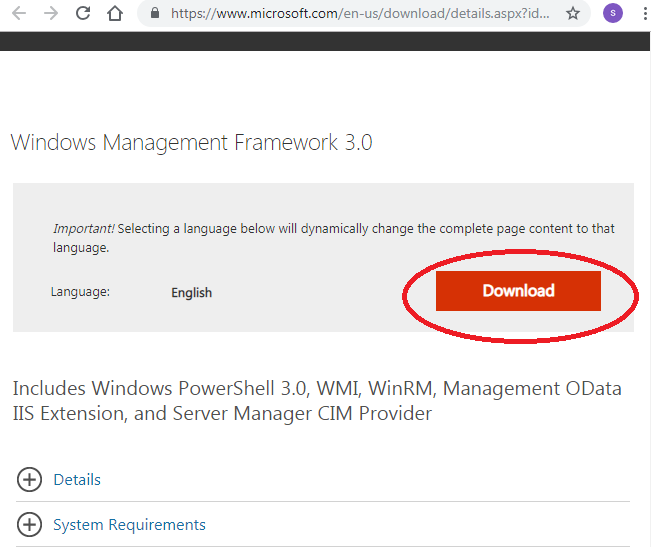
Step 3: You have to download Windows Management Framework 3.0, which has Windows PowerShell 3.0 already included from Microsoft Download Centre. (https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=34595)
When you open this URL following window will appear; click on download to download the Windows Management Framework 3.0.
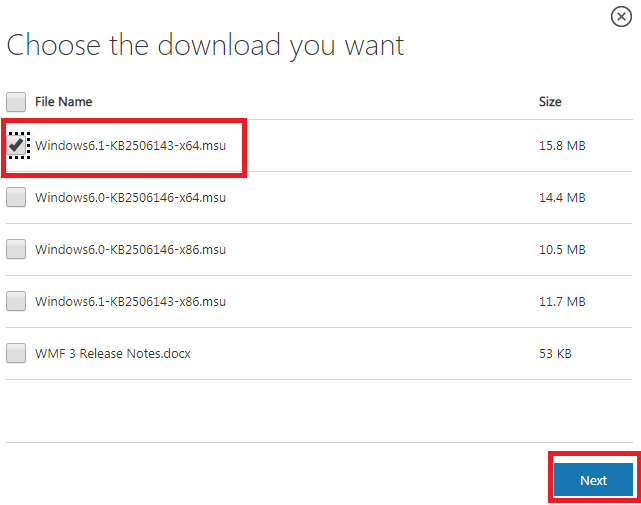
Step 4: Choose the desired file and click on next.
Step 5: The file would be downloaded on your system. Open it.
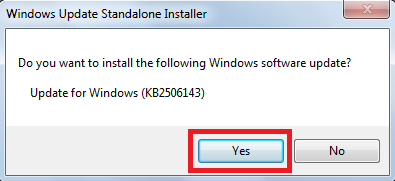
Step 6: It will ask you whether to install it or not. Click on YES.
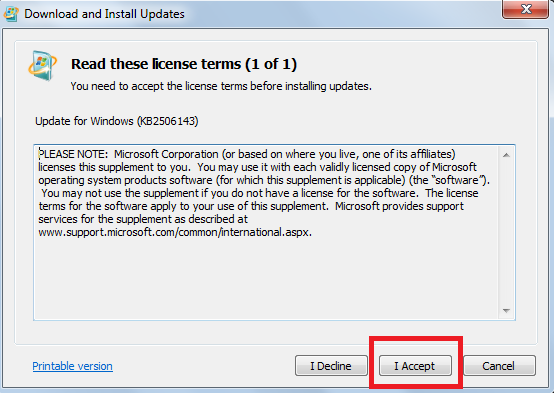
Step 7: License terms document would appear. Select “I Accept”.
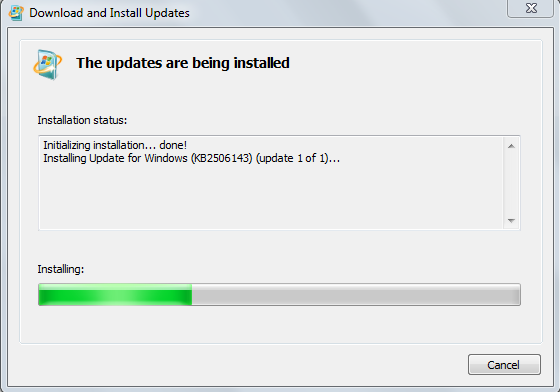
The installation will begin.
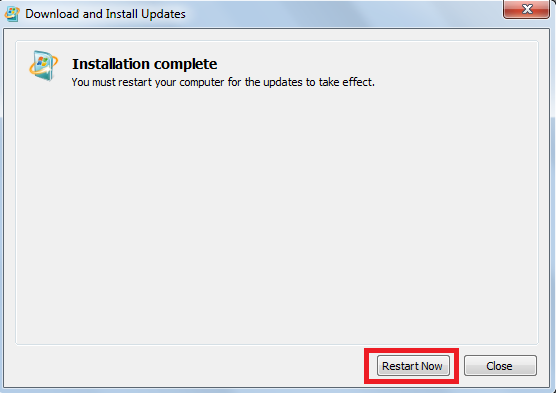
Step 8: It will ask to restart the system. Click on Restart Now.
After proper installation, you must ensure that it has been configured for running remote scripts; to do that, run it as an administrator.
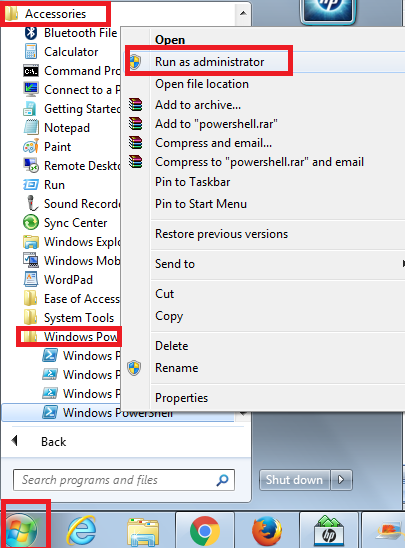
Step 9: Click Start -> All Programs -> Accessories -> Windows PowerShell -> right click Windows PowerShell -> Run as administrator.
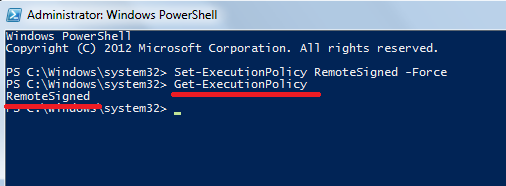
Step 10: After this, change the execution policy to allow the running of remote scripts.
- Type: Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned –Force.
And press ENTER.
To verify that execution policy.
- Type: Get-ExecutionPolicy.
If the output is RemoteSigned, then everything is configured, and you can start working.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to How to Install PowerShell. Here we have discussed the basic concept, different versions and steps to install PowerShell on our system. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –