Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Stop Service
Stop-Service cmdlet in PowerShell is used to stop the running service on the local computer or remote computers. You can stop one or multiple services together. For example, service can be stopped by Name, Display Name, or the Input Object.
Syntax:
The Stop-Service command uses the below syntaxes.
Stop-Service
[-Force]
[-NoWait]
[-Name] <String[]>
[-InputObject] <ServiceController[]>
[-DisplayName] <String[]>
[-PassThru]
[-Include <String[]>]
[-Exclude <String[]>]
[-WhatIf]
[-Confirm]
[<CommonParameters>]
Parameters
Here are the following parameters of PowerShell Stop-Service
1. -Name
This parameter is used for the service name or the alias name. You can use the wildcard character (*). To stop the multiple services, you can separate them by comma (,). For example, the Print Spooler service has the alias name Spooler, like all other services have their own alias names.
2. –DisplayName
When you use this parameter, you need to provide the display name of the service. It is a string datatype. You can provide multiple display names separated by comma (,). Wildcard character (*) is permitted. For example, “Windows Management Instrument” is the display name of the winmgmt service alias.
3. –InputObject
You can provide multiple services as a variable to the input object parameter to stop the services on the local and remote computers.
4. –Include
This parameter specifies the service name to include when you stop any service. The value of this parameter qualifies the Name parameter. You can use the wildcard character (*). For example, When you specify S*, it will stop all the services starting with S.
5. –Exclude
This parameter specifies the service name to exclude when you stop any service. The value of this parameter qualifies the Name parameter. You can use the wildcard character (*). For example, when you specify S*, it will stop the remaining services, excluding the services starting with S.
6. –Passthru
By default, Stop-Service doesn’t display the output in the PowerShell console. When you use this parameter, the output will be displayed in the PowerShell console.
7. –WhatIf
When this parameter is used, it shows the operation going to perform when the Stop-Service will run, without running the actual command.
8. –Confirm
This parameter will prompt for user consent before stopping the service(s). Below options are available with the –Confirm parameter.
[Y] Yes [A] Yes to All [N] No [L] No to All [S] Suspend [?] Help (default is “Y”):
Y (Yes) – It will stop the single service, and if there are multiple services, the check will run again for the next service.
A (Yes to All) – It will stop all the services provided in the Stop-Service command.
N (No): It will not stop the single service, and if there are multiple services, the check will run again for the next service.
L (No to All): It will not stop all the services provided in the Stop-Service command.
S (Suspend): It will skip the service from stopping, which means it will leave the service in the current state.
9. –Force
Using the Force parameter will stop the services even if the service has the dependent services running. So it first stops the dependent services and, latter, the service itself.
10. –NoWait
When you specify the –Nowaitparameter, the PowerShell console doesn’t wait for the service to stop, and execution moves to the next code.
11. –CommonParameters
Below common parameters are supported by the Stop-Service.
-Verbose, -Debug, -ErrorAction, -ErrorVariable, -WarningVariable, -WarningAction, -OutBuffer, -OutVariable.
Examples of PowerShell Stop Service
Different examples are mentioned below:
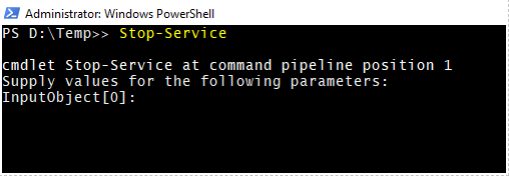
1. Stop-Service cmdlet
When you just write the Stop-Service, it will wait for the input object, as shown below. Input Object can be Service alias name, Display Name, or the InputObject like a variable.
Stop-Service
Output:
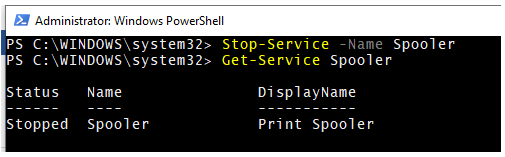
2. Stop-Service with the –Name Parameter
You can provide the Service name (alias name) after the –Name parameter. Stop-Service cmdlet takes the –Name as the default parameter. You will not get any output in the console when you stop the service. You need to use the Get-Service command to retrieve the status of the service. You can also use –PassThru parameter that is explained later in subsequent examples.
Stop-Service -Name Spooler
Get-Service Spooler
Output:
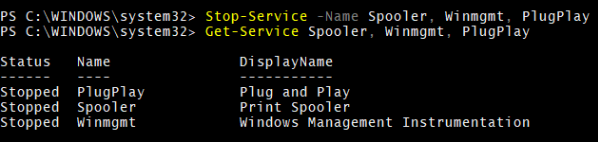
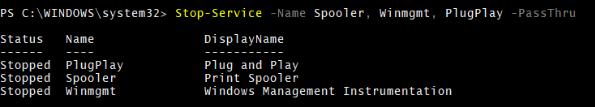
You can stop multiple services by separating them with a comma (,). For example,
Stop-Service -Name Spooler, Winmgmt, PlugPlay
Get-Service Spooler, Winmgmt, PlugPlay
Output:
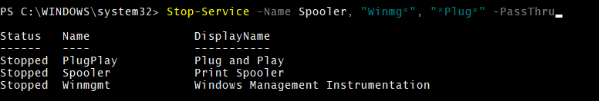
You can also use the wildcard character (*) as well.
For example,
Stop-Service -Name Spooler, "Winmg*", "*Plug*" -PassThru
Output:
3. Stop-Service with the –Passthru parameter
In the above example, we have seen that we need to use the Get-Service cmdlet to get the service status. You can also use –Passthru parameter, which displays the output in the console itself.
Stop-Service -Name Spooler, Winmgmt, PlugPlay -PassThru
Output:
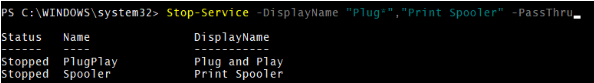
4. Stop-Service with the –DisplayName parameter
You can provide the display names as an input to the Stop-Service to stop the services.
For example,
Stop-Service -DisplayName "Plug*","Print Spooler" -PassThru
Output:
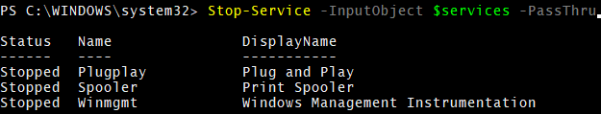
5. Stop-Service with the –InputObject Parameter
Here, we will store a few service alias names in the variable and pass it to the InputObject parameter.
$services = "Spooler","Plugplay","Winmgmt"
Stop-Service -InputObject $services -PassThru
Output:
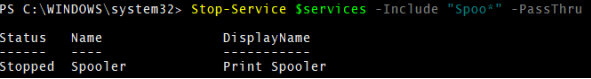
6. Stop-Service with the –Include Parameter
In the given variable below, we will need to stop only the “Print Spooler” service. So when we use –Include parameter, it will include Spooler service only.
$services = "Spooler","Plugplay","Winmgmt"
Stop-Service $services -Include "Spoo*" -PassThru
Output:
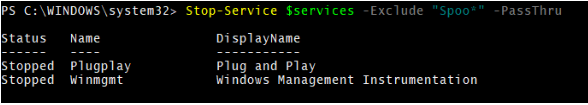
7. Stop-Service with –Exclude Parameter
The variable given below will exclude the Spooler service, so the other two services will be restarted automatically.
$services = "Spooler","Plugplay","Winmgmt"
Stop-Service $services -Exclude "Spoo*" -PassThru
Output:
8. Stop-Service with –WhatIf parameter
Whatif parameter will predict the command execution without actually executing the command. An example is shown below.
Stop-Service -Name Spooler -WhatIf
Output:
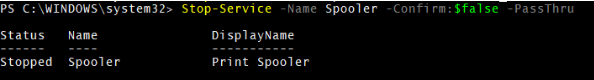
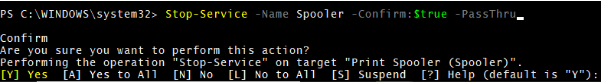
9. Stop-Service with –Confirm Parameter
You can use the –Confirm parameter with the Boolean values ($true or $false). When you specify $true, service will not be stopped, but it will prompt for user consent, and with the $false, service will be stopped.
Stop-Service -Name Spooler -Confirm:$false -PassThru
Output:
Stop-Service -Name Spooler -Confirm:$true -PassThru
Output:
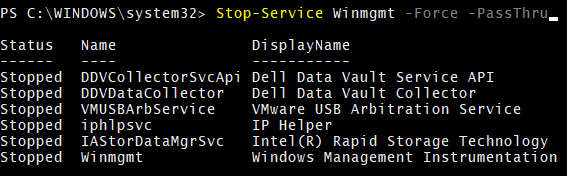
10. Stop-Service with –Force Parameter
Few services have dependent services and can’t be stopped directly without stopping the dependent services. So –Force parameter stops the service and its dependent services. For example, Winmgmt service.
Stop-Service Winmgmt -Force -PassThru
Output:
11. Stop-Service with –NoWait parameter
Some services take time to stop, and execution halts until then. For example, the –NoWait parameter stops in the background, and execution moves to the next code.
For example,
Stop-Service Winmgmt -NoWait -PassThru
Output:
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Stop Service. Here we discuss the Examples of PowerShell Stop Service along with the syntax and parameters. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –