Updated May 19, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Number Types
PostgreSQL number type consists of two, four, and 8 byte integer or floating point number values, there multiple types of number is available in PostgreSQL. Basically, there are main four number types available in PostgreSQL, i.e., integer types, arbitrary precision numbers, floating point types, and serial types, each numeric type have its subtypes available in PostgreSQL. It is used to store the number values in the database table.
Different PostgreSQL Number Types
Given below are the different Number Types:
- Smallint
- Integer
- Bigint
- Decimal
- Numeric
- Real
- Double precision
- Smallserial
- Serial
- Big serial
Each number type have its different storage size and have its own range. Number type in PostgreSQL consist of the 2 byte, 4 byte, and 8 byte integer types, 4 byte and 8 byte floating point numbers, and the precision decimal in PostgreSQL.
1. Smallint
The storage size of the smallint number type in PostgreSQL is 2 bytes, and the range of the small int type in PostgreSQL is -32768 to 32767. Smallint numeric type is used when disk size is less, and we don’t require a value greater than 32767.
Syntax:
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column smallint, name_of_column datatype);Example:
Code:
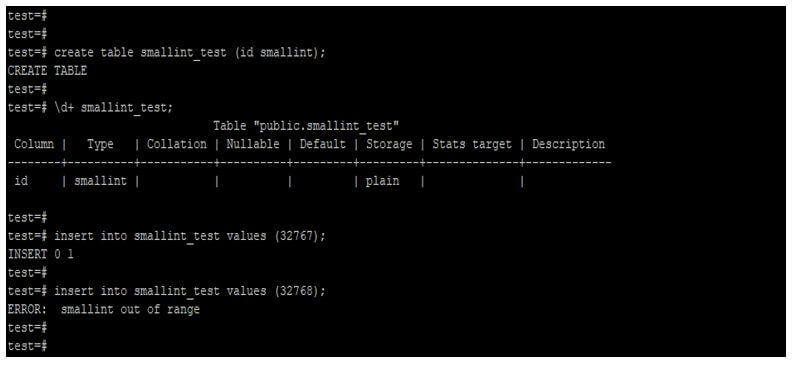
create table smallint_test (id smallint);
\d+ smallint_test;
insert into smallint_test values (32767);
insert into smallint_test values (32768);Output:
2. Integer
The storage size of the integer number type is 4 bytes, and the range of integer type in PostgreSQL is -2147483648 to 2147483647.
Syntax:
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column int, name_of_column datatype);Example:
Code:
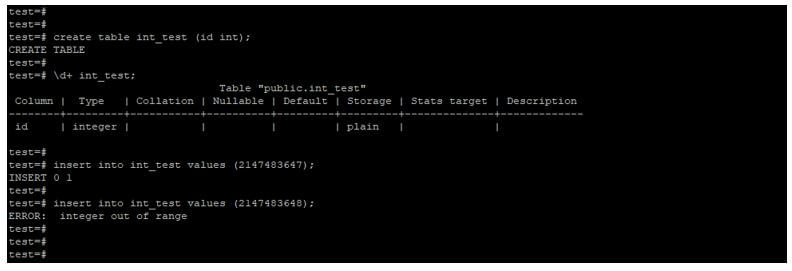
create table int_test (id int);
\d+ int_test;
insert into int_test values (2147483647);
insert into int_test values (21474836478);Output:
3. Bigint
The storage size of the bigint number type is 8 bytes, and the range of the bigint int type is -9223372036854775808 to +9223372036854775807.
Syntax:
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column bigint, name_of_column datatype);Example:
Code:
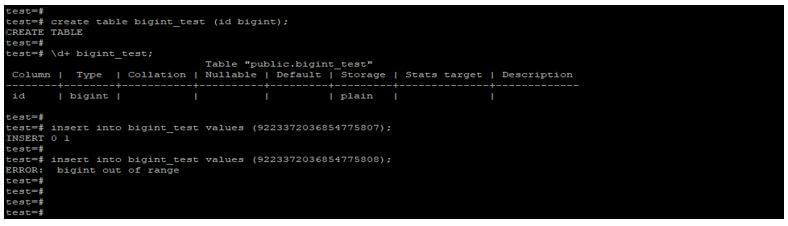
create table bigint_test (id bigint);
\d+ bigint_test;
insert into bigint_test values (9223372036854775807);
insert into bigint_test values (9223372036854775808);Output:
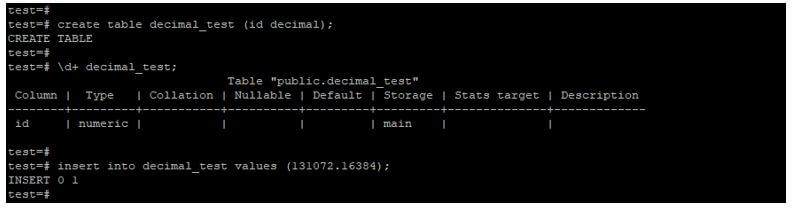
4. Decimal
The decimal number type storage size is variable, and the range of decimal type is 16384 digits after the decimal point and 131072 before the decimal point.
Syntax:
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column decimal, name_of_column datatype);Example:
Code:
create table decimal_test (id decimal);
\d+ decimal_test;
insert into decimal_test values (131072.16384);Output:
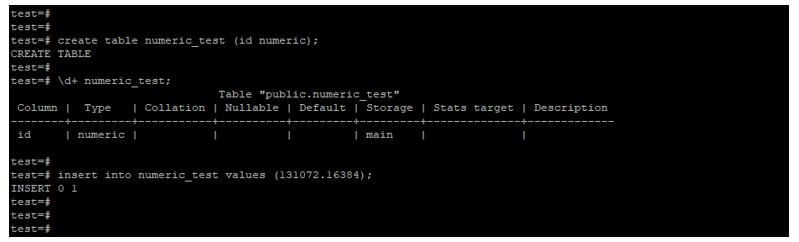
5. Numeric
The storage size of the numeric number type is variable, and the range of the numeric type is 16384 digits after the decimal point and 131072 before the decimal point.
Syntax:
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column numeric, name_of_column datatype);Example:
Code:
create table numeric_test (id numeric);
\d+ numeric_test;
insert into numeric_test values (131072.16384);Output:
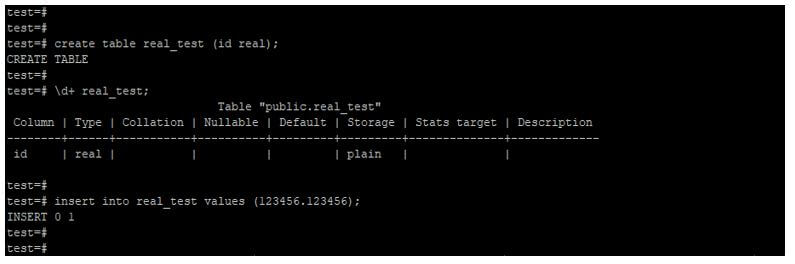
6. Real
The storage size of the real number type is 4 bytes, and the range of the real type is 6 decimal digits precision.
Syntax:
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column real, name_of_column datatype);Example:
Code:
create table real_test (id real);
\d+ real_test;
insert into real_test values (123456.123456);Output:
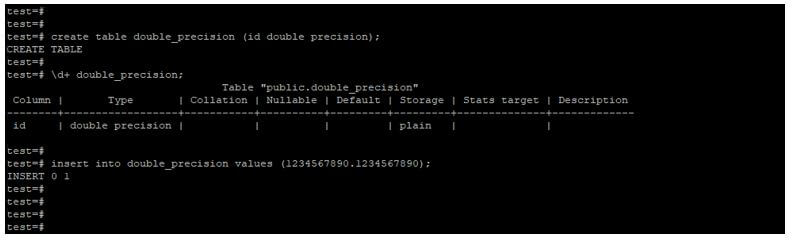
7. Double precision
The storage size of the double precision number type is 8 bytes, and the range of the double precision type is 15 decimal digits precision.
Syntax:
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column double precision, name_of_column datatype);Example:
Code:
create table double_precision (id double precision);
\d+ double_precision;
insert into double_precisionvalues (1234567890.1234567890);Output:
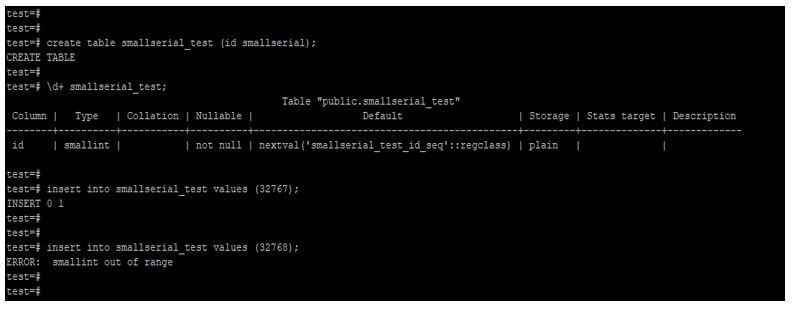
8. Smallserial
The storage size of smallserial number type is 2 bytes, and the range of smallserial type is 1 to 32767.
Syntax:
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column smallserial, name_of_column datatype);Example:
Code:
create table smallserial_test (id smallserial);
\d+ smallserial_test;
insert into smallserial_test values (32767);
insert into smallserial_test values (32768);Output:
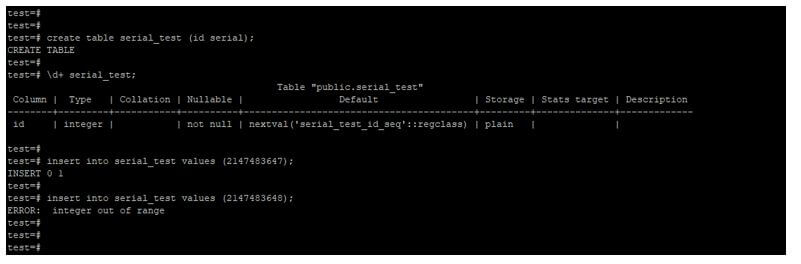
9. Serial
The storage size of the serial number type is 4 bytes, and the range of serial type is 1 to 2147483647.
Syntax:
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column serial, name_of_column datatype);Example:
Code:
create table serial_test (id serial);
\d+ serial_test;
insert into serial_test values (2147483647);
insert into serial_test values (2147483648);Output:
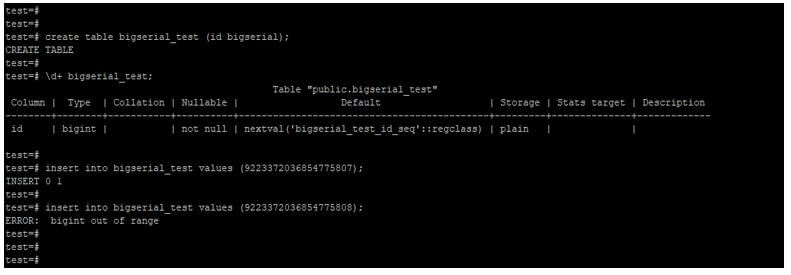
10. Bigserial
The storage size of bigserial number type is 8 bytes, and the range of bigserial type is 1 to 9223372036854775807.
Syntax:
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column bigserial, name_of_column datatype);Example:
Code:
create table bigserial_test (id bigserial);
\d+ bigserial_test;
insert into bigserial_test values (9223372036854775807);
insert into bigserial_test values (9223372036854775808);Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Number Types” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.