Updated May 8, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Interval
We can store and manage the time period in seconds, minutes, hours, days, months, years, etc., by using the interval data type provided by PostgreSQL. The interval value is quite easy to understand, and it is human-readable. The interval value needs 16 bytes storage size, which stores a period with a low value of -178000000 years and a high value of 178000000 years. They provide us with different interval styles like Postgres, sql_standard, and ISO-8601 postgres_verbose to format the interval value; by default, PostgreSQL uses Postgres style to format the interval values. It contains various functions to manipulate the interval value data; also, we can perform different arithmetic operations on an interval value.
Syntax:
1. Interval Syntax
interval [ fields ] [ (p) ]Explanation:
p: defines the number of fraction digits that should remain in the seconds. In the case of the interval types, the valid range for p is 0 to 6.
2. Interval value
We can write the interval values with the help of the following syntax:
quantity unit [quantity unit...] [direction]Explanation:
- Quantity: Quantity defines a number that can be either positive or negative so that we can also add a + or – sign.
- Unit: It can be any of the following:(decade, century, millennium), (week, month, year), (minute, hour, day), (microsecond, millisecond, second,) abbreviations like d, m, y, etc., plural forms like days, months, years, etc.
- Direction: The direction can be an empty string or ago.
How Does Interval Function Work in PostgreSQL?
1. PostgreSQL internally stores the interval values as seconds, days, and months. The value of days and months is stored as integers, and the second field’s value might contain some fractions.
2. We can restrict the set of stored fields by using any of the following words in case of the interval type:
YEAR, MONTH, DAY, HOUR. MINUTE. SECOND. YEAR TO MONTH. DAY TO HOUR, DAY TO MINUTE, DAY TO SECOND, HOUR TO MINUTE, HOUR TO SECOND, MINUTE TO SECOND, etc.
3. The PostgreSQL provides various functions like TO_CHAR(), justify_days(), justify_hours(), justify_interval() and EXTRACT() etc. to manipulate the PostgreSQL interval value.
4. The value returned by the extract function retains double precision.
Examples
1. Consider the following statements and snapshots, to begin with, examples of interval values:
Query:
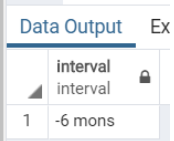
select interval '6 months ago';Output:
Query:
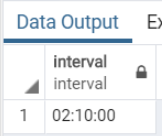
select interval '2 hours 10 minutes';Output:
2. Consider the following statements and snapshots to know the time of 1 hour 10 minutes ago of the last two years at the current time.
Query:
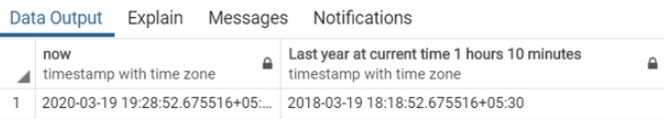
SELECT
now(), now() - INTERVAL '2 year 1 hours 10 minutes' AS "Last year at current time 1 hours 10 minutes";Output:
3. PostgreSQL Interval operators
We can manipulate the interval values using arithmetic operators like +, -, *, etc.
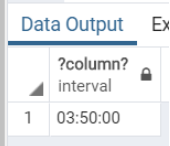
Query:
SELECT
INTERVAL '3h 30m' + INTERVAL '20m';Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot:
Output:
Query:
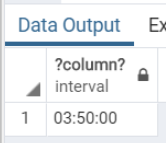
SELECT
INTERVAL '4h 20m' - INTERVAL '30m';Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot:
Output:
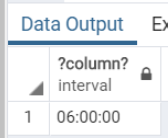
Query:
SELECT
180 * INTERVAL '2 minute';Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot:
Output:
4. PostgreSQL interval value to string conversion
We can convert an interval value to the string by using a TO_CHAR() function provided by PostgreSQL as follows:
Syntax:
TO_CHAR(interval, format)Explanation:
- Interval: The interval value.
- Format: the format to which we want to convert the interval value.
The TO_CHAR() function returns us the string of interval values converted in the specified format.
Consider the following statement to understand the TO_CHAR() Function:
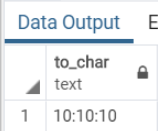
Query:
SELECT
TO_CHAR(
INTERVAL '10h 10m 10s',
'HH24:MI:SS'
);Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot:
Output:
5. Extract fields from a PostgreSQL interval value.
We can extract data like date, month, year, etc., from an interval value using the EXTRACT() Function provided by PostgreSQL.
Syntax:
EXTRACT(field FROM interval)Explanation:
- Field: This can be the minutes, hours, date, month, year, etc., which we want to extract.
- Interval: The interval value.
Consider the following statement to understand the EXTRACT() Function:
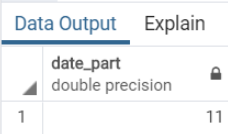
Query:
SELECT
EXTRACT (
MINUTE
FROM
INTERVAL '4 hours 11 minutes'
);Here we have extracted the minute field as 4 hours 11 minutes, and as a result, we have the expected minute value of 11.
Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot:
Output:
6. Adjust the PostgreSQL interval value.
We can use the justify_days and justify_hours functions provided by PostgreSQL to adjust the interval values.
Consider the the following statement to understand the justify_days() and justify_hours() functions:
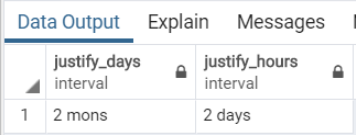
Here we will adjust an interval value of 60 days and an interval value of 48 hours by using the justify_days() and justify_hours() functions.
Query:
SELECT
justify_days(INTERVAL '60 days'),
justify_hours(INTERVAL '48 hours');Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot:
Output:
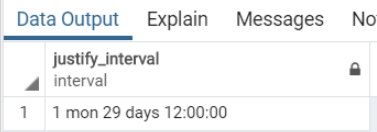
Also, PostgreSQL provides the justify_interval Function, which will adjust interval value by using justify_days and justify_hours functions, having a sign adjustment as follows.
Query:
SELECT
justify_interval(interval '60 days -12 hour');Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot:
Output:
Advantages
- The PostgreSQL interval values are helpful when dealing with date and time manipulation.
- We can use various functions provided by PostgreSQL, like O_CHAR(), justify_days(), justify_hours(), justify_interval(), and EXTRACT(), etc. to manipulate the PostgreSQL interval value.
- As having various Function to deal with an interval in PostgreSQL, we can use it in the scheduling mechanism.
- The interval data type is very easy and human-readable.
- We do not need to worry about managing the quantity – unit order, as explained in syntax in the interval; because of this, handling the interval is very easy.
Conclusion
We hope from the above article, you have understood how to use the PostgreSQL interval data type and how the PostgreSQL interval data type works to store the data. Also, we have added some examples of PostgreSQL intervals to understand them in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Interval” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.