Updated May 29, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL DATE_PART()
PostgreSQL DATE_PART() function is mainly used to return the part of the date and time; the date_part function in PostgreSQL will subtract the subfield from the date and time value. PostgreSQL date_part function will allow retrieving subfields from the date and time value, e.g., week, month, and year. Basically, there are two parameters we have a pass with the date_part function, i.e., field and source; field determines which field we have extracted from the source.
Syntax:
Given below is the syntax of the PostgreSQL date_part function:
date_part (text, timestamp)date_part (text, interval)date_part (unit, date)date_part (field, source)Given below is the parameter description of the above syntax:
- Date part: We use the date_part function in PostgreSQL to extract the date part values from an expression. We can provide an argument with the date_part function as text and timestamp in PostgreSQL.
- Text: The first parameter used with the date_part function in PostgreSQL is “text”.
- Timestamp: This is the second parameter of the date_part function in PostgreSQL. We have used to define the timestamp value with the date_part function in PostgreSQL.
- Interval: In PostgreSQL, we use the interval value the same as a timestamp value. We can use an interval instead of a timestamp value in PostgreSQL.
- Unit: Unit type in date_part function is interval such as minute, hour, and month. Unit is an essential parameter in the date_part function.
- Date: We use a date, timestamp, time, or interval value to perform partial execution.
- Field: The date_part function in PostgreSQL uses a parameter to specify which field to extract from the source.
- Source: In the date_part function, we define the second parameter as the source. This parameter specifies the date or timestamp to extract the specified field. This is the same as the interval parameter in the date_part function in PostgreSQL.
How PostgreSQL DATE_PART() Function works?
If we want to return only the date and time value in PostgreSQL same time, we are using the date_part function. Using the date_part function in PostgreSQL, we can extract the century from the time stamp. We must pass the field argument in the date_part function to extract the year from the date timestamp.
In PostgreSQL, the unit type has the following form used in the date_part function. The unit type is a day, month, minute, and hour.
- Century: It uses the Gregorian calendar in which the first century will start from the ‘0001-01-01 00:00:00 AD’.
- Day: Defined as the day of the month from 1 to 31.
- Decade: In the date_part function of PostgreSQL, we define a decade as the year divided by 10.
- Day of week: Defined as a day of the week from Sunday to Saturday.
- Day of year: We define this as the day of the year, ranging from January to December.
- Epoch: This is defined as several interval values in the date_part function.
- Hour: Defined as an hour of the day from 0 to 23.
- Millennium: In the date_part function, we define the millennium value.
- Milliseconds: This is defined as a second multiply with 1000.
- Microseconds: This is defined as a second multiply with 100000.
- Minute: This is defined as a minute of the hour from 0 to 59.
- Quarter: Quarter is defined in date_part function is 1 to 4.
- Second: This is a fractional second in the date_part function.
- Year: This is defined as a year in four-digit value.
To extract the second, minute, and hour from the timestamp using the date_part function, we need to pass the corresponding value that is second, minute, and hour.
Examples of PostgreSQL DATE_PART()
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
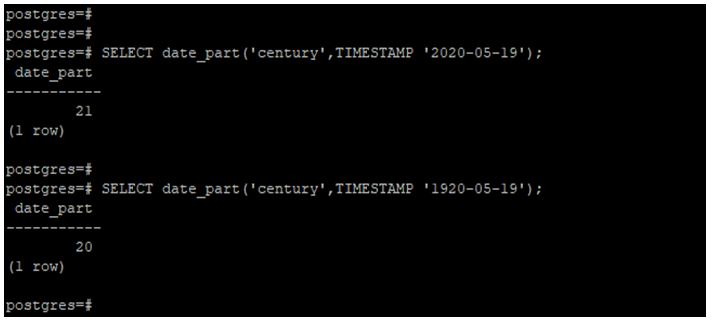
Extract the century from a timestamp using the date_part function.
In the example below, we used the years 2020 and 1920 to extract a century from the timestamp.
Code:
SELECT date_part('century', TIMESTAMP '2020-05-19');SELECT date_part('century', TIMESTAMP '1920-05-19');Output:
In the above example, the year 1920 will display a century as 20, and the year 2020 will display the century as 21.
Example #2
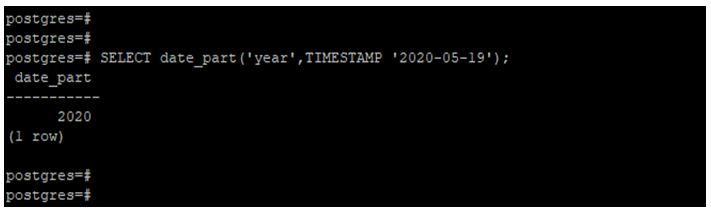
Extract the year from a timestamp using the date_part function.
In the below example, we have used the year 2020 to extract the year from the timestamp.
Code:
SELECT date_part('year', TIMESTAMP '2020-05-19');Output:
Example #3
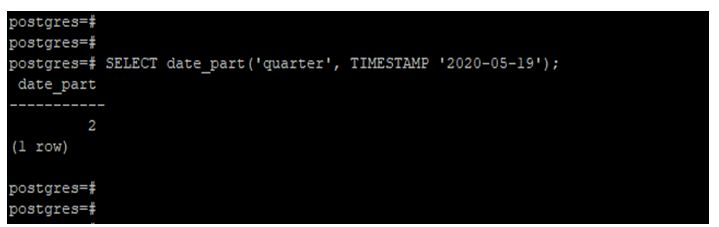
Extract a quarter from a timestamp using the date_part function.
In the below example, we have used the year 2020 to extract a quarter from the timestamp.
Code:
SELECT date_part('quarter', TIMESTAMP '2020-05-19');Output:
Example #4
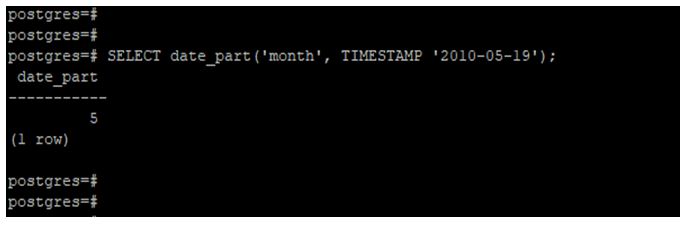
Extract a month from a timestamp using the date_part function.
In the below example, we have used a month as May to extract the month from the timestamp.
Code:
SELECT date_part('month', TIMESTAMP '2010-05-19');Output:
Example #5
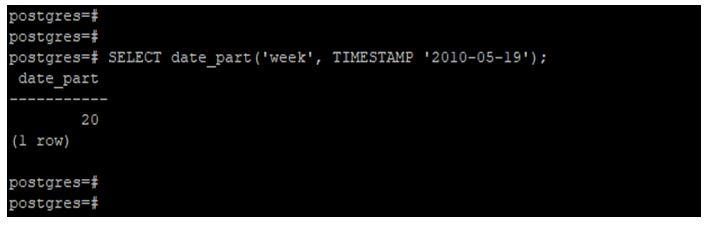
Extract a week from a timestamp using the date_part function.
In the below example, we have used the year 2010 and the month of May to extract the week from the timestamp.
Code:
SELECT date_part(week, TIMESTAMP '2010-05-19');Output:
Example #6
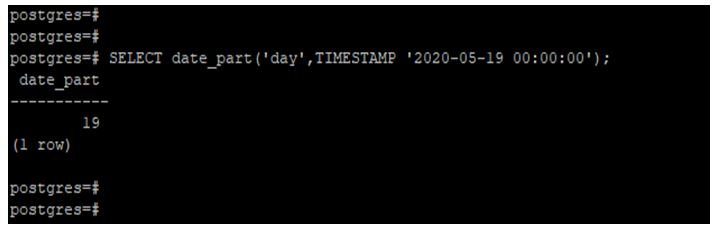
Extract the day from a timestamp using the date_part function.
In the below example, we have used the year 2020 and the month of May to extract the day from the timestamp.
Code:
SELECT date_part('day',TIMESTAMP '2020-05-19 00:00:00');Output:
Example #7
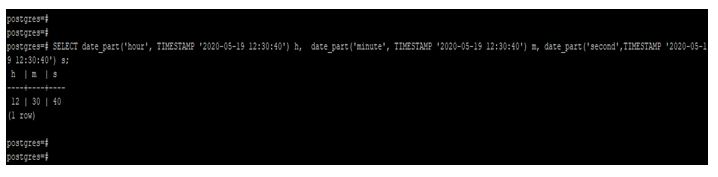
Extract hour, minute, and second from a timestamp using the date_part function.
The below example shows that Extract hour, minute, and second from a timestamp using the date_part function.
Code:
SELECT date_part('hour', TIMESTAMP '2020-05-19 12:30:40') h, date_part('minute', TIMESTAMP '2020-05-19 12:30:40') m, date_part('second',TIMESTAMP '2020-05-19 12:30:40') s;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL DATE_PART()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.