Updated May 10, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER
The PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER() function is a windows function. The ROW_NUMBER() function manipulates the set of rows, and the row’s set is termed as a window. We can use the PARTITION BY clause with the ROW_NUMBER() function, which is optional; if we have defined it, then it handles the set of rows or window like splitting the set of rows into subsets if the PARTITION BY clause is not defined, then the entire result set of rows considered as the single partition. Also, we can use the ORDER BY clause with the ROW_NUMBER() function to order the rows.
Syntax
Consider the following syntax:
ROW_NUMBER()
OVER
(
[PARTITION BY column_name_1, column_name_2,…]
[ORDER BY column_name_3,column_name_4,…]
)Explanation:
PARTITION BY: This is an optional clause in the case of the ROW_NUMBER() function. The PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER() divides a set of rows into partitions or smaller sets.
ORDER BY: This defines how the order of the numbers should be assigned in the OVER clause.
How does the PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER function work?
The ROW_NUMBER() function operates on a set of rows termed s a window.mIf the PARTITION BY clause is specified, then the row number will increment by one and start with one.
If we have not specified then PARTITION BY clause, then the ROW_NUMBER function will consider the entire window or set of results as a single partition.
We will create tables named ‘category’ and ‘items’ to understand the examples of the PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER() function in detail.
Consider the following CREATE TABLE statement to create the category and items tables.
CREATE TABLE category
Code:
(
category_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
category_name VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL
);CREATE TABLE items
Code:
(
item_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
item_name VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
item_price numeric,
category_id numeric
);Now, we will insert some data in the ‘category’ and ‘items’ tables by using the INSERT TABLE statement:
Code:
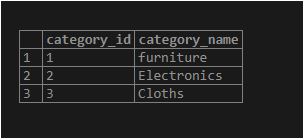
INSERT INTO category(category_name) values
('furniture'),
('Electronics'),
('Cloths');Output:
select * from category;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
Code:
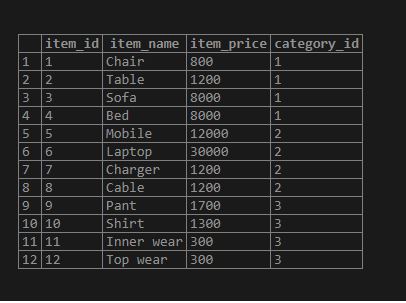
INSERT INTO items(item_name,item_price,category_id)
VALUES ('Chair',800,1),
('Table',1200,1),
('Sofa',8000,1),
('Bed',8000,1),
('Mobile',12000,2),
('Laptop',30000,2),
('Charger',1200,2),
('Cable',1200,2),
('Pant',1700,3),
('Shirt',1300,3),
('Inner wear',300,3),
('Top wear',300,3);Output:
select * from items;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
Examples of implementing the ROW_NUMBER function in PostgreSQL
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Code:
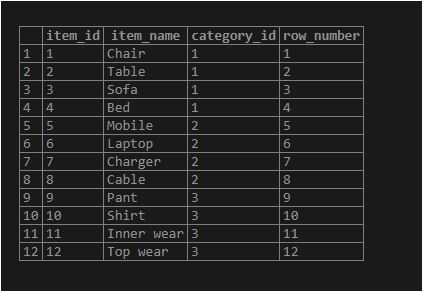
SELECT
item_id,
item_name,
category_id,
ROW_NUMBER () OVER (ORDER BY item_id)
FROM
items;Output:
Explanation: In the above example, we have not defined the PARTITION BY clause, which results in the entire result as a single PARTITION in the ROW_NUMBER() function. We have defined the ORDER BY clause, which in result sorts the result set by item_id. The PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER() function assigns numeric values based on the item_id order for each row.
Example #2
Consider the following statement where we use the item_name in the ORDER BY clause.
So for each row, the numbers are assigned as per the item name order.
Code:
SELECT
item_id,
item_name,
category_id,
ROW_NUMBER () OVER (
ORDER BY item_name
)
FROM
items;Output:
Example #3
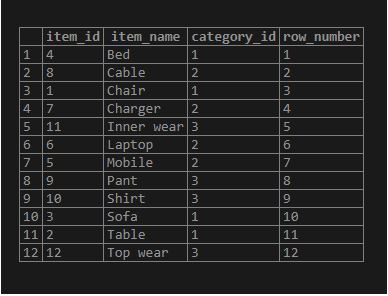
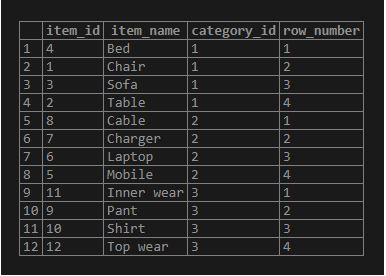
Consider the following statement where we will use the PARTITION BY clause on the category_id column, which will divide the result set into partitions based on the values of the category_id column. Each row of the partition starts with one and then increases by one for the remaining rows in the same partition. As per the values in the item_name column, the PostgreSQL ORDER BY clause sorts the rows in every partition.
Code:
SELECT
item_id,
item_name,
category_id,
ROW_NUMBER () OVER (
PARTITION BY category_id
ORDER BY item_name
)
FROM
items;Output:
Example #4
DISTINCT operator with the PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER() function
For each distinct row in the items table, the ROW_NUMBER() function assigns a number.
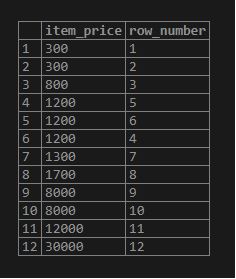
Code:
SELECT DISTINCT
item_price,
ROW_NUMBER () OVER (ORDER BY item_price)
FROM
items
ORDER BY
item_price;Output:
Example #5
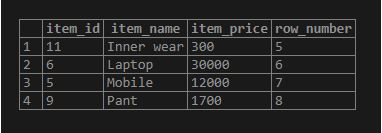
We can use the pagination technique to display the subset of rows. There are various methods to achieve the Pagination, like using the LIMIT clause or the use of the ROW_NUMBER() function. Consider the following statement to select the 4 rows starting at row index 5:
Code:
SELECT
*
FROM
(
SELECT
item_id,
item_name,
item_price,
ROW_NUMBER () OVER (ORDER BY item_name)
FROM
items
) x
WHERE
ROW_NUMBER BETWEEN 5 AND 8;Output:
Advantages of using the ROW_NUMBER function in PostgreSQL
- This function is used to generate the sequential numbers on the fly.
- This function is used to perform pagination.
- We can find out the duplicate rows by using this function.
- We can find rows from a range of rows using the PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER function.
- This function is used to sort rows.
Conclusion
From the above article, we hope you understand how to use the PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER() function and how the PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER() function works. Also, we have added some examples of this function to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.