Updated May 11, 2023
Introduction to Array in PostgreSQL
An array has a very important role in PostgreSQL. We can create variable-length columns for a specific table. The data types defined in PostgreSQL have their own type, like the character having character[], the integer having integer[] array, etc. If we have specified our own data types, then in the background, it will create an array type for the defined data type. We can define an array type for any data type column, like user-defined type, built-in type, or enum types.
How to Create an Array in PostgreSQL?
Let’s create a ‘student’ table with thelet’sowing structure to understand the data type insertion.
The student table consists of two columns:
- stud_id: The column is the primary key column that uniquely identifies the student.
- stud_name: The column is for showing student name
- stud_mob_num: The column stores the student’s contact information in the fostudent’sarray.
Let’s create the table by using the CRELet’sABLE statement:
Query:
CREATE TABLE student (
stud_id serial NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
stud_name VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL ,
stud_mob_num TEXT []
);Illustrate the result of the above statement table using the following snapshot and statement:
SELECT * FROM student;How to Add Array Elements in PostgreSQL?
There are two ways to add elements in the array type column; we will go through them one by one as follows:
1. Using [] Subscript Operator
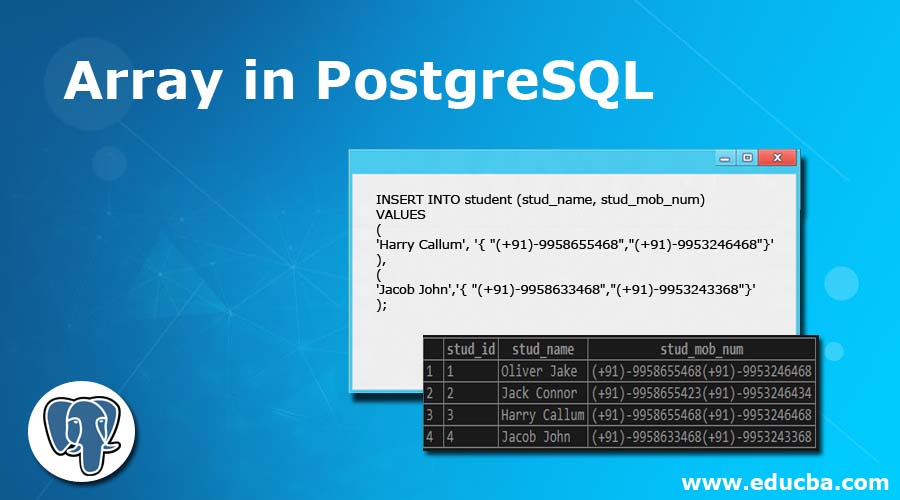
We can insert the data using the subscript operator in the array column of the table as follows; here, we have to use single quotes around each element as we are using the [] operator for insertion:
Query:
INSERT INTO student (stud_name, stud_mob_num)
VALUES
(
'Oliver Jake',
ARRAY [ '(+91)-9958655468',
'(+91)-9953246468' ]
),
(
'Jack Connor',
ARRAY [ '(+91)-9958655423',
'(+91)-9953246434' ]
);
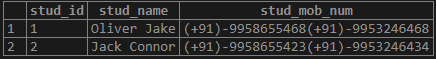
Illustrate the result of the above statement table using the following snapshot and statement:
SELECT * FROM student;
Output:
2. Using {} Curly Braces
We can insert the data using curly braces in a column of the table as follows; here, we have to use double quotes around each array element as we are using curly {} braces for insertion:
Query:
INSERT INTO student (stud_name, stud_mob_num)
VALUES
(
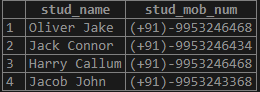
'Harry Callum', '{ "(+91)-9958655468","(+91)-9953246468"}'
),
(
'Jacob John','{ "(+91)-9958633468","(+91)-9953243368"}'
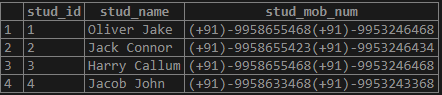
);Illustrate the result of the above statement table using the following snapshot and statement:
SELECT * FROM student;Output:
Examples
Below are the examples:
Example #1 – Access Array Data
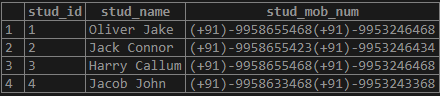
- We can retrieve the data using the following snapshot and statement:
Query:
SELECT * FROM student;Output:
- PostgreSQL allows us to access the array elements using the subscript [] operator
The array elements are numbered with one based indexing in PostgreSQL, which means the array’s base index is one. Consider the thearray’sing example where we will get the student’s name and second mobile numberstudent’s help of the following statement:
Query:
SELECT
stud_name,
stud_mob_num [ 2 ]
FROM
student;Output:
- PostgreSQL allows us to use array elements in the WHERE clause to filter out the rows.
Consider the following example where we will check for mobile number (+91)-9953243368 as the first mobile number with the help of the following statement:
Query:
SELECT
stud_name
FROM
student
WHERE
stud_mob_num [ 1 ] = '(+91)-9958633468';Output:
Example #2 – Modify PostgreSQL Array Data
We can update the individual elements of an array or the entire array.
- Update Individual Element
We will update the first mobile number of ‘Harry Callum’. Before updating Harry C’llum’s first’mobile number, we will eCallum’she the following statement and will have a look at the snapshot:
Query:
SELECT
stud_name,
stud_mob_num [ 1 ]
FROM
student
WHERE
stud_id = 3;Output:
Now update the first mobile number of ‘Harry Callum’ using the following stat’ment:
Query:’Illustrate the result of the above statement table using the following snapshot and statement:
SELECT
stud_name,
stud_mob_num [ 1 ]
FROM
student
WHERE
stud_id = 3;
Output:
- Update the Entire Array
Now we will update the entire mobile number array of ‘Harry Callum’ using the following stat’ment:
Query:’Illustrate the result of the above statement table using the following snapshot and statement:
SELECT
stud_name,
stud_mob_num
FROM
student
WHERE
stud_id = 3;Output:
- PostgreSQL Array Data Search
With the ANY() function provided, we can find any record if beforehand we know the mobile number of the student irrespective of the position in the array, consider the following statement and snapshot:
Query:
SELECT
stud_name,
stud_mob_num
FROM
student
WHERE
'(+91)-9958633468' = ANY (stud_mob_num);Output:
- PostgreSQL Array Expand
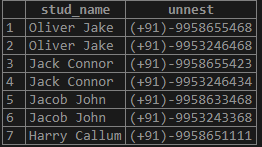
With the unnest() function provided by PostgreSQL to expand an array to a list of rows. Consider the following statement to expand the mobile numbers of the stud_mob_num array.
Query:
SELECT
stud_name,
unnest(stud_mob_num)
FROM
student;Output:
Advantages
- We can access the elements with the index’s help, leading to faster access.
- PostgreSQL provides various functions to work with an array.
- We can insert and update the array element by using an index.
- Insertion on the array element is very easy as we can use multiple syntaxes like [] operator or {} braces.
Conclusion
We Frome the above article, we hope you have understood how to use the PostgreSQL Array data type and how the PostgreSQL array data type works to store the data. Also, we have added some examples of array type to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Array in PostgreSQL” was beneficial to”you. You can view E”UCBA’s recommended articles for more EDUCBA’sion.