Updated October 4, 2023
Introduction to Object Cloning in Java
Being one of the most widely used programming languages, Java comes with a wide range of features and functions. An object in Java is used to get the task done; you create objects, alter, move, call their respective methods, etc. As we all know, references to the objects are stored in Java. So, when we have two references pointing at the same object, changes in anyone will be completely reflected in the same changes in the other. Now, this factor may not work in our favor every time, so cloning is the answer to obstruct such situations. In other words, to create an exact replica of such objects is known as Object Cloning in Java.
By definition, Object Cloning is the process of creating an exact copy of an original object with a similar state. When cloning, all the properties are carry forwarded to the newly cloned object, but these properties can be changed or manipulated as per needs. The clone() method has to be defined in the Object class. Implementation of java.lang.A cloneable interface is mandatory for the class where we intend to clone object. In case of failing to implement the Cloneable interface, an exception will be thrown. Let us now have a look at the syntax for Object Cloning.
Syntax:
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedExceptionFor the class Object, specific cloning operations are performed by the clone method. This method will create an exact duplicate of the class and initialize all the fields with the content of the object’s fields. If the interface Cloneable is not implemented by the class of the mentioned object, it will throw “CloneNotSupportedException”. All the arrays are considered to implement the Cloneable interface. Here, the interface Cloneable is not implemented on the class Object. So when we call the clone method on an object, it throws a run time error.
Working of Object Cloning in Java
Let us now understand the working of the clone() method by demonstration.
Code:
class obj_clone implements Cloneable{
int phone_code;
String f_name;
obj_clone(int phone_code,String f_name){
this.phone_code=phone_code;
this.f_name=f_name;
}
public Object clone()throws CloneNotSupportedException{
return super.clone();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
obj_clone s1=new obj_clone(99,"sulaksh");
obj_clone s2=(obj_clone)s1.clone();
System.out.println(s1.phone_code+" "+s1.f_name);
System.out.println(s2.phone_code+" "+s2.f_name);
}catch(CloneNotSupportedException c){}
}
}Code Explanation: As you can see, we initialized our class and implemented cloneable. Here, it is checked if the actual class implements the cloneable, with clone() in object and then it proceeds with creating a copy. Then we have our two variables phone number with integer data type and first name with the string data type. We then created a constructor of our class obj_clone along with the variables with .this keyword. As you can see, we have our object with clone() method and the exception CloneNotSupportedException, which we earlier discussed. Moreover, super.clone() here will possibly throw the error CloneNotSupportedException, which we have caught later.
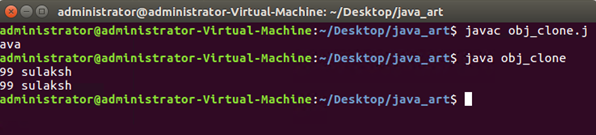
Then we have our main class, and we have used a try-catch for everything inside it. We then created an object of our class as s1 and s2. We have passed both the parameters for s1, our first object, and then we have implemented the clone() method to clone s1 into s2. Finally, we have two output print statements. Out of the try block, we have our catch block with the exception discussed earlier. On the 8th line of the example, we have implemented the clone() as mentioned and explained in the syntax part. Upon execution, the above program will print output as “99sulaksh 99sulaksh”. For output refer to the below-attached screenshot.
Output:
Types of Object Cloning in Java
Now that we have understood what object cloning is and how it is done let us understand which are the types of cloning that Java supports.
- Shallow Cloning: Whenever the default cloning method is implemented, shallow cloning happens. Shallow Cloning simply copies all the fields of the object into the new instance. Shallow cloning is supported by clone().
- Deep Cloning: Now, every time we don’t implement the default cloning method, we are exercising Deep Cloning. Deep Cloning works as per our needs. Now, the major difference here is that Deep Cloning copies all the fields along with the object’s values, while Shallow Cloning only copies the fields.
- Lazy Cloning: There’s a third type of cloning that is supported in Java, which is a combination of above mentioned two types of cloning; it is known as Lazy Cloning. And there is no specific rule on when to use which cloning type; it is upon us to decide as per our needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Object Cloning
Now, let us understand the advantages and disadvantages of Object Cloning.
Advantages
Understanding that everything or every method has its own limitations and functions, below are the advantages of Cloning.
- It saves time and work because cloning is a time-saving method; you don’t have to write the same long codes.
- When implementing on already developed projects, Cloning is the most efficient method of copying objects.
- It has the fastest method to cop arrays with Clone().
Disadvantages
Like mentioned earlier, every method has its limitations and functions, now let us understand the Disadvantages with Clone().
- In order for JVM to understand that we will be using clone(), we have to implement the Cloneable interface, even though this cloneable interface does not have any methods.
- In the case of deep cloning, we’ll have to override object.clone(), as it basically supports shallow cloning.
- We have no control over object construction, as the clone() does not invoke any constructor.
- Basically, to implement the object.clone(), we have to make quite a few changes in our code, starting with the implementation of Cloneable interface, then clone() method definition to handling CloneNotSupportedException, etc.
With the proper understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of clone() or any other method, the implementation of such wonderful methods and functions can greatly benefit the programmer.
Conclusion
We understood what clone() is, its functionality and its uses. Difference between deep and shallow cloning, along with lazy cloning. Shallow cloning copies only the fields while Deep Cloning copies the fields and the values and can be implemented as per needs. While Lazy Copy is a combination of these both. We also understood the advantages and disadvantages of clones ().
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Object Cloning in Java. Here we discuss the syntax, example, and types of Object Cloning in Java along with advantages and disadvantages. You can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –


