Updated November 4, 2023
Introduction to JVM
The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) serves as a robust engine, enabling the execution of Java software across various computing environments. It takes Java bytecode, an intermediate language, and translates it into the host machine’s native language. JVM is a pivotal component of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), known for its platform independence. Regardless of the underlying operating system, JVM interprets bytecode, making Java truly portable. JVM is implemented in the C programming language, ensuring independence from the host OS. It plays a crucial role in Java architecture, managing memory allocation and deallocation, while its core tasks include loading, verifying, and executing code, providing a runtime environment. JVM encompasses components such as Classloader, memory allocation like Stack, an Execution Engine, and native libraries.
Table of Contents
What does it do?
The crucial operations which JVM performs are as follows:
- Code Loading
- Code Verifying
- Code Execution
- Runtime Environment Provision
Apart from all this, it rolls out classifications for Class file format, Memory area, Garbage-collected heap, Register set, Fatal error reporting, etc.
JVM Architecture
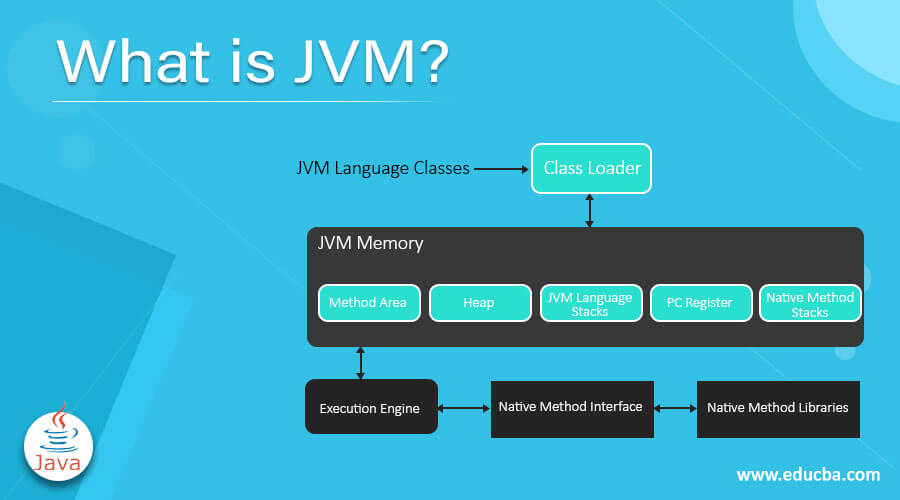
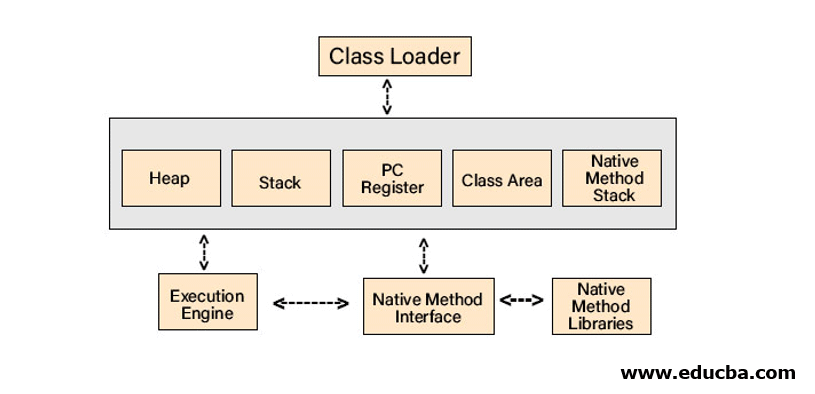
Given below are some key insights about the internal architecture of JVM, which comprises of:
1. Classloader
The classloader is a subsystem of the JVM that loads class files when you run a Java program.
The three classloaders which Java includes are as follows:
- Bootstrap ClassLoader: It’s the superclass of Extension classloader. It assists in loading the rt.jar files that carry all the class files.
- Extension ClassLoader: It is the parent classloader of the System classloader and child classloader of Bootstrap. The jar files inside the $JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/ext directory can be extracted through the Extension ClassLoader.
- System/Application ClassLoader: It is the child of the Extension classloader, also known as the Application classloader. The class files from the classpath can be extracted through it. The Classpath, set to the current directory, can be changed by default using the ‘-cp’ or ‘-classpath’ switch.
2. Class (Method) Area
The Class (Method) Area stores pre-class structures such as field and method data, the runtime constant pool, and the code for methods. The JVM creates the memory area on startup, and it is shared among all threads, similar to the Heap.
3. Heap
Details of an object and instance variables are all stored here. It is a shared memory area, which means the data stored here is not thread-safe.
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
One of the most relatable errors is the “OutOfMemoryError” exception, which means the JVM cannot allocate an object in the Heap area, or memory allocation cannot be done for the same object.
4. Stack
Along with storing frames, Java Stack holds variables and partial results. It also plays a pivotal role in method, invocation, and return. Every individual thread consists of its private JVM stack, created simultaneously as the thread. Whenever a method escalates, a new frame is generated and shattered when the method invokes.
5. Program Counter (PC) Register
The PC register contains the JVM instruction address at its execution. Thus, keeping track of instructions has value for every instruction, which is undefined for the native methods.
6. Native Method Stack
The native procedures used in the applications are part of the Native Method Stack. These methods are written in languages other than Java. Associated with each thread, JVM implementations can’t rely on conventional stacks and cannot load native methods. To be precise, it is similar to stack but used for native methods.
7. Execution Engine
We now have a Java program converted into bytecode, and a class loader assigns this bytecode to the data areas, as previously explained. The bytecode is subsequently executed by the execution engine, which reads it in units, much like a machine reading code lines one by one. Since bytecode is in a human-readable format, the machine cannot interpret it as is; it needs to convert it into a machine-readable format. To accomplish this, the following components are utilized for interpretation.
The Execution Engine has three major components, which are Interpreter, JIT Compiler, and a Garbage Collector.
Garbage Collector: As the name suggests, it does have something to do with garbage. Garbage Collector searches for every possible object available in the JVM heap space, checks if it is in use, and then deletes the unused ones. So, it simply marks the pieces of memory which are in use or not. Then, it goes on sweeping, where it merely removes the object marked. The best use case is that you don’t need a manual memory allocation system because the Garbage Collector automatically removes unused memory space. As this is an automatic task, no programmer has control over scheduling any time slot for specific cleaning tasks, and it requires more CPU power as it searches for object references.
Interpreter: Executes the bytecode in a sequential method. A command-line query makes a call with a compiled file as an argument. The interpreter is quite quick in interpreting and executing commands one by one, which happens faster than the JIT compiler compiles the code.
java class name
A main() class is a must in a compiled .class file.
Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler: One of the most important components of the Java Runtime Environment, which enhances the Java Application performance at run time. No other component has more impact on performance than the JIT Compiler. This compiler is the default and activates when any Java method is called.
8. Java Native Interface (JNI)
JNI simply interacts with the below-mentioned Native Method Libraries, which are of C C++ implementation, and provides the same to the execution engine. JNI allows direct access to assembly code. For a JVM, Java, and Native are the two types of codes. The JNI smoothly establishes a well-defined link between these two.
The JVM has two primary functions: to allow Java programs to run on any device or operating system (known as the “Write once, run anywhere” principle) and to manage and optimize program memory.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The JVM aptly executes Java programs. It compiles Java programs into bytecode, which serves as an intermediate language and executes them. Any platform powered by the JVM can run any individual program that compiles bytecode. This enables Java software to be more effective and compatible as the various computing platforms are concerned. However, the JVM has a few notable advantages and disadvantages that developers should weigh carefully before investing in Java development.
1. Security
Through JVM’s security knacks, the programmers can effectively write high-end secured Java programs. Furthermore, it empowers the Operating System resources to identify the malicious software and helps its prevention accordingly.
2. Performance
Java programs that run on a JVM are likely to offer slower execution than the programs written in C++. This is due to code optimization, which excessively relies on different system-specific features. Also, the Java bytecode cannot be optimized for a specific hardware set, as it is system-neutral.
3. Correctness
Correct is the program that performs effectively and meets a user’s expectations to the fullest. JVM’s in-built features enable it to operate correctly and free of errors.
Why should we use JVM?
Despite having Java syntactical code, JVM can run on various language programs.
Widespread use and utilization across various platforms are enjoyed for several reasons, including:
- It uses heap memory: Dynamic memory allocation uses heap memory as a core component for defining classes and initializing objects. Since JVM supports heap memory, it has wide acceptance.
- Providing security for remote code location: The JVM framework facilitates the easy execution of remote applications. This theory applies when executing Java Applets.
Conclusion
The fact that JVM works on multiple operating systems gives it a thumbs-up in the technology domain. You can use it on Windows, Linux, and other operating systems to transform bytecode, regardless of the hardware and the OS on which it will be executed. In addition, its ability to offer security to the host computer by securing their data and program is another reason why JVM has been so successful and continues to be dominant in the future.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is JVM? Here, we discuss the basic concepts with the list of architecture and uses of JVM, respectively. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –