Updated June 30, 2023
Introduction to clone() in C#
Clone() in C# is a string method used to return the exact copy of an object. It returns the instance of the string. The return is just a copy with a different view. This method is also useful if we want to clone an array. In the case of the array, it creates a copy of the array with the same number of elements. The Clone method in the ICloneable interface allows for the copying of data. You do not need to provide any parameters for this method.
Syntax of implementing clone ()
public object Clone()Syntax of implementing ICloneable()
public interface ICloneable
{
object Clone();
}As you can see, it won’t require any parameter and returns a reference.
If we want to modify a cloned object, we can, and doing this will not modify the original object.
Using the clone () method makes it easy for the developers as they need to write less code that is easy to understand. No other special attribute is required along with this; it copies all properties. We can call this method inside the class only. It returns an object, so we need to do casting when we use this method. It is good to implement this method in all classes to clone. We can achieve it by using two techniques 1. Deep copy 2. Shallow copy.
Shallow copying is creating a new object and then copying the non-static fields of the current object to the new object. On the other hand, deep copying is creating a new object and then copying the non-static fields of the current object to the new object.
Examples of clone() in C#
Below are the examples that show how we can implement clone () and ICloneable interface in C#.
Example #1
Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Clone
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string s1 = "This is C# programming";
string s2 = (String)s1.Clone();
// Displaying both the strings
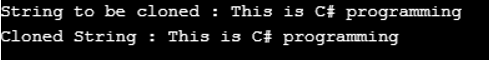
Console.WriteLine("String to be cloned : {0}", s1);
Console.WriteLine("Cloned String : {0}", s2);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}In the above example, there is a string that we need to clone. Clone() is used to clone this string object. It returns another copy of the data. So we can say that the return value is the same data with another view. This method doesn’t require any parameters. In the output, you can see that it displays the original and cloned strings, which is the exact copy of the original one.
Output
Example #2
Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Clone
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// array initialization
string[] arraytobecloned = { "This", "is", "C#", "clone", "example"};
string[] clonedarray = arraytobecloned.Clone() as string[]; //cloning array
// display original and cloned arrays
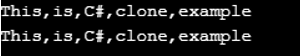
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", arraytobecloned));
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", clonedarray));
Console.WriteLine();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}In the above example, an array with a set of elements is defined, which needs to be cloned. Clone() is used to clone all the elements of the array. In the output, you can see that it has created a similar copy of an array.
Output
Example #3
Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Clone
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] arraytobecloned = { "This", "is", "C#", "clone", "example" };
string[] clonedarray = arraytobecloned.Clone() as string[];
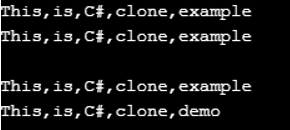
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", arraytobecloned));
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", clonedarray));
Console.WriteLine();
clonedarray[4] = "demo"; // providing new value to cloned array element
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", arraytobecloned)); // displaying arrays
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", clonedarray));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}In the above example, an array set is defined, containing different elements. The clone () method is used to clone those elements. We can also change the value of any element of that cloned array. The output first displays the given array and the cloned array. We can also change the value by passing its indexing position. After passing the value, it shows the cloned array with a new set of values. So this means we can modify the value of cloned array, which doesn’t disturb the original array elements’ value.
Output
Example #4
Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Clone
{
class Employee : ICloneable // implementing ICloneable interface
{
int empcode;
string name;
public Employee(int empcode, string name)
{
this.empcode = empcode;
this.name = name;
}
public object Clone()
{
return new Employee(this.empcode, this.name);
}
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("empcode = {0}, name = {1},",
this.empcode,
this.name
);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main() // main method
{
Employee e1 = new Employee(10, "John");
Employee e2 = e1.Clone() as Employee;
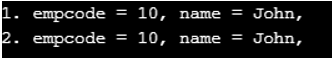
Console.WriteLine("1. {0}", e1);
Console.WriteLine("2. {0}", e2);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}In the example above, we use the ICloneable interface and the clone() method to duplicate the object. After calling the public constructor with a set of arguments, you should then call the clone method.
Output
Example #5
Code
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Clone
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//declare and initialize a stack
Stack stack1 = new Stack();
stack1.Push(10);
stack1.Push(20);
stack1.Push(30);
stack1.Push(40);
stack1.Push(50);
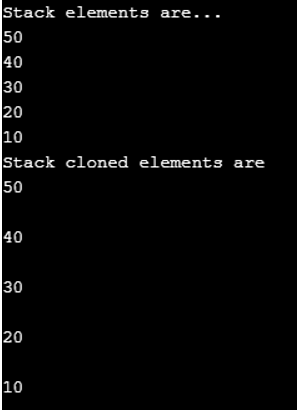
Console.WriteLine("Stack elements are...");
foreach (int val in stack1)
{
Console.WriteLine(val);
}
Stack stack2 = (Stack)stack1.Clone();
Console.WriteLine("Stack cloned elements are");
foreach (int val in stack2)
{
Console.WriteLine(val);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
}The above example defines a stack using the push method to insert elements. Stack. The clone () method clones the stack with all its elements. It displays the original stack and cloned stack with all the elements using foreach.
Output
Conclusion
The clone() function copies an object and returns the instance. Using this method, we can clone an array also with the same number of elements. An implementation of ‘ICloneable’ also includes the call to the clone method for data copying. It is t good to implement clones as it makes code easier for developers.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to clone () in C#. Here we discuss the introduction to clone () in C#, the various examples, and the appropriate syntax. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more–