Updated May 25, 2023
Introduction to Network Topologies
Network Topology is a technique for setting up the network’s design based on few mandatory parameters, namely the physical location of the nodes or devices, the required data flow through the connection pattern, wiring or cable connection prototype between the nodes, the hub, the switch and/ or the routers, etc. The various types are ‘point to point’, ‘Mesh’, ‘Bus’, ‘star’, ‘ring’ and ‘hybrid’, amongst which Mesh has further two kinds of networks like ‘Full Mesh Topology’ and ‘Partial Mesh Topology’. Another notable feature of Mesh network is the transmission methods, such as the Routing method and Flooding method
Network Design involves key parameters like:
- The physical locations of computers/devices (Nodes).
- The logical connection between nodes describing the data.
- The physical connection between nodes and network devices like Hub/Switch/Routers through transmission media like cable/Wire/Fiber.
- Network management parameters like the level of control/fault tolerance.
- Application requirements and user expectations.
Network Topology for an organization is decided by the above parameters. First, we will understand what is network topology.
What is Network Topology?
Network Topology is a blueprint of the network describing the way different computers/devices are interconnected and how they communicate among themselves. It explains various ways the nodes are connected such as:
- Nodes are placed serially one after the other.
- Each node has meshed with all other nodes.
- All the nodes go through a common device (Hub or Switch) They are logical and physical.
Logical Aspects: It highlights the path of the data flow or the signal flow between nodes and it is independent of physical connections.
Physical Aspects:
- Geographical Locations of Nodes and the distance between them.
- Wired or Wireless.
- Transmission media like Coaxial Cable, Wires, and Optical Fibers.
- Signal Types.
- Rate of Transmission.
Two identical Network Topologies may differ in physical aspects like distance between the nodes, physical connections, transmission rate, and signal types. Logical and physical topologies of a network need not be the same. Further, let us analyze various topologies of the network.
Types of Network Topologies
There are several types of topologies available in the computer networks and the organization will have to choose the right type depending upon its requirements and budget availability:
1. Point to Point
Two nodes are connected through the dedicated links, the platform for a simple and easy way of communicating. It is dynamically set up as and when needed and used mainly in telephone networks, connecting caller with the receiver using circuit switching technologies. The advantage in this is the uninterrupted connection between the nodes after establishing the connection.
2. Mesh
Each node in this network is connected to every other node directly in a point to point (non-hierarchical) mode. If there are n number of computers then the number of links in this network is factorial of (n – 1) i.e. n*(n-1)/2.
Transmission of data takes place in 2 ways in this network.
- Routing: Every node in this topology has a routing logic and the best route to the receiver is arrived based on the shortest distance to the receiver after bypassing the faulty Transmission of data to the receiver happens through this route.
- Flooding: In the absence of any routing logic, the data to be sent to a receiver is sent to all the nodes in the network and receiver picks Though it provides a robust and fool-proof method of transmitting data, load on the network is generally high.
There are 2 categories of Mesh Topology.
- Full Mesh Topology: Full-fledged mesh is used in critical backbone It provides redundancy but at a higher cost.
- Partial Mesh Topology: Some of the nodes are not connected to all nodes unlike full Peripheral networks are normally connected by partial mesh and they are connected with full-mesh backbone.
3. Bus
In a bus topology, all the individual’s nodes are connected to a bus thro drop line and Tap with a single central cable (twisted pair, coaxial cable). All Communications are sent thro this common bus, every node connected in the bus receives them and the actual receiver only processes them. The endpoints of the central cable are closed with a device called terminator to avoid unwanted interferences.
Linear Bus topology has a common bus with two endpoints whereas Distributed Bus topology has more than two endpoints made possible by adding branches to the main network. Bus topology is easy to set up/configure and cheaper due to less cabling. A faulty node will not affect the performance whereas the failure of the central node affects the network.
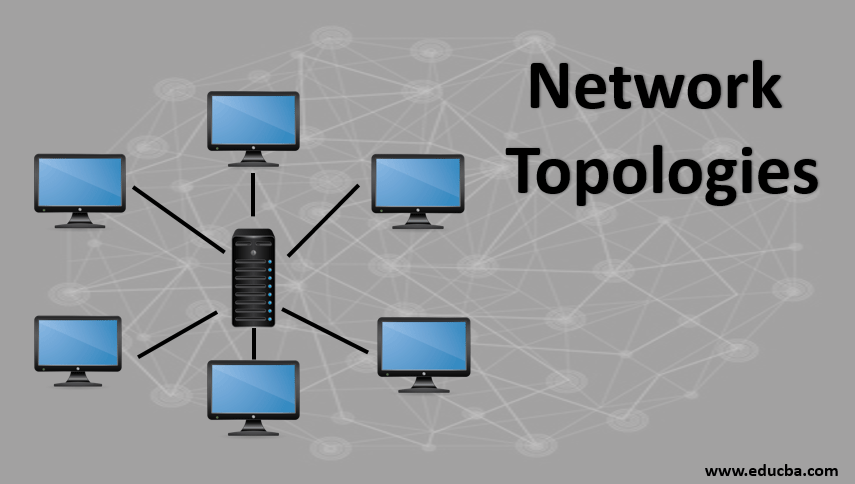
4. Star
In this topology, a common network device Hub or Switch connects all the nodes to its centrally thro UTP, Coaxial cable or optical fiber medium. Any communication is sent to the central device and in turn, it diverts the message to the right receiver. Central Hub is responsible for data transmission between its nodes, monitors the overall performance of the nodes, detects any faults and alerts administrators. New nodes can be added easily in this network. Star topology network is easy to install and manage but expensive. Failure in central Hub affects the whole network.
5. Ring
In this network, each node is connected to two other nodes and so on, in the form of a ring. UTP cables are used as a transmission medium. Any communication from a node is transmitted in clockwise to its next node and repeated until it reaches the right receiver. It can be construed as an extended bus topology with its ends looped.
The data packets are passed from one pocket to another as tokens and there are no data collisions and token passing ring network performs better than the bus network under heavy traffic. There is no need to control or monitoring as every node has equal functions. Failure of one node affects the network completely. This topology is used in the Telecom network and communication in the network can be bi-directional also.
6. Hybrid
Large Hybrid networks are formed by combining multiple heterogeneous topologies and this network has cumulative features and functionalities. It is more complex to maintain.
Advantages
Below are the advantages of Networks Topologies:
- Plays an important role in the functioning of the network.
- Enhances the performance of the network and its manageability.
- Reduces the network project cost by optimizing the network equipment and cables usage.
- Saves operation & maintenance costs.
Conclusion
Deploying the right type of network topology helps the Organization to effectively utilize its network resources and improve the performance of the network. This will enhance the end-user experience and increase its topline and bottom line.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Network Topologies. Here we discuss brief overview, various types, and the advantages of Network Topologies respectively. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


