Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to Matlab Legend
Graphs are the graphical form of the explained data in the data set. Legends are the way of adding them to the graph to explain the displayed data that have different properties and forms. They are mainly used in graphs, charts or spreadsheets. For each legend, there is a legend key that is linked to every data displayed in the chart. Legends can be used in various graphs or charts like a bar graph, line graph, pie chart, etc. It should be always noted that the parameters that we define in the legend command should be equal to the number of attributes in the plot command.
Working of Matlab Legend
In Matlab, legends are used to label the plotted data for every parameter that is mentioned. For labels, it uses one of the properties of data series which is known as DisplayName. The legend updates automatically whenever we include any new or remove data series from the current axes. If there are no current axes present, then there is no legend and it is empty.
Syntaxes that are used in Matlab:
- L=legend: This is used to include the legend in the plotted data series.
- L=legend (label of the legend 1…label of the legend N): This includes the legend labels in the graph as specified in the labels argument. We can mention the label in the form of strings or characters. For example, legend (‘Mon’,’Tue’,’Wed’)
- L=legend (labels of the legend): This is used to mention the labels in the legend. Labels can be a string array, character vectors or a character matrix.
- L=legend (subset included): This includes only the values that are present in the subset. We can specify the subset as the values or no arguments in the input.
- L=legend (target axes, ___): This is used to specify the required axes or chart in the target axes argument.
- L=legend (__,’location of the legend’): This is used to specify the location of the legend that should be placed in the plot. This property of the legend should always be given after all the input arguments.
- L=legend (__,’orientation of the legend’): This is used to specify the orientation of the legend that should be placed in the plot. The default value of the orientation is vertical.
- L=legend (___,’Name of the property’, ‘value of the property’): This is used when we want to customize the appearance of legends in the plot. We can give the property name in ‘Name of the property’ argument and the required value after that. There are various properties of the legends which are discussed below.
- L=legend(bkgd): This is used to set the background appearance and its outline. The default value of it is ‘boxon’.
- L=legend(visibility): This is used to set the visibility of the legend which has different values like the show, hide and toggle.
- L=legend(off): This is used to delete the legend and its customization from the plot.
Examples of Matlab Legend
Please find the below examples that explain the use of legends in Matlab:
Example #1
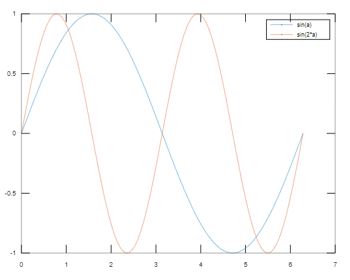
To plot two lines and display the legend in the present chart.
Code:
a = linspace(0,2*pi);
y = sin(a);
plot(a,y)
hold on
y1 = sin(2*a);
plot(a,y1)
legend('sin(a)','sin(2*a)')
Output:
In the above example, the legend for the two lines is shown in the top right corner of the plot, one line depicting the values for the function sin(a) and the other line depicting the values for the function sin(2a).
Example #2
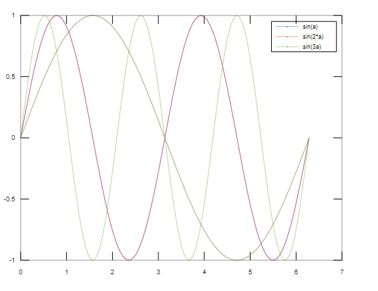
To plot another line and specify the labels of the legend using DisplayName property of the legend in the plot command. In this example, we have added another line to the existing line as mentioned in the above example.
Code:
a = linspace(0,2*pi);
y = sin(a);
plot(a,y)
hold on
y1 = sin(2*a);
plot(a,y1)
legend('sin(a)','sin(2*a)')
y2 = sin(3*a);
plot(a,y2,'DisplayName','sin(3a)')
hold off
Output:
In the above example, another line is added to an existing plot using the legend label in the plot command as shown in the highlighted part. This can be done by using the legend property ‘DisplayName’ and the label of the legend as its value. Here sin(3a) is the value and it is added as legend label to the plot.
There are various properties of the legend in Matlab which are discussed below. Location is one of the main property of the legend which decides the location of the legend.
There are various values that can be assigned to the property like:
- north: This is used to plot the legend in top of the axes or chart and is placed inside of the chart.
- northeast: This is used to plot the legend in the top right of the axes or chart.
- northwest: This is used to plot the legend in the top left of the axes or chart.
- northoutside: This is used to plot the legend on top of the axes and it is outside.
- south: This is used to plot the legend at the bottom of the axes or chart and is placed inside of the chart.
- southeast: This is used to plot the legend in the bottom right of the axes or chart.
- southwest: This is used to plot the legend in the bottom left of the axes or chart.
- southoutside: This is used to plot the legend at the bottom of the axes and it is outside.
- east: This is used to plot the legend in the right of the axes or chart and is placed inside of the chart.
- eastoutside: This is used to plot the legend in the right of the axes and it is outside.
- west: This is used to plot the legend in the left of the axes or chart and is placed inside of the chart.
- westoutside: This is used to plot the legend in the left of the axes and it is outside.
- There are many other locations apart from this which are also used in Matlab.
- We can also decide the visibility, orientation of the legend which can be horizontal and vertical depending on the requirements.
Example #3
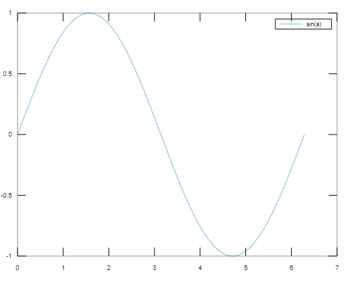
To delete the legend from the plot.
Code:
a = linspace(0,2*pi);
y = sin(a);
plot(a,y)
legend('sin(a)')
Output:
Code:
a = linspace(0,2*pi);
y = sin(a);
plot(a,y)
legend(‘off’)
Output:
Conclusion
Legend is used in most of the graphs to label the behavior of different lines in the plot. There are many other properties that are associated with the customization of the legend in Matlab.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Matlab Legend. Here we discuss the introduction and working of Matlab Legend with examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –