Updated June 13, 2023
Introduction to Magento Architecture
The following article provides an outline for Magento Architecture. Even if you do not know more about the Zend framework, you can learn it as it is entirely MVC pattern and fully utilizes an Object-oriented approach. Magento uses a PHP object-oriented approach. Here we will see a few essential things like modularity, Security, MVS, Extensibility of Magento, etc.
Architecture of Magento
We can divide Magento architecture into two parts one is Magento internal architecture, and another one is Magento ERP or UI architecture.
The general architecture of Magento, from request to response for internal architecture, is given below.
- Magento Internal Architecture
- Magento ERP Architecture
1. Magento Internal Architecture
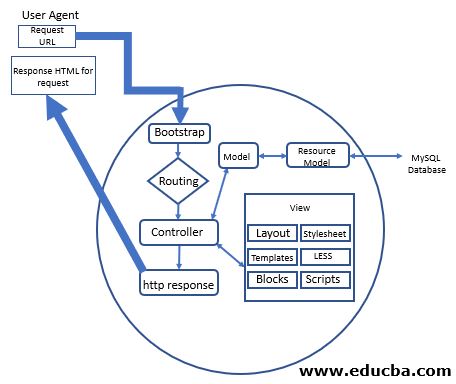
Given below is Magento’s internal architecture:
a. User-Agent: A user agent is software from which any request is made to Magento, and the software can read the response from Magento. The response can be in HTML format. Examples of some user agents are web browsers (chrome, opera, etc). The user-agent section is the front part of the application; it could be a web application visible to customers.
b. Bootstrap: Bootstrap creates environments for the Magento app to run it. At first, it will check and sets a few things like the PHP version, the setting of error reporting, defining the base path, and initializing and invoking the autoloader.
Below are some tasks performed by Bootstrap:
- Check for the version of PHP (display error if the version is lower than 5.5), setting default error, defining path (like root directories), running autoloader and setting of time zone, etc.
- Object manager initialization, fetching the main configuration from /app/etc/config.php
- Launch the application by getting the controller instance and calling the routing dispatch function.
c. Routing: In Magento, routing plays an important role; it has the algorithm to decide which controller will be dispatched.
Before dispatch, it will go through several steps:
Fetch active Routers—>Search for the requested controller and action—>After that, find the exact request controller and action in an interpreter class file —>new dispatch function of the interpreter class will be called.
d. Controller: After routing, can decide which controller function needs to call; that particular action will be invoked. This invoked function can call to model for any specific data, as the model contains business logic. Once the controller function gets data from the model, it can either bind data with a view of HTML with a specific design or simply return according to requirements.
e. Model: The model is where we can write our business logic. The business logic, like getting order details and calculating the sum of the total amount and any discount, will be calculated here only.
f. Mysql: This is the section where we store all important data. These data are user details; user orders detail many essential items.
g. View: This section contains all the HTML and CSS styles. It also added less from the magento2. It gets data from the controller and binds it with html and CSS. After binding data with HTML and CSS, it will be returned to the respective controller action, which called it.
h. HTTP Response: This section contains the final response for the requested user agent.
i. Security Work: Magento provides better security to resources from unwanted users and calls.
They are given below:
- User password encrypted while transmitted means the unencrypted password is not allowed to transmit.
- Salted hash has been used to store user passwords, which makes it harder for anyone to decrypt.
- Admin or any authorized user can access and review the log files of customer activity to perform audits and reviews. The log files contain records of all the end customers’ actions and tasks.
- Logs are stored very securely.
j. Magento API: Magento 2 comes with SOAP and REST API. From Magento 2, it stopped supporting XML-RPC concepts. When an HTTP request comes from any URL, first, it will come to the routing system, where it will decide on the controller and action of the controller for dispatch. It will use the Mage_Api module.
2. Magento ERP Architecture
The Magento ERP section is the section from which we can control the complete flow of the front end visible to customers.
There are several important sections of any ERP system in the Magento system; they are given below.
a. Sales: In sales, we can manage all the orders. Here managing orders means we can see who made the orders, who has paid, and whose payment is still pending. It also allows us to download order reports for analysis purposes.
b. Catalog: This section contains the management of products. It allows us to add new products. In this section, we can also add categories. We can associate any product in any category. We can disable any product and add images for the products. This section gives power to Magento admin to control layout and visibility related to products to end customers. Admin can also see reviews and ratings for the products.
c. Customers: You must have registered with many e-commerce applications like Amazon and Flipkart. All these platforms capture your details and store them on their end. In Magento, the Customer section also stores the customer details similarly. These details may be the customer’s name, phone number, email, etc. From here, we can disable, enable or send any specific notification to any specific customers.
d.Promotions: In this section, a Magento admin can set some notifications of the website for all end customers and users. These notifications can be upcoming discounts, upcoming products, and events.
e. CMS: It allows Magento admin to manage all the static blocks of websites. It can be like the layout of the footer and layout of headers etc.
f. Reports: You can generate reports for monthly and weekly orders by all customers. You can generate a report of orders for any specific customers etc.
g. System: It allows the Magento admin to define some system-level configuration. This configuration may be about enabling or disabling services for particular attributes etc.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Magento Architecture. Here we discuss the introduction and various architecture of Magento. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –